J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci.
2017 Dec;33(4):284-290. 10.14368/jdras.2017.33.4.284.
Treatment of the cleft lip and palate patient with few remaining posterior teeth using hybrid telescopic crown denture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea. prosth95@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2405541
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14368/jdras.2017.33.4.284
Abstract
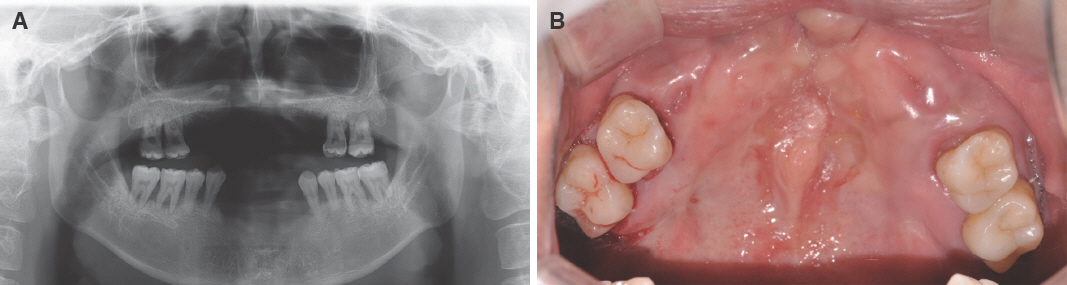
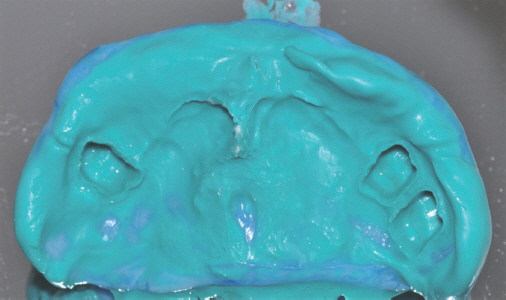
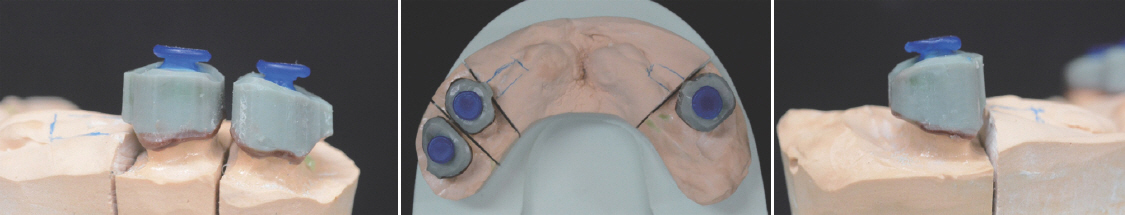
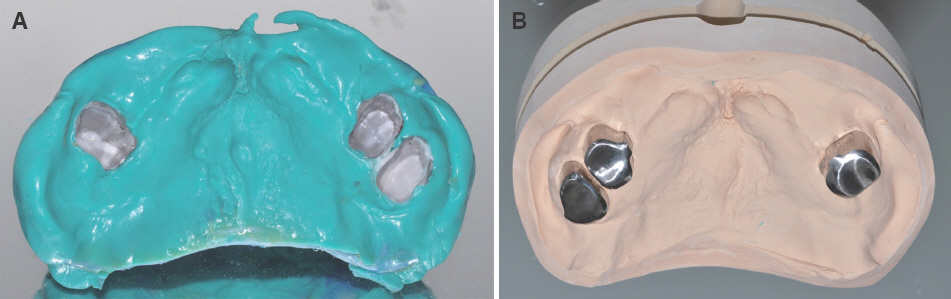
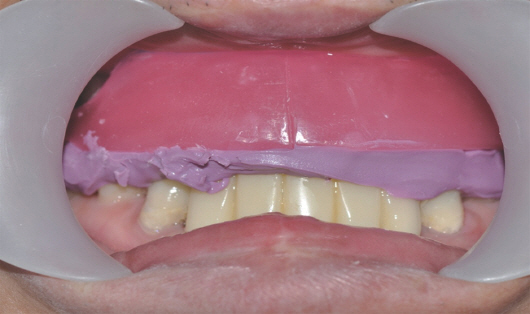
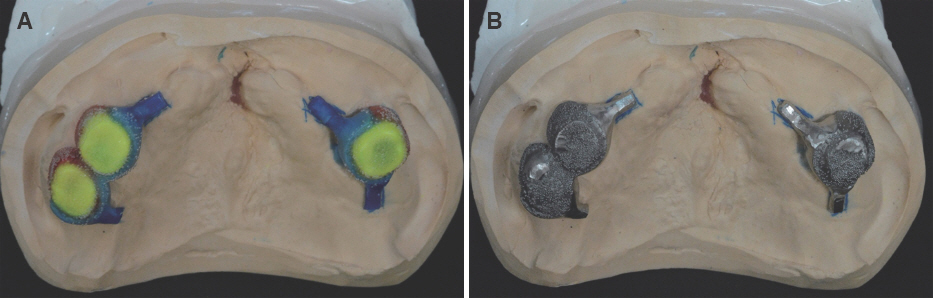
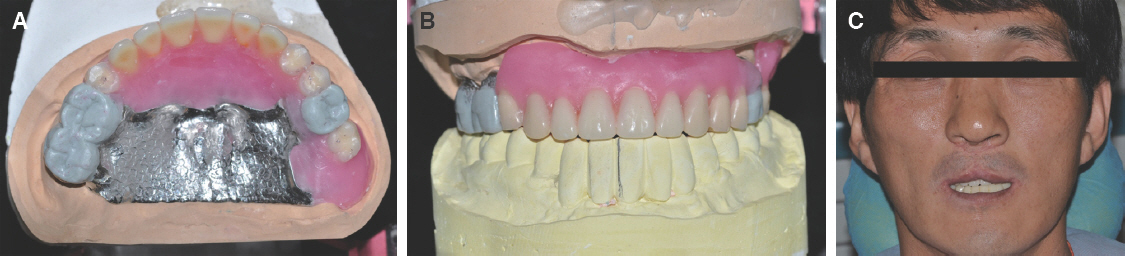
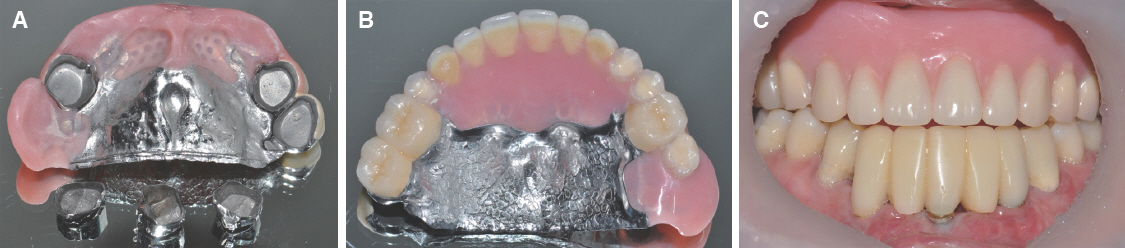
- For individuals with cleft lip and palate, the removable partial dentures (RPDs) have been an important treatment option. Some modifications from conventional prosthetic treatment may be necessary to achieve satisfactory functional and esthetic results in cleft patients. In case of cleft palate patient with periodontally compromised and only posterior few remaining teeth, removable partial prosthesis connected to telescopic crown can be the alternative treatment option. When connected to the RPD, telescopic crowns increase the prosthetic stability and retention, optimize favorable force transmission to the long dental axis, and improve esthetics. And the cross arch stabilization of double crown denture helps to stabilize both divided maxillary ridges in CLP patient. This case present one adult CLP patient using an RPD connected with hybrid telescopic crowns with friction pins to improve not only retention and stability but also aesthetics.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Dixon MJ, Marazita ML, Beaty TH, Murray JC. Cleft lip and palate: understanding genetic and environmental influences. Nat Rev Genet. 2011; 12:16778. DOI: 10.1038/nrg2933. PMID: 21331089. PMCID: PMC3086810.2. Palmeiro MR, Piffer CS, Brunetto VM, Maccari PC, Shinkai RS. Maxillary rehabilitation using a removable partial denture with attachments in a cleft lip and palate patient: a clinical report. J Prosthodont. 2015; 24:250–3. DOI: 10.1111/jopr.12188. PMID: 24975940.3. Balkaya MC, Sultan H, Erdem S, Mutlu D. Prosthetic rehabilitation of a patient with a unilateral cleft palate: a clinical report. J Prosthet Dent. 2014; 111:269–72. DOI: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2013.06.024. PMID: 24388721.4. Bishara SE, de Arrendondo RS, Vales HP, Jakobsen JR. Dentofacial relationships in persons with unoperated clefts: comparison between three cleft types. Am J Orthod. 1985; 87:481–507. DOI: 10.1016/0002-9416(85)90086-7.5. Oiler DK, Wieman LA, Doyle WJ, Ross C. Infant babbling and speech. J Child Lang. 1976; 3:1–11. DOI: 10.1017/S0305000900001276.6. Krogman WM, Mazaheri M, Harding RL, Ishiguro K, Bariana G, Meier J, Canter H, Ross P. A longitudinal study of the craniofacial growth patterns in children with clefts as compared to normal, birth to six years. Cleft Palate J. 1975; 12:59–84. PMID: 1053964.7. Schweckendiek W, Doz P. Primary veloplasty: long term results without maxillary deformity: a twentyfive year report. Cleft Palate J. 1978; 15:268–74. PMID: 278679.8. Pearl RM, Kaplan EN. Cephalometric study of facial growth in children after combined pushback and pharyngeal flap operations. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1976; 57:480–3. DOI: 10.1097/00006534-197604000-00011.9. Cho JH, Cho SA. The use of telescopic crowns in removable partial denture treatment for patients with severe periodontal disease: two patient case history reports. Int J Prosthodont. 2016; 29:175–8. DOI: 10.11607/ijp.4205. PMID: 26929960.10. Breitman JB, Nakamura S, Freedman AL, Yalisove IL. Telescopic retainers: an old or new solution?A second chance to have normal dental function. J Prosthodont. 2012; 21:79–83. DOI: 10.1111/j.1532-849X.2011.00797.x. PMID: 22126322.11. Wöstmann B, Balkenhol M, Weber A, Ferger P, Rehmann P. Long-term analysis of telescopic crown retained removable partial dentures: survival and need for maintenance. J Dent. 2007; 35:939–45. DOI: 10.1016/j.jdent.2007.09.010. PMID: 17961902.12. Wenz HJ, Lehmann KM. A telescopic crown concept for the restoration of the partially edentulous arch: the Marburg double crown system. Int J Prosthodont. 1998; 11:541–50. PMID: 10023216.13. Weber H, Frank G. Spark erosion procedure: a method for extensive combined fixed and removable prosthodontic care. J Prosthet Dent. 1993; 69:222–7. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3913(93)90144-D.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prosthetic treatment for patient with congenital bilateral cleft lip and palate to close oro-nasal communication using maxillary double crown and clasp retained removable denture
- Clinical Report by using hybrid telescopic double crown Removable Partial Denture on a few remaining teeth with severe periodontal disease
- A clinical case of hybrid telescopic double crown using friction pin with an isolated few remaining teeth
- Prosthetic treatment for patient with anterior overbite and partial edentulism using maxillary hybrid telescopic double crown RPD and mandibular fixed prostheses: A 11-yr follow-up
- Causes of failures of long-term used double crown denture and new rehabilitation with dental implant and tooth combined denture using remaining teeth and implants