Korean J Phys Anthropol.
2018 Dec;31(4):151-158. 10.11637/kjpa.2018.31.4.151.
Spinal Nerve Position and Morphometric Analysis with Silicon Molds in the Cadaveric Lumbar Intervertebral Foramen
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu, Korea. anatomy3@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2430460
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11637/kjpa.2018.31.4.151
Abstract
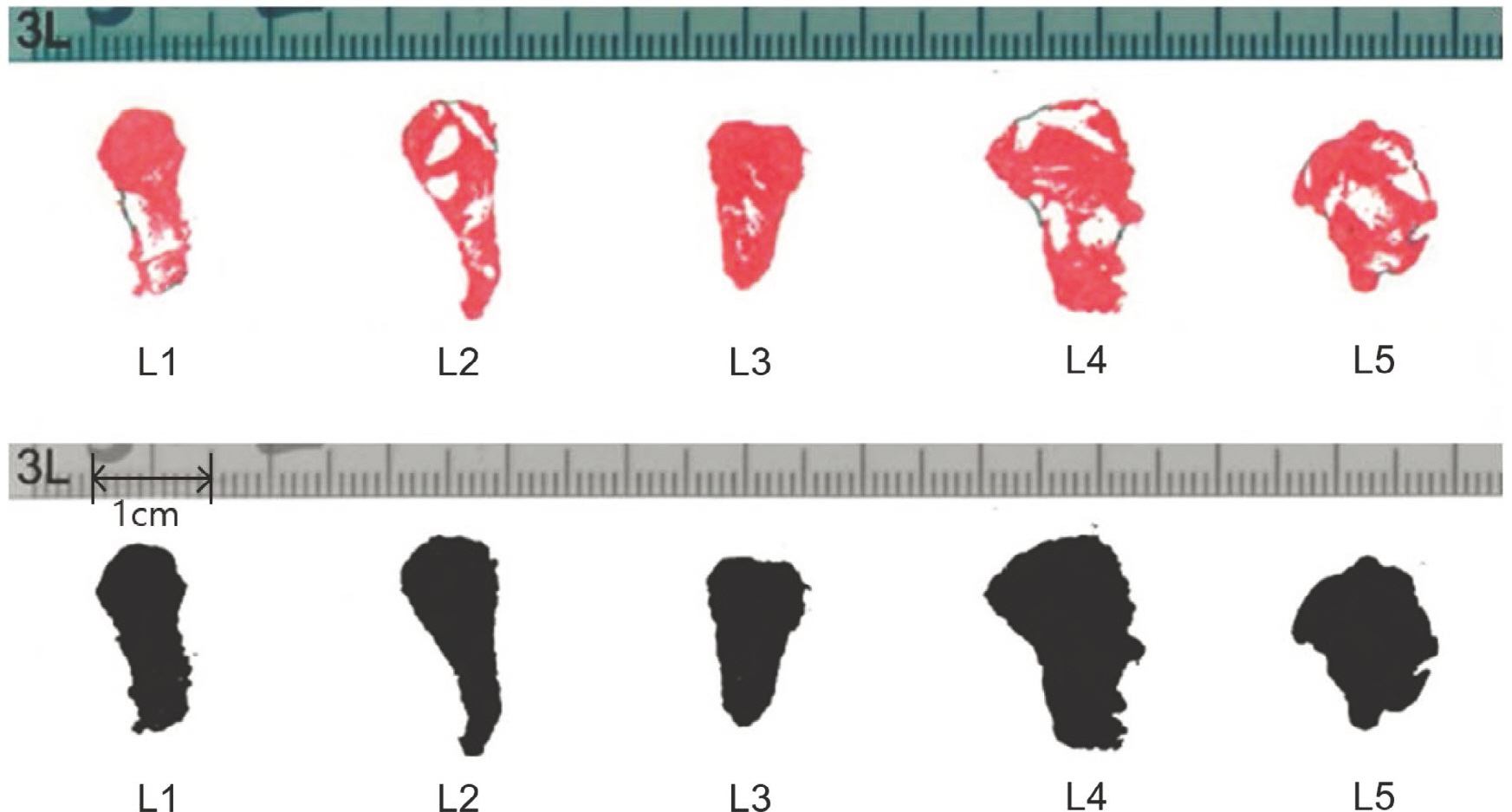
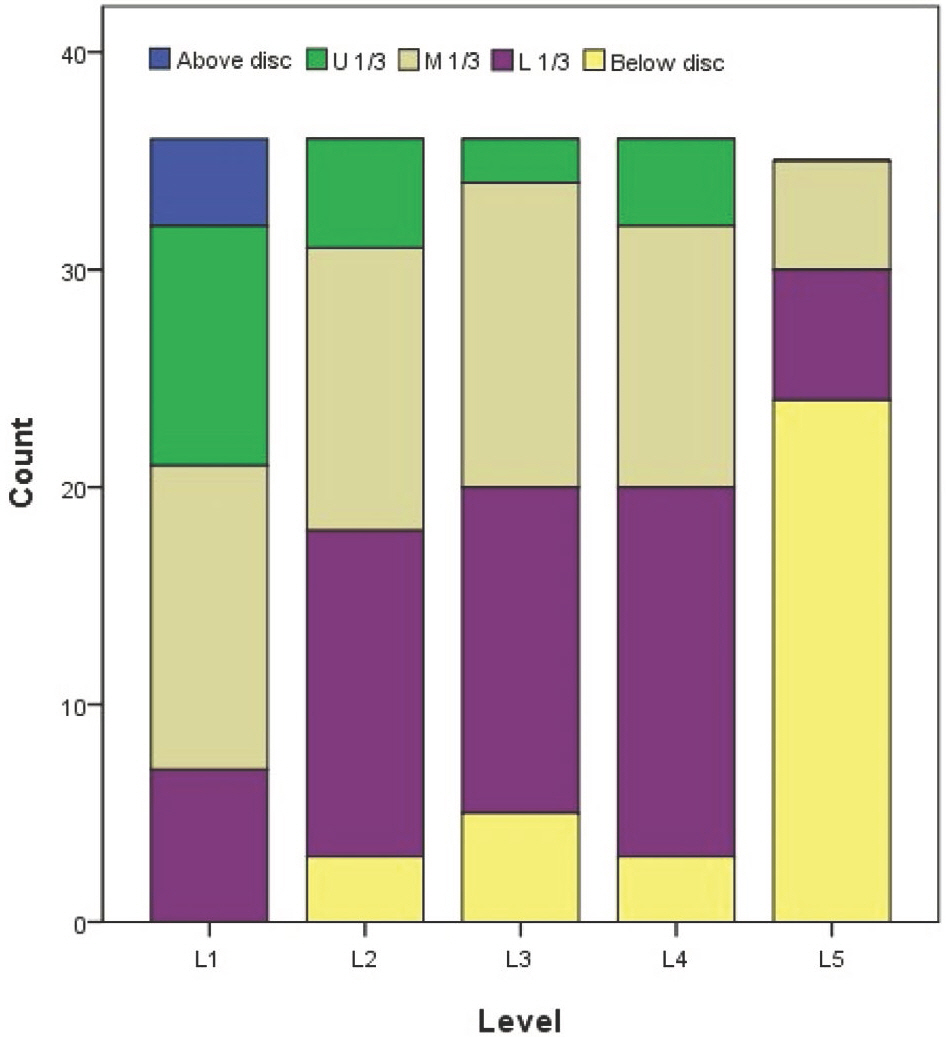
- The intervertebral foramen is formed by two adjacent vertebrae and an intervertebral disc. Previous studies examining the foramen have been performed using various methods. The author obtained characteristics of the intervertebral foramen based on silicon mold. The author used 18 cadavers and dissected the lumbar intervertebral foramen. First, positional levels of the spinal nerve in the intervertebral foramen were measured. Second, after being removed all tissues covering the intervertebral, bony foramen was filled with melted silicon to mold the cross section. Subsequently, the solidified silicon mold was removed and stamped on a paper. The paper was scanned and analyzed area, perimeter, height and width of the intervertebral foramen on a computer. Area (average, 9.43 mm²) and perimeter (average, 48.02 mm) did not show any statistical significant pattern for any lumbar vertebral levels. However, the height and width significantly differed at the fifth lumbar vertebra, which had the shortest height (the fifth, 13.00 mm; average, 15.78 mm) and longest width (the fifth, 8.61 mm; average, 7.87 mm), although there were similar patterns in case of area and perimeter of the first to fourth lumbar vertebra. Height had a decrease tendency while width had an increase tendency both from the second to fifth lumbar vertebra. Spinal nerves went through near the intervertebral disc level from the first to fourth lumbar vertebra, although they passed below the disc at the fifth level. This study provides a different view of methodology for the 3-dimensional aspect for the intervertebral foramen. Results of this study may indicate that height and width of the intervertebral foramen changed along all lumbar vertebral levels; nevertheless, area and perimeter of the intervertebral foramen remained constant.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Sunderland S. Meningeal-neural relations in the intervertebral foramen. J Neurosurg. 1974; 40:756–63.
Article2. Fujiwara A, An HS, Lim TH, Haughton VM. Morphologic changes in the lumbar intervertebral foramen due to flex-ion-extension, lateral bending, and axial rotation: an in vitro anatomic and biomechanical study. Spine. 2001; 26:876–82.3. Inman VT, Saunders JB. The clinico-anatomical aspects of the lumbosacral region. Radiology. 1942; 38:669–78.4. Cramer GD, Cantu JA, Dorsett RD, Greenstein JS, McGregor M, Howe JE, et al. Dimensions of the lumbar intervertebral foramina as determined from the sagittal plane magnetic resonance imaging scans of 95 normal subjects. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2003; 26:160–70.
Article5. Hasegawa T, Mikawa Y, Watanabe R, An HS. Morphometric analysis of the lumbosacral nerve roots and dorsal root ganglia by magnetic resonance imaging. Spine. 1996; 21:1005–9.
Article6. Karabekir HS, Gocmen-Mas N, Edizer M, Ertekin T, Yazici C, Atamturk D. Lumbar vertebra morphometry and ste-reological assesment of intervertebral space volumetry: a methodological study. Ann Anat. 2011; 193:231–6.
Article7. Smith GA, Aspden RM, Porter RW. Measurement of vertebral foraminal dimensions using three-dimensional computerized tomography. Spine. 1993; 18:629–36.
Article8. Torun F, Dolgun H, Tuna H, Attar A, Uz A, Erdem A. Morphometric analysis of the roots and neural foramina of the lumbar vertebrae. Surg Neurol. 2006; 66:148–51.
Article9. Knapik DM, Abola MV, Gordon ZL, Seiler JG, Marcus RE, Liu RW. Differences in cross-sectional intervertebral foraminal area from C3 to C7. Global Spine J. 2018; 8:600–6.
Article10. Senoo I, Espinoza Orias AA, An HS, Andersson GB, Park DK, Triano JJ, et al. In vivo 3-dimensional morphometric analysis of the lumbar foramen in healthy subjects. Spine. 2014; 39:E929–35.
Article11. Epstein BS, Epstein JA, Lavine L. The effect of anatomic variations in the lumbar vertebrae and pinal canal on cauda equina and nerve root syndromes. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1964; 91:1055–63.12. Al-Hadidi MT, Abu-Ghaida JH, Badran DH, Al-Hadidi AM, Ramadan HN, Massad DF. Magnetic resonance imaging of normal lumbar intervertebral foraminal height. Saudi Med J. 2003; 24:736–41.13. Min JH, Kang SH, Lee JB, Cho TH, Suh JG. Anatomic analysis of the transforaminal ligament in the lumbar intervertebral foramen. Neurosurgery. 2005; 57:37–41.
Article14. Inufusa A, An HS, Lim TH, Hasegawa T, Haughton VM, Nowicki BH. Anatomic changes of the spinal canal and intervertebral foramen associated with flexion-extension movement. Spine. 1996; 21:2412–20.
Article15. Magnuson PB. Differential diagnosis of causes of pain in the lower back accompanied by sciatic pain. Ann Surg. 1944; 119:878–91.
Article16. Cinotti G, De Santis P, Nofroni I, Postacchini F. Stenosis of lumbar intervertebral foramen: anatomic study on predisposing factors. Spine. 2002; 27:223–9.17. Miller JA, Schmatz C, Schultz AB. Lumbar disc degeneration: correlation with age, sex, and spine level in 600 autopsy specimens. Spine. 1988; 13:173–8.18. Schlegel JD, Champine J, Taylor MS, Watson JT, Champine M, Schleusener RL, et al. The role of distraction in improving the space available in the lumbar stenotic canal and foramen. Spine. 1994; 19:2041–7.
Article19. Rühli FJ, Müntener M, Henneberg M. Human osseous intervertebral foramen width. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2006; 129:177–88.
Article20. Kitagawa T, Fujiwara A, Kobayashi N, Saiki K, Tamai K, Saotome K. Morphologic changes in the cervical neural foramen due to flexion and extension: in vivo imaging study. Spine. 2004; 29:2821–5.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison with Magnetic Resonance Three-Dimensional Sequence for Lumbar Nerve Root with Intervertebral Foramen
- The Changes of the Dimension of Intervertebral Disc,-Neural Foramen and Spinal Canal after Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in the Lumbar Spine
- Spinal Nerve Root Swelling Mimicking Intervertebral Disc Herniation in Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Case Report
- The Relationship between Disc Degeneration and Morphologic Changes in the Intervertebral Foramen of the Cervical Spine: A Cadaveric MRI and CT Study
- Height Changes of Intervertebral Disc and Neural Foramen after Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in the Lumbar Spine