J Rhinol.
2018 Nov;25(2):99-102. 10.18787/jr.2018.25.2.99.
A Rare Case of Subcutaneous Emphysema following Lateral Pharyngoplasty for Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hyungjucho@yuhs.ac
- 2The Airway Mucus Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2431223
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2018.25.2.99
Abstract
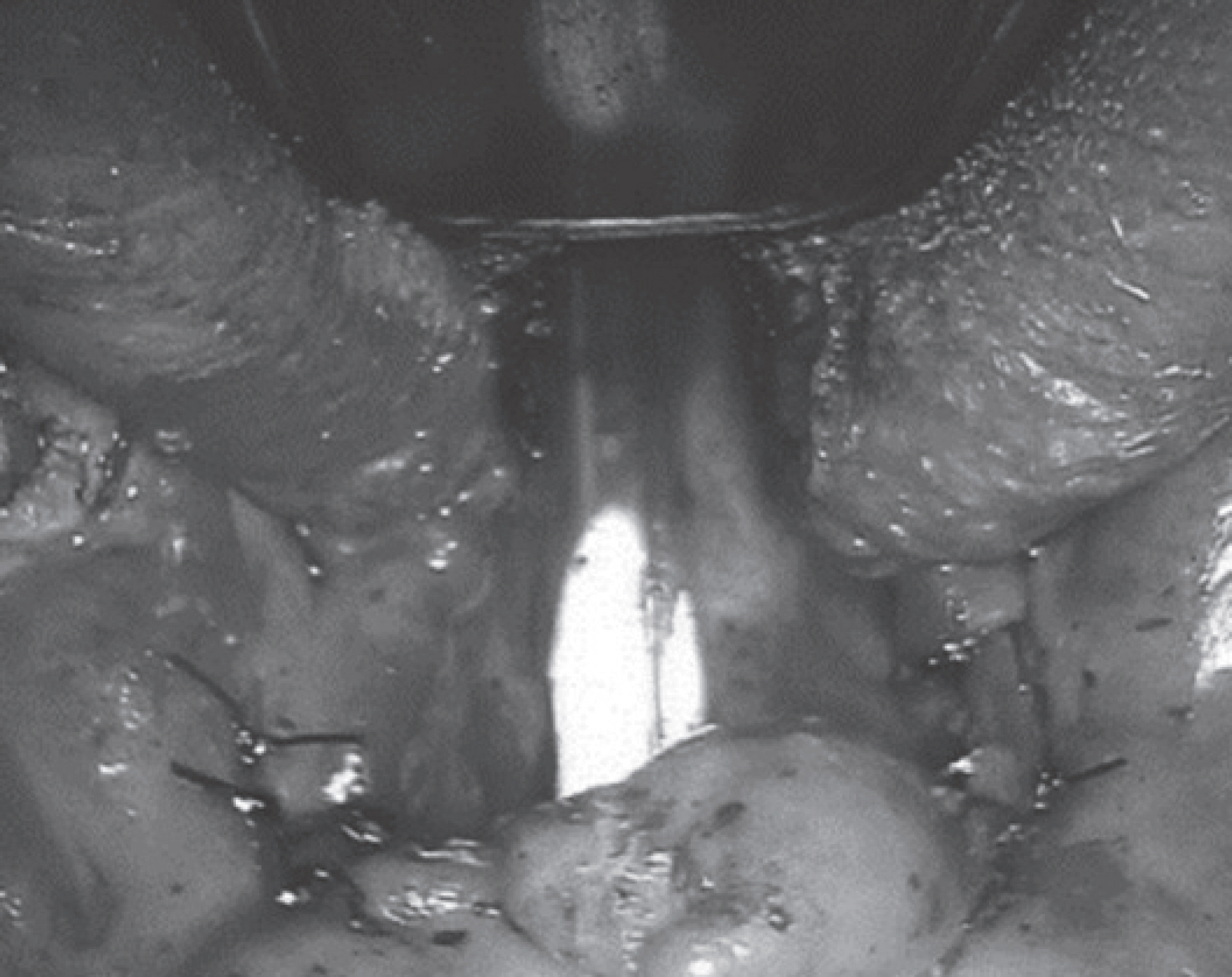
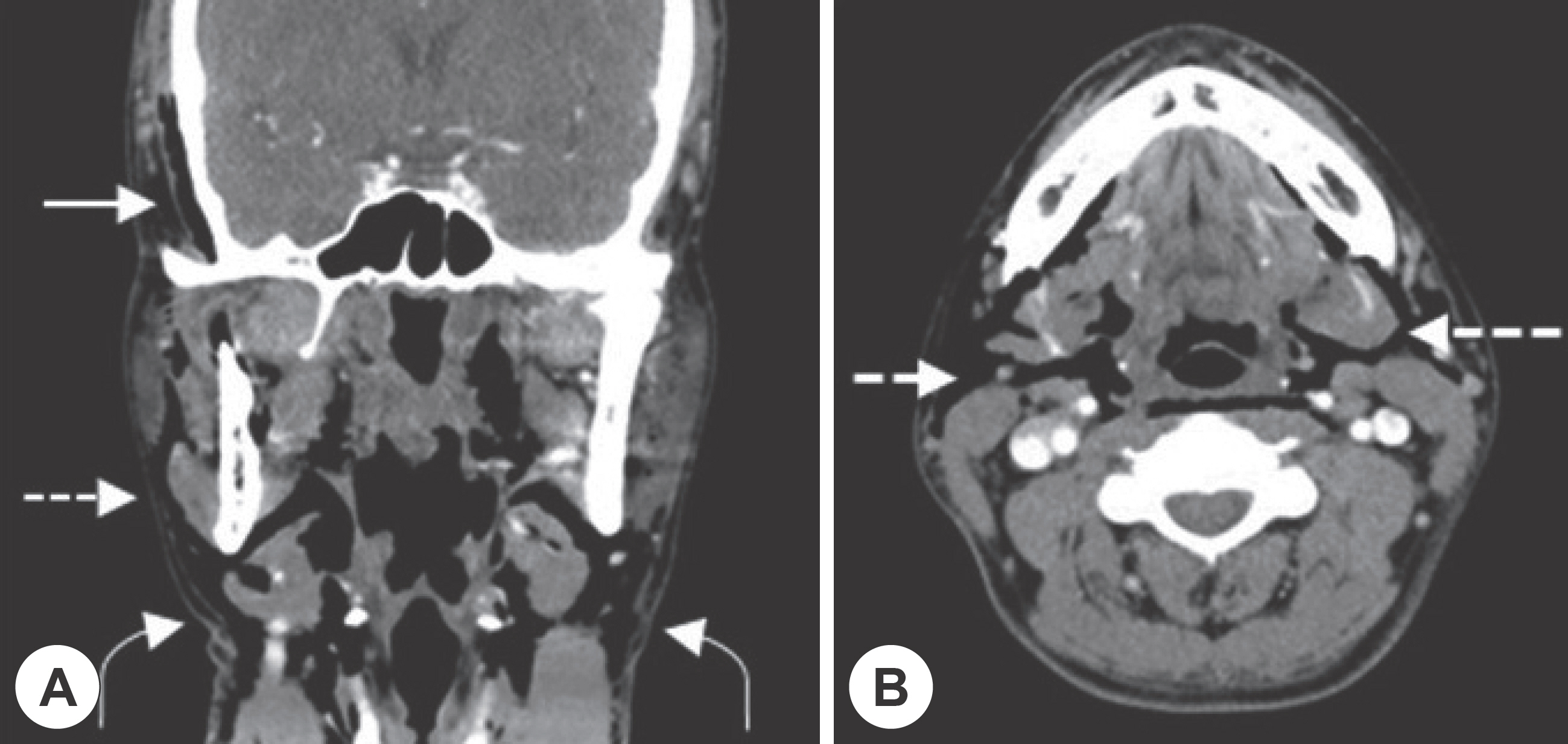
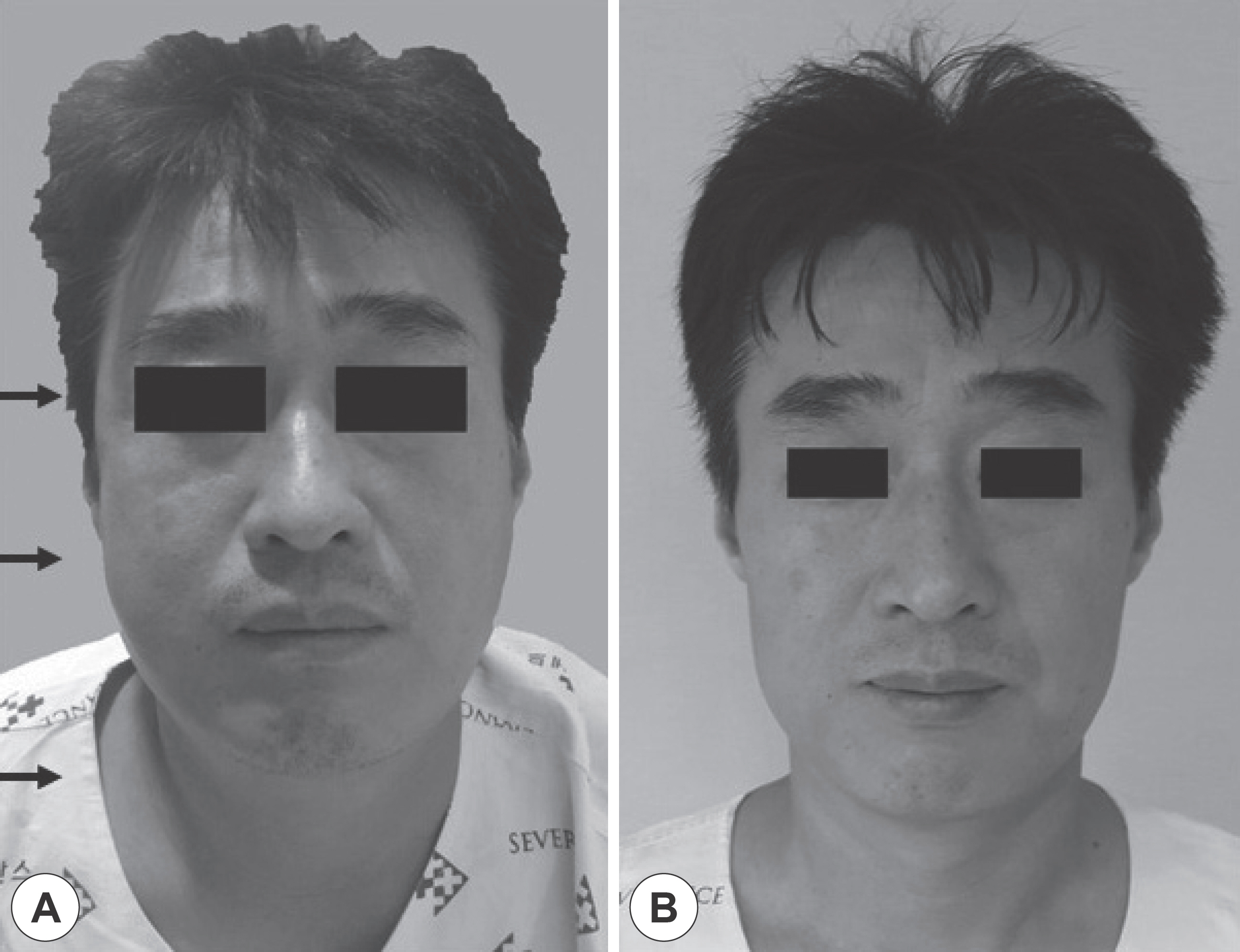
- Lateral pharyngoplasty is a surgical option for treatment of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Here, we present a case involving a 40-year-old healthy man who underwent surgery, including lateral pharyngoplasty and robotic tongue base resection, for OSA. There were no intraoperative or immediate postoperative complications. However, on postoperative day 3, the patient presented with swelling in the temporal and buccal areas and was diagnosed with subcutaneous emphysema, later confirmed by computed tomography. The patient was carefully monitored under conservative care and discharged without complications. Although subcutaneous emphysema following tonsillectomy is a rare complication and usually resolves with conservative management, in certain cases, it might require surgical intervention. Lateral pharyngoplasty involves tonsillectomy and additional incision along the tonsillar fossa, which makes it susceptible to pharyngeal wall defects and, consequently, subcutaneous emphysema. Additionally, lateral pharyngoplasty and robotic tongue base resection cause pain and might thus contribute to the increase in intrapharyngeal pressure, which might aggravate subcutaneous emphysema. Lateral pharyngoplasty should be performed with meticulous dissection of the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. Healthcare providers should be aware of these complications and, upon suspicion of the same, place the patient under close observation to prevent life-threatening situations.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Fechner FP., Kieff D. Cervical emphysema complicating tonsillectomy with argon beam coagulation. Laryngoscope. 2003. 113:920–1.
Article2). Kim JP., Park JJ., Kang HS., Song MS. Subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum after tonsillectomy. Am J Otolaryngol. 2010. 31:212–5.
Article3). Bizaki A., Kääriäinen J., Harju T., Rautiainen M. Facial subcutaneous emphysema after tonsillectomy. Head Face Med. 2014. 10:11.
Article4). Lim HG., Jung GW., Lim JY., Choi JS. Two Cases of Cervical Emphysema after Tonsillectomy. Korean J Otolaryngol. 2015. 58(4):267–70.
Article5). Tran DD., Littlefield PD. Late presentation of subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum following elective tonsillectomy. Am J Otolaryngol. 2015. 36:299–302.
Article6). Yelnoorkar S., Issing W. Cervicofacial Surgical Emphysema following Tonsillectomy. Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2014. 2014:746152.
Article7). Yammine NV., Alherabi A., Gerin-Lajoie J. Post-tonsillectomy subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum. J Otolaryngol. 2004. 33:403–4.
Article8). El-Chazali AM. Spontaneous emphysema of the neck. J Laryngol Otol. 1983. 97:383–6.9). Hampton SM., Cinnamond MJ. Subcutaneous emphysema as a complication of tonsillectomy. J Laryngol Otol. 1997. 111:1077–8.
Article10). Vos GD., Marres EH., Heineman E., Janssens M. Tension pneumoperitoneum as an early complication after adenotonsillectomy. J Laryngol Otol. 1995. 109:440–1.
Article11). Ferguson CC., McGarry PM., Beckman IH., Broder M. Surgical emphysema complicating tonsillectomy and dental extraction. Can Med Assoc J. 1955. 72:847–8.