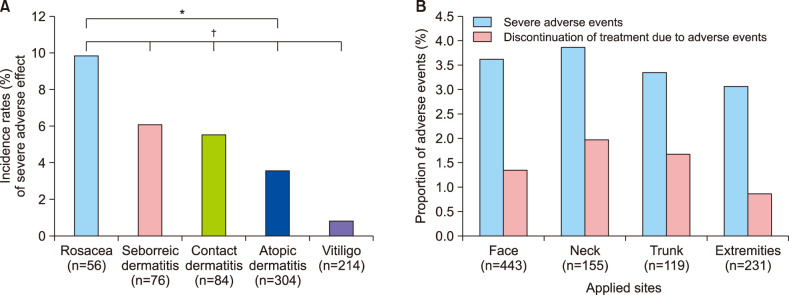
Ann Dermatol.
2019 Feb;31(1):90-92. 10.5021/ad.2019.31.1.90.
Incidence of Topical Tacrolimus Adverse Effects in Chronic Skin Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. haddal@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2430810
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2019.31.1.90
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Luger T, Paul C. Potential new indications of topical calcineurin inhibitors. Dermatology. 2007; 215(Suppl 1):45–54.
Article2. Rustin MH. The safety of tacrolimus ointment for the treatment of atopic dermatitis: a review. Br J Dermatol. 2007; 157:861–873. PMID: 17854353.
Article3. Ständer S, Ständer H, Seeliger S, Luger TA, Steinhoff M. Topical pimecrolimus and tacrolimus transiently induce neuropeptide release and mast cell degranulation in murine skin. Br J Dermatol. 2007; 156:1020–1026. PMID: 17388925.
Article4. Powell FC, Corbally N, Powell D. Substance P and rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993; 28:132–133.
Article5. Lim YY, Kim HM, Lee HI, Mun SK, Kim CW, Kim MN, et al. A comparison of neuropeptide expression in skin with allergic contact dermatitis in human and mouse. Int J Dermatol. 2012; 51:939–946. PMID: 22788810.
Article6. Teresiak-Mikołajczak E, Czarnecka-Operacz M, Jenerowicz D, Silny W. Neurogenic markers of the inflammatory process in atopic dermatitis: relation to the severity and pruritus. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2013; 30:286–292. PMID: 24353488.
Article7. Al'Abadie MS, Senior HJ, Bleehen SS, Gawkrodger DJ. Neuropeptide and neuronal marker studies in vitiligo. Br J Dermatol. 1994; 131:160–165. PMID: 7522512.8. Falabella R, Barona MI, Echeverri IC, Alzate A. Substance P may play a part during depigmentation in vitiligo. A pilot study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003; 17:355–356. PMID: 12702089.
Article9. Hristakieva E, Lazarova R, Lazarov N, Stanimirović A, Shani J. Markers for vitiligo related neuropeptides in human skin nerve fibers. Acta Med Croatica. 2000; 54:53–57. PMID: 11028109.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Chronic Actinic Dermatitis Treated with 0.03% Topical Tacrolimus
- A Case of Pyoderma Gangrenosum Treated with Topical Tacrolimus and Oral Cyclosporin
- Current status of atopic dermatitis in Japan
- Clinical Effects of 0.1% Tacrolimus Ointment for the Treatment of Lichen Striatus
- Three Cases of Oral Lichen Planus Treated with Topical Tacrolimus