World J Mens Health.
2019 Jan;37(1):105-112. 10.5534/wjmh.180051.
Effect of Korean Herbal Formula (Modified Ojayeonjonghwan) on Androgen Receptor Expression in an Aging Rat Model of Late Onset Hypogonadism
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. ksw1227@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Urology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Urology, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Urology, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Urology, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Catholic Integrative Medicine Research Institute, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Urology, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital, Yeonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 9KEMIMEDI, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2429728
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.180051
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Testosterone replacement therapy is an effective treatment for late-onset hypogonadism (LOH) despite a few contraindications and side-effects. The aim of this study was to determine whether modified Ojayeonjonghwan (KH-204, Korean herbal formula) improved LOH. KH-204 is a strong antioxidant herbal formula. We evaluated the effect of Korean herbal prescription on androgen receptor (AR) expression in an aged rat model of LOH.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eighteen-month-old rats were used as aged LOH rat models. Eighteen Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into three equal groups of six animals each and treated with one of the following: 1) normal control group (oral administration with distilled water, n=6), 2) KH-204 200 group (oral administration with 200 mg/kg of KH-204, n=6), and 3) KH-204 400 group (oral administration with 400 mg/kg of KH-204, n=6). After four weeks of treatment (once daily, distilled water or KH-204), serum testosterone levels, changes in testicular and epididymal weight, Western blotting analysis of AR expression and measurement of oxidative stress were examined.
RESULTS
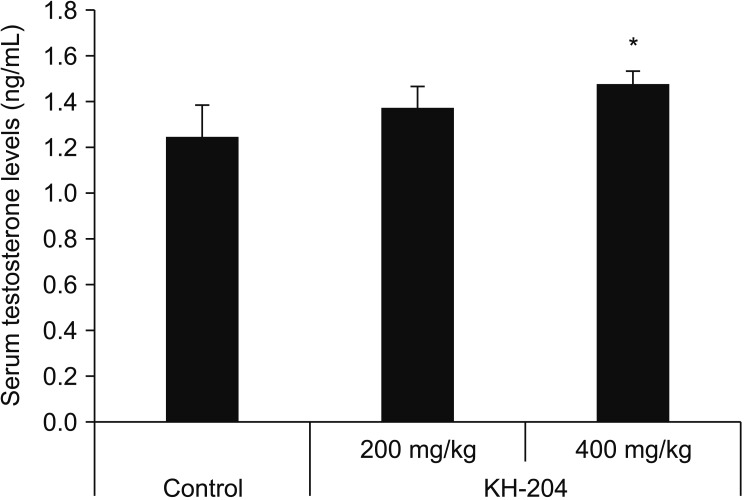
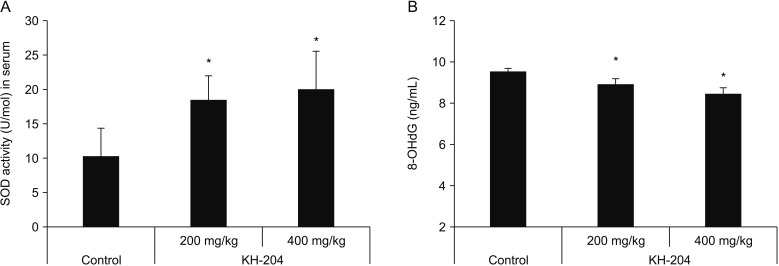
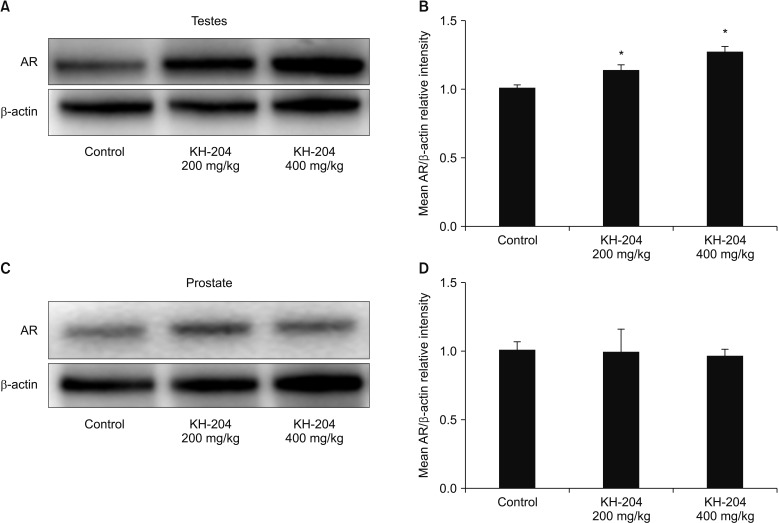
Treatment with the herbal formulation KH-204 200 mg/kg and 400 mg/kg (1) increased the weights of testis and epididymis; (2) increased the level of serum testosterone; (3) increased the level of superoxide dismutase and reduced the level of 8-hydroxy-20-deoxyguanosine; and (4) upregulated AR expression in testicular tissue.
CONCLUSIONS
KH-204 might be an effective alternative for LOH. It improves antioxidant mechanisms and increases testicular AR expression without side-effects.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Synergistic effects of extracorporeal shockwave therapy and modified Ojayeonjonghwan on erectile dysfunction in an animal model of diabetes
Hyun Cheol Jeong, Woong Jin Bae, Guan Qun Zhu, Seung Hwan Jeon, Sae Woong Choi, Su Jin Kim, Hyuk Jin Cho, Sung-Hoo Hong, Ji Youl Lee, Sung Yeoun Hwang, Sae Woong Kim
Investig Clin Urol. 2019;60(4):285-294. doi: 10.4111/icu.2019.60.4.285.
Reference
-
1. Lunenfeld B, Mskhalaya G, Kalinchenko S, Tishova Y. Recommendations on the diagnosis, treatment and monitoring of late-onset hypogonadism in men: a suggested update. Aging Male. 2013; 16:143–150. PMID: 24188520.2. Dean JD, McMahon CG, Guay AT, Morgentaler A, Althof SE, Becher EF, et al. The International Society for Sexual Medicine's process of care for the assessment and management of testosterone deficiency in adult men. J Sex Med. 2015; 12:1660–1686. PMID: 26081680.
Article3. Gray A, Feldman HA, McKinlay JB, Longcope C. Age, disease, and changing sex hormone levels in middle-aged men: results of the Massachusetts male aging study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991; 73:1016–1025. PMID: 1719016.
Article4. Feldman HA, Longcope C, Derby CA, Johannes CB, Araujo AB, Coviello AD, et al. Age trends in the level of serum testosterone and other hormones in middle-aged men: longitudinal results from the Massachusetts male aging study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 87:589–598. PMID: 11836290.
Article5. Wu FC, Tajar A, Beynon JM, Pye SR, Silman AJ, Finn JD, et al. Identification of late-onset hypogonadism in middle-aged and elderly men. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:123–135. PMID: 20554979.
Article6. Corona G, Rastrelli G, Maggi M. Diagnosis and treatment of late-onset hypogonadism: systematic review and meta-analysis of TRT outcomes. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 27:557–579. PMID: 24054931.
Article7. Amano T, Imao T, Takemae K. Clinical efficacy of Japanese traditional herbal medicine (Kampo) in patients with late-onset hypogonadism. Aging Male. 2010; 13:166–173. PMID: 20143961.
Article8. Zang ZJ, Ji SY, Dong W, Zhang YN, Zhang EH, Bin Z. A herbal medicine, saikokaryukotsuboreito, improves serum testosterone levels and affects sexual behavior in old male mice. Aging Male. 2015; 18:106–111. PMID: 25259618.
Article9. Park CS, Ryu SD, Hwang SY. Elevation of intracavernous pressure and NO-cGMP activity by a new herbal formula in penile tissues of aged and diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2004; 94:85–92. PMID: 15261967.
Article10. Choi MJ, Choi BT, Shin HK, Shin BC, Han YK, Baek JU. Establishment of a comprehensive list of candidate antiaging medicinal herb used in Korean medicine by text mining of the classical Korean medical literature, “Dongeuibogam,” and preliminary evaluation of the antiaging effects of these herbs. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015; 2015:873185. PMID: 25861371.
Article11. Sohn DW, Kim HY, Kim SD, Lee EJ, Kim HS, Kim JK, et al. Elevation of intracavernous pressure and NO-cGMP activity by a new herbal formula in penile tissues of spontaneous hypertensive male rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008; 120:176–180. PMID: 18762238.
Article12. Ma W, Wang KJ, Cheng CS, Yan GQ, Lu WL, Ge JF, et al. Bioactive compounds from Cornus officinalis fruits and their effects on diabetic nephropathy. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014; 153:840–845. PMID: 24694395.
Article13. Jang H, Bae WJ, Kim SJ, Cho HJ, Yuk SM, Han DS, et al. The herbal formula KH-204 is protective against erectile dysfunction by minimizing oxidative stress and improving lipid profiles in a rat model of erectile dysfunction induced by hypercholesterolaemia. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017; 17:129. PMID: 28235412.
Article14. Bae WJ, Ha US, Kim KS, Kim SJ, Cho HJ, Hong SH, et al. Effects of KH-204 on the expression of heat shock protein 70 and germ cell apoptosis in infertility rat models. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014; 14:367. PMID: 25269420.
Article15. Kim SJ, Kim MR, Hwang SY, Bae WJ, Kim S, Hong SH, et al. Preliminary report on the safety of a new herbal formula and its effect on sperm quality. World J Mens Health. 2013; 31:254–261. PMID: 24459660.
Article16. Bae WJ, Ha US, Choi JB, Kim KS, Kim SJ, Cho HJ, et al. Protective effects of KH-204 in the bladder of androgen-deprived rats. World J Mens Health. 2015; 33:73–80. PMID: 26331123.
Article17. Jin HQ, Jiang F, Deng DM, Chen WX, Yang GZ, Zhuang TQ. [Regulatory effect of Bushenfang on the serum testosterone level of naturally aging rats and its mechanism]. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2011; 17:758–762. PMID: 21899001.18. Miller VM, Zhu Y, Bucher C, McGinnis W, Ryan LK, Siegel A, et al. Gestational flu exposure induces changes in neurochemicals, affiliative hormones and brainstem inflammation, in addition to autism-like behaviors in mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2013; 33:153–163. PMID: 23880236.
Article19. Edelstein D, Sivanandy M, Shahani S, Basaria S. The latest options and future agents for treating male hypogonadism. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2007; 8:2991–3008. PMID: 18001258.
Article20. Chen H, Cangello D, Benson S, Folmer J, Zhu H, Trush MA, et al. Age-related increase in mitochondrial superoxide generation in the testosterone-producing cells of brown Norway rat testes: relationship to reduced steroidogenic function? Exp Gerontol. 2001; 36:1361–1373. PMID: 11602210.
Article21. Cao L, Leers-Sucheta S, Azhar S. Aging alters the functional expression of enzymatic and non-enzymatic anti-oxidant defense systems in testicular rat Leydig cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2004; 88:61–67. PMID: 15026084.
Article22. Luo L, Chen H, Trush MA, Show MD, Anway MD, Zirkin BR. Aging and the brown Norway rat leydig cell antioxidant defense system. J Androl. 2006; 27:240–247. PMID: 16304208.
Article23. Bae WJ, Zhu GQ, Choi SW, Jeong HC, Bashraheel F, Kim KS, et al. Antioxidant and antifibrotic effect of a herbal formulation in vitro and in the experimental andropause via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017; 2017:6024839. PMID: 29075365.24. Murugesan P, Muthusamy T, Balasubramanian K, Arunakaran J. Studies on the protective role of vitamin C and E against polychlorinated biphenyl (Aroclor 1254)--induced oxidative damage in Leydig cells. Free Radic Res. 2005; 39:1259–1272. PMID: 16298753.
Article25. Zhu LJ, Hardy MP, Inigo IV, Huhtaniemi I, Bardin CW, Moo-Young AJ. Effects of androgen on androgen receptor expression in rat testicular and epididymal cells: a quantitative immunohistochemical study. Biol Reprod. 2000; 63:368–376. PMID: 10906039.26. Bhanmeechao C, Srisuwatanasagul S, Prapaiwan N, Ponglowhapan S. Reproductive aging in male dogs: the epididymal sperm defects and expression of androgen receptor in reproductive tissues. Theriogenology. 2018; 108:74–80. PMID: 29197295.
Article27. Carruthers M. The paradox dividing testosterone deficiency symptoms and androgen assays: a closer look at the cellular and molecular mechanisms of androgen action. J Sex Med. 2008; 5:998–1012. PMID: 18221290.
Article28. Wu X, Gu Y, Li L. The anti-hyperplasia, anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory properties of Qing Ye Dan and swertiamarin in testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia in rats. Toxicol Lett. 2017; 265:9–16. PMID: 27866977.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Management of Late-onset Hypogonadism
- Recent Update on Late-onset Hypogonadism in Males
- Male climacteric syndrome: Late Onset Hypogonadism (LOH) in males
- The Effects of Androgen on Androgen Receptor, Apoptosis and Proliferation in the Penile Erectile Tissue of Adult Rat
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism Syndrome and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms