Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2018 Sep;11(3):192-198. 10.21053/ceo.2017.01284.
Effect of Lifestyle Modification Using a Smartphone Application on Obesity With Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Short-term, Randomized Controlled Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. kimemails7@gmail.com
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Bundang Jesaeng General Hospital, Daejin Medical Center, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Center for Medical Informatics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4User Experience Lab, Seoul National University Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2429009
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2017.01284
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
To investigate the short-term effects of a lifestyle modification intervention based on a mobile application (app) linked to a hospital electronic medical record (EMR) system on weight reduction and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
METHODS
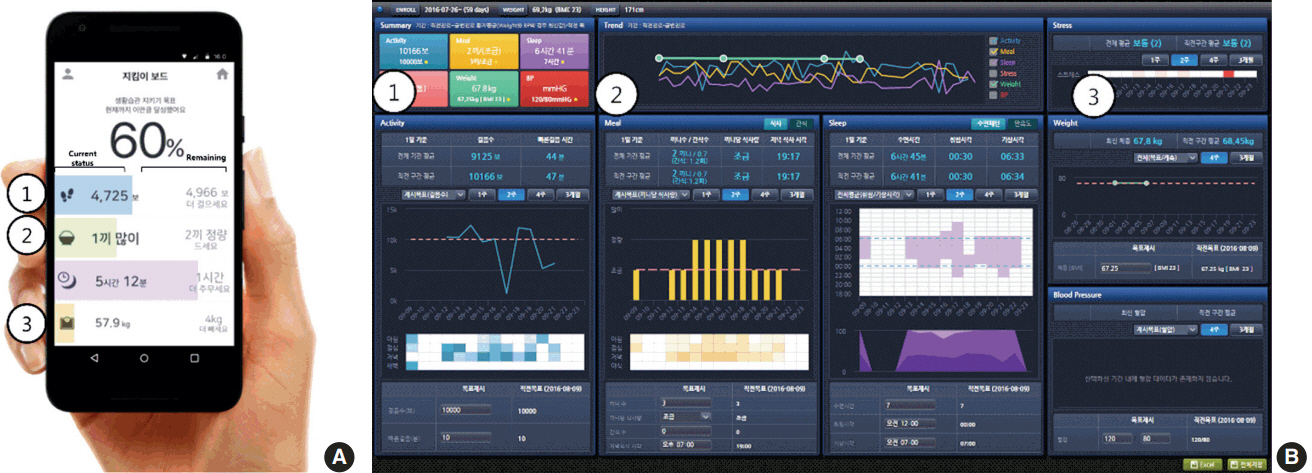
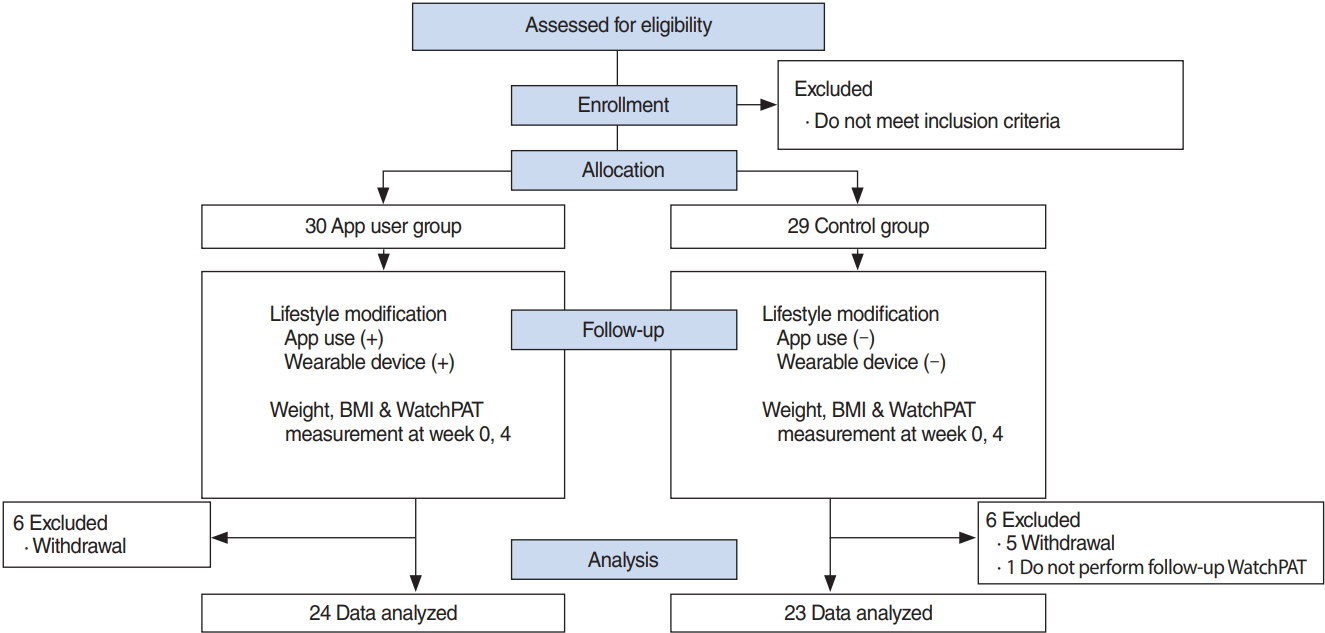
We prospectively enrolled adults (aged >20 years) with witnessed snoring or sleep apnea from a sleep clinic. The patients were randomized into the app user (n=24) and control (n=23) groups. The mobile app was designed to collect daily lifestyle data by wearing a wrist activity tracker and reporting dietary intake. A summary of the lifestyle data was displayed on the hospital EMR and was reviewed. In the control group, the lifestyle modification was performed as per usual practice. All participants underwent peripheral arterial tonometry (WatchPAT) and body mass index (BMI) measurements at baseline and after 4 weeks of follow-up.
RESULTS
Age and BMI did not differ significantly between the two groups. While we observed a significant decrease in the BMI of both groups, the decrease was greater in the app user group (P < 0.001). Apnea-hypopnea index, respiratory distress index, and oxygenation distress index did not change significantly in both groups. However, the proportion of sleep spent snoring at >45 dB was significantly improved in the app user group alone (P =0.014). In either group, among the participants with successful weight reduction, the apnea-hypopnea index was significantly reduced after 4 weeks (P =0.015). Multiple regression analyses showed that a reduction in the apnea-hypopnea index was significantly associated with BMI.
CONCLUSION
Although a short-term lifestyle modification approach using a mobile app was more effective in achieving weight reduction, improvement in OSA was not so significant. Long-term efficacy of this mobile app should be evaluated in the future studies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fung JW, Li TS, Choy DK, Yip GW, Ko FW, Sanderson JE, et al. Severe obstructive sleep apnea is associated with left ventricular diastolic dysfunction. Chest. 2002; Feb. 121(2):422–9.
Article2. Engleman HM, Douglas NJ. Sleep. 4: sleepiness, cognitive function, and quality of life in obstructive sleep apnoea/hypopnoea syndrome. Thorax. 2004; Jul. 59(7):618–22.3. Gami AS, Howard DE, Olson EJ, Somers VK. Day-night pattern of sudden death in obstructive sleep apnea. N Engl J Med. 2005; Mar. 352(12):1206–14.
Article4. Bradley TD, Floras JS. Obstructive sleep apnoea and its cardiovascular consequences. Lancet. 2009; Jan. 373(9657):82–93.
Article5. Rajala R, Partinen M, Sane T, Pelkonen R, Huikuri K, Seppalainen AM. Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome in morbidly obese patients. J Intern Med. 1991; Aug. 230(2):125–9.
Article6. Young T, Skatrud J, Peppard PE. Risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea in adults. JAMA. 2004; Apr. 291(16):2013–6.
Article7. Peppard PE, Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J. Longitudinal study of moderate weight change and sleep-disordered breathing. JAMA. 2000; Dec. 284(23):3015–21.
Article8. Veasey SC, Guilleminault C, Strohl KP, Sanders MH, Ballard RD, Magalang UJ. Medical therapy for obstructive sleep apnea: a review by the medical therapy for obstructive sleep apnea task force of the standards of Practice Committee of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. Sleep. 2006; Aug. 29(8):1036–44.
Article9. Thomasouli MA, Brady EM, Davies MJ, Hall AP, Khunti K, Morris DH, et al. The impact of diet and lifestyle management strategies for obstructive sleep apnoea in adults: a systematic review and metaanalysis of randomised controlled trials. Sleep Breath. 2013; Sep. 17(3):925–35.
Article10. Greenburg DL, Lettieri CJ, Eliasson AH. Effects of surgical weight loss on measures of obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2009; Jun. 122(6):535–42.
Article11. Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM, Walker EA, et al. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002; Feb. 346(6):393–403.
Article12. ter Bogt NC, Bemelmans WJ, Beltman FW, Broer J, Smit AJ, van der Meer K. Preventing weight gain: one-year results of a randomized lifestyle intervention. Am J Prev Med. 2009; Oct. 37(4):270–7.13. Martin CK, Miller AC, Thomas DM, Champagne CM, Han H, Church T. Efficacy of SmartLoss, a smartphone-based weight loss intervention: results from a randomized controlled trial. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2015; May. 23(5):935–42.14. Kang HT, Shim JY, Lee HR, Park BJ, Linton JA, Lee YJ. Trends in prevalence of overweight and obesity in Korean adults, 1998-2009: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Epidemiol. 2014; Mar. 24(2):109–16.15. Rogers RJ, Lang W, Barone Gibbs B, Davis KK, Burke LE, Kovacs SJ, et al. Applying a technology-based system for weight loss in adults with obesity. Obes Sci Pract. 2016; Mar. 2(1):3–12.
Article16. Yilmaz Avci A, Avci S, Lakadamyali H, Can U. Hypoxia and inflammation indicate significant differences in the severity of obstructive sleep apnea within similar apnea-hypopnea index groups. Sleep Breath. 2017; Sep. 21(3):703–11.
Article17. Prasad B, Usmani S, Steffen AD, Van Dongen HP, Pack FM, Strakovsky I, et al. Short-term variability in apnea-hypopnea index during extended home portable monitoring. J Clin Sleep Med. 2016; Jun. 12(6):855–63.
Article18. Levy P, Pepin JL, Deschaux-Blanc C, Paramelle B, Brambilla C. Accuracy of oximetry for detection of respiratory disturbances in sleep apnea syndrome. Chest. 1996; Feb. 109(2):395–9.
Article19. Nakano H, Ikeda T, Hayashi M, Ohshima E, Itoh M, Nishikata N, et al. Effect of body mass index on overnight oximetry for the diagnosis of sleep apnea. Respir Med. 2004; May. 98(5):421–7.
Article20. Sola-Soler J, Jane R, Fiz JA, Morera J. Automatic classification of subjects with and without sleep apnea through snoring analysis. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2007; Aug. 2007:6094–7.
Article21. Maimon N, Hanly PJ. Does snoring intensity correlate with the severity of obstructive sleep apnea? J Clin Sleep Med. 2010; Oct. 6(5):475–8.
Article22. Mei ZF, Song LJ, Jin H, Li Y, Zhang XW. Investigation of respiratory events interval between snores in obstructive sleep apnoea hypopnea syndrome. China J Mod Med. 2013; 27:71–4.23. Ong CW, O’Driscoll DM, Truby H, Naughton MT, Hamilton GS. The reciprocal interaction between obesity and obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Med Rev. 2013; Apr. 17(2):123–31.
Article24. Ballester E, Badia JR, Hernandez L, Carrasco E, de Pablo J, Fornas C, et al. Evidence of the effectiveness of continuous positive airway pressure in the treatment of sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999; Feb. 159(2):495–501.
Article25. Chirinos JA, Gurubhagavatula I, Teff K, Rader DJ, Wadden TA, Townsend R, et al. CPAP, weight loss, or both for obstructive sleep apnea. N Engl J Med. 2014; Jun. 370(24):2265–75.
Article26. Mitchell LJ, Davidson ZE, Bonham M, O’Driscoll DM, Hamilton GS, Truby H. Weight loss from lifestyle interventions and severity of sleep apnoea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2014; Oct. 15(10):1173–83.
Article27. Dixon JB, Schachter LM, O’Brien PE, Jones K, Grima M, Lambert G, et al. Surgical vs conventional therapy for weight loss treatment of obstructive sleep apnea: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2012; Sep. 308(11):1142–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome Associated with Primary Hypothyroidism and Dilated Cardiomyopathy
- Pathogenesis of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Effects of Menopause on Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Abnormal Glucose Metabolism
- A Case of Childhood Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome