Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2019 Mar;11(2):231-240. 10.4168/aair.2019.11.2.231.
Eperisone-Induced Anaphylaxis: Pharmacovigilance Data and Results of Allergy Testing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Allergy and Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. parkjw@yuhs.ac
- 2Institute of Allergy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2431855
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2019.11.2.231
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Eperisone is an oral muscle relaxant used in musculoskeletal disorders causing muscle spasm and pain. For more effective pain control, eperisone is usually prescribed together with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). As such, eperisone may have been overlooked as the cause of anaphylaxis compared with NSAIDs. This study aimed to analyze the adverse drug reaction (ADR) reported in Korea and suggest an appropriate diagnostic approach for eperisone-induced anaphylaxis.
METHODS
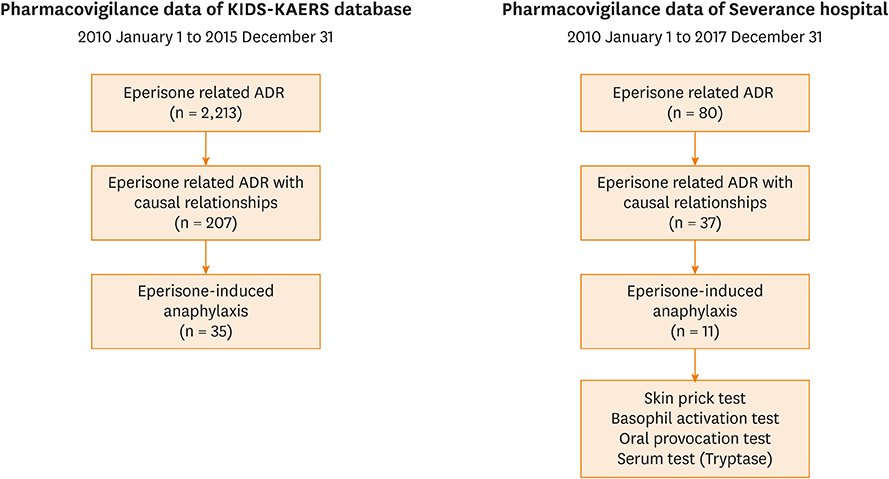
We reviewed eperisone-related pharmacovigilance data (Korea Institute of Drug Safety-Korea Adverse Event Reporting System [KIDS-KAERS]) reported in Korea from 2010 to 2015. ADRs with causal relationship were selected. Clinical manifestations, severity, outcomes, and re-exposure information were analyzed. For further investigation, 7-year ADR data reported in a single center were also reviewed. Oral provocation test (OPT), skin prick test (SPT) and basophil activation test (BAT) were performed in this center.
RESULTS
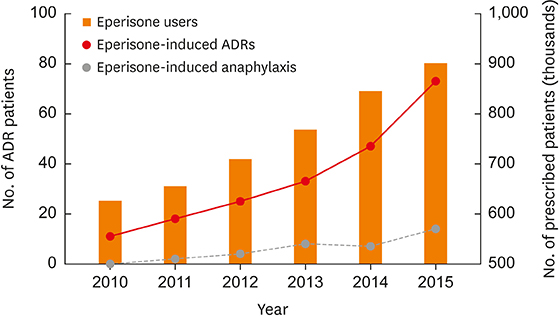
During the study period, 207 patients had adverse reactions to eperisone. The most common ADRs were cutaneous hypersensitive reactions (30.4%) such as urticaria, itchiness or angioedema. Fifth common reported ADR was anaphylaxis. There were 35 patients with anaphylaxis, comprising 16.9% of the eperisone-related ADRs. In the single center study, there were 11 patients with eperisone-induced anaphylaxis. All the patients underwent OPT and all the provoked patients showed a positive reaction. Four of the 11 patients with anaphylaxis also underwent SPT and BAT, which were all negative.
CONCLUSIONS
Incidence of eperisone-induced anaphylaxis calculated from the KIDS-KAERS database was 0.001%. Eperisone can cause hypersensitive reactions, including anaphylaxis, possibly by inducing non-immunoglobulin E-mediated immediate hypersensitivity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Adverse Skin Reactions with Antiepileptic Drugs Using Korea Adverse Event Reporting System Database, 2008–2017
Hyun Kyung Kim, Dae Yeon Kim, Eun-Kee Bae, Dong Wook Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(4):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e17.
Reference
-
1. Kang DY, Lee J, Sohn KH, Kang SY, Cho YS, Kang HR. A case series of eperisone-induced immediate hypersensitivity. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017; 5:228–231.
Article2. Bresolin N, Zucca C, Pecori A. Efficacy and tolerability of eperisone and baclofen in spastic palsy: a double-blind randomized trial. Adv Ther. 2009; 26:563–573.
Article3. Bresolin N, Zucca C, Pecori A. Efficacy and tolerability of eperisone in patients with spastic palsy: a cross-over, placebo-controlled dose-ranging trial. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2009; 13:365–370.4. Iwase S, Mano T, Saito M, Ishida G. Effect of a centrally-acting muscle relaxant, eperisone hydrochloride, on muscle sympathetic nerve activity in humans. Funct Neurol. 1992; 7:459–470.5. Chandanwale AS, Chopra A, Goregaonkar A, Medhi B, Shah V, Gaikwad S, et al. Evaluation of eperisone hydrochloride in the treatment of acute musculoskeletal spasm associated with low back pain: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Postgrad Med. 2011; 57:278–285.
Article6. Cabitza P, Randelli P. Efficacy and safety of eperisone in patients with low back pain: a double blind randomized study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2008; 12:229–235.7. Bavage S, Durg S, Ali Kareem S, Dhadde SB. Clinical efficacy and safety of eperisone for low back pain: a systematic literature review. Pharmacol Rep. 2016; 68:903–912.
Article8. Park KH, Pai J, Song DG, Sim DW, Park HJ, Lee JH, et al. Ranitidine-induced anaphylaxis: clinical features, cross-reactivity, and skin testing. Clin Exp Allergy. 2016; 46:631–639.
Article9. Karch FE, Lasagna L. Adverse drug reactions. A critical review. JAMA. 1975; 234:1236–1241.
Article10. Simons FE, Ardusso LR, Bilò MB, El-Gamal YM, Ledford DK, Ring J, et al. World Allergy Organization guidelines for the assessment and management of anaphylaxis. World Allergy Organ J. 2011; 4:13–37.
Article11. Miki Y, Washio K, Masaki T, Nakata K, Fukunaga A, Nishigori C. A case of eperisone hydrochloride-induced anaphylaxis: a true type I reaction? Allergol Int. 2017; 66:152–153.
Article12. Doña I, Torres MJ, Montañez MI, Fernández TD. In vitro diagnostic testing for antibiotic allergy. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017; 9:288–298.13. Kim MJ, Lim HS, Noh YH, Kim YH, Choi HY, Park KM, et al. Pharmacokinetic interactions between eperisone hydrochloride and aceclofenac: a randomized, open-label, crossover study of healthy Korean men. Clin Ther. 2013; 35:1528–1535.
Article14. Ryu JH, Kim JI, Kim HS, Noh GJ, Lee KT, Chung EK. Pharmacokinetic interactions between pelubiprofen and eperisone hydrochloride: a randomized, open-label, crossover study of healthy Korean men. Clin Ther. 2017; 39:138–149.
Article15. Kim SH, Lee J, Kim SH, Kim HW, Kim YU, Lim Y, et al. Anaphylaxis caused by muscle relaxant (eperisone hydrochloride). Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:172–175.
Article16. Hur GY, Hwang EK, Moon JY, Ye YM, Shim JJ, Park HS, et al. Oral muscle relaxant may induce immediate allergic reactions. Yonsei Med J. 2012; 53:863–865.
Article17. Tanno K, Narimatsu E, Takeyama Y, Asai Y. Infantile case of seizure induced by intoxication after accidental consumption of eperisone hydrochloride, an antispastic agent. Am J Emerg Med. 2007; 25:481–482.
Article18. Yamagiwa T, Morita S, Amino M, Miura N, Saito T, Inokuchi S. Serum concentration of eperisone hydrochloride correlates with QT interval. Am J Emerg Med. 2014; 32:75–77.
Article19. Yamagiwa T, Amino M, Morita S, Yamamoto R, Saito T, Inokuchi S. A case of torsades de pointes induced by severe QT prolongation after an overdose of eperisone and triazolam in a patient receiving nifedipine. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2010; 48:149–152.20. Sartini S, Guerra L. Open experience with a new myorelaxant agent for low back pain. Adv Ther. 2008; 25:1010–1018.
Article21. Ribi C, Vermeulen C, Hauser C. Anaphylactic reactions to tolperisone (Mydocalm). Swiss Med Wkly. 2003; 133:369–371.22. Ueno T, Kawana S. A case of eperisone hydrochloride (myonal)--induced drug eruption leading to erythema and angioedema. Arerugi. 2007; 56:709–713.23. Balaraddiyavar N, Bhushan A, Kotinatot BC, Huggi G. Eperisone hydrochloride-induced maculopapular rash. Indian J Pharmacol. 2016; 48:604–605.
Article24. Choonhakarn C. Non-pigmenting fixed drug eruption: a new case due to eperisone hydrochloride. Br J Dermatol. 2001; 144:1288–1289.
Article25. Yamamoto Y, Kadota M, Nishimura Y. A case of eperisone hydrochloride-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. J Dermatol. 2004; 31:769–770.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Characteristics of Adverse Drug Reactions of Central Muscle Relaxants Including Eperisone: Analysis of KAERS Data
- Drug-induced anaphylaxis: Analysis of the Pharmacovigilance Database
- A case series of eperisone-induced immediate hypersensitivity
- Anaphylaxis caused by muscle relaxant (eperisone hydrochloride)
- Causes and Diagnostic Usefulness of Tryptase Measurements for Anaphylaxis in a Korean Tertiary Care General Hospital