Yonsei Med J.
2018 Sep;59(7):843-851. 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.7.843.
Effects of Early Exercise Rehabilitation on Functional Recovery in Patients with Severe Sepsis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. seran@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 3AIDS Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Anesthesiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Rehabilitation Medicine and Research Institute of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2428910
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.7.843
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Severe sepsis is associated with functional disability among patients surviving an acute phase of infection. Efforts to improve functional impairment are important. We assessed the effects of early exercise rehabilitation on functional outcomes in patients with severe sepsis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
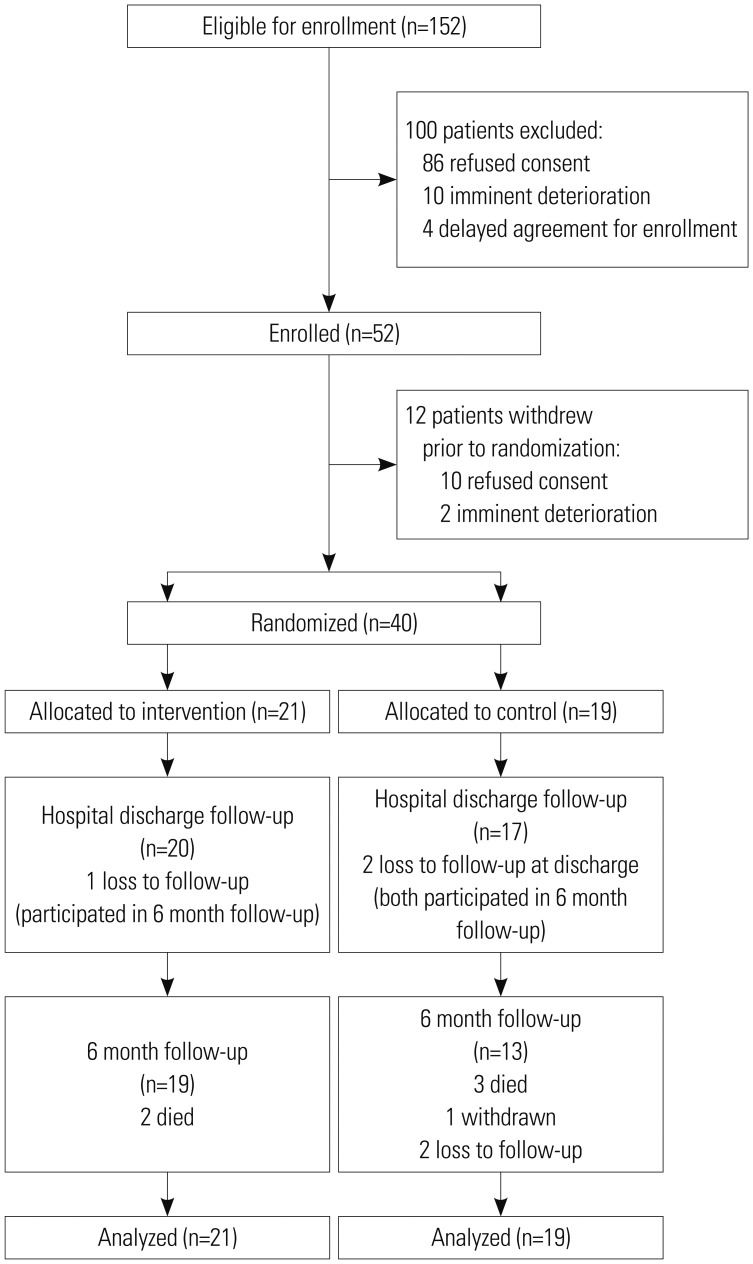
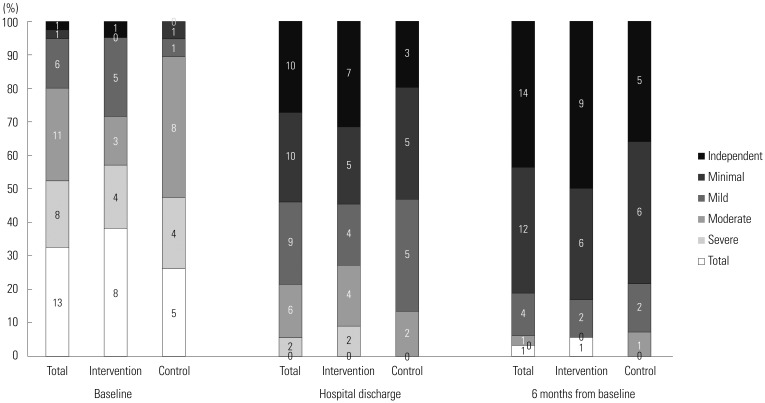
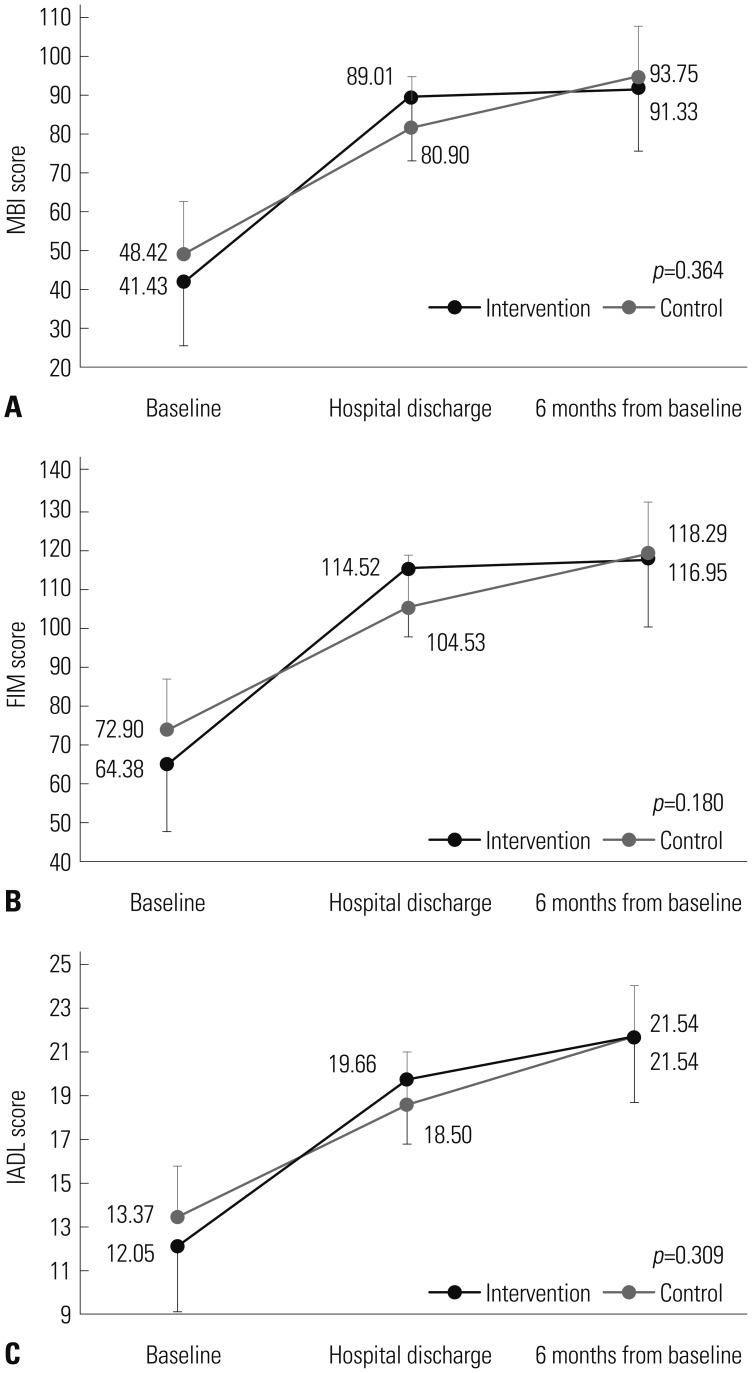
A prospective, single-center, case-control study was conducted between January 2013 and May 2014 at a tertiary care center in Korea. Patients with severe sepsis and septic shock were enrolled and randomized to receive standard sepsis treatment or intervention. Intervention involved early targeted physical rehabilitation with sepsis treatment during hospitalization. Participants were assessed at enrollment, hospital discharge, and 6 months after enrollment. Functional recovery was measured using the Modified Barthel Index (MBI), Functional Independence Measure (FIM), and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADL).
RESULTS
Forty participants (21 intervention patients) were included in an intention-to-treat analysis. There were no significant differences in baseline MBI, FIM, and IADL between groups. Intervention yielded greater improvement of MBI, FIM, and IADL in the intervention group at hospital discharge, but not significantly. Subgroup analysis of patients with APACHE II scores ≥10 showed significantly greater improvement of physical function at hospital discharge (MBI and FIM) in the intervention group, compared to the control group (55.13 vs. 31.75, p=0.048; 52.40 vs. 31.25, p=0.045). Intervention was significantly associated with improvement of MBI in multiple linear regression analysis (standardized coefficient 0.358, p=0.048).
CONCLUSION
Early physical rehabilitation may improve functional recovery at hospital discharge, especially in patients with high initial severity scores.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Heyland DK, Hopman W, Coo H, Tranmer J, McColl MA. Long-term health-related quality of life in survivors of sepsis. Short Form 36: a valid and reliable measure of health-related quality of life. Crit Care Med. 2000; 28:3599–3605. PMID: 11098960.
Article2. Hofhuis JG, Spronk PE, van Stel HF, Schrijvers AJ, Rommes JH, Bakker J. The impact of severe sepsis on health-related quality of life: a long-term follow-up study. Anesth Analg. 2008; 107:1957–1964. PMID: 19020144.
Article3. Iwashyna TJ, Ely EW, Smith DM, Langa KM. Long-term cognitive impairment and functional disability among survivors of severe sepsis. JAMA. 2010; 304:1787–1794. PMID: 20978258.
Article4. Goodwin AJ, Rice DA, Simpson KN, Ford DW. Frequency, cost, and risk factors of readmissions among severe sepsis survivors. Crit Care Med. 2015; 43:738–746. PMID: 25746745.
Article5. Prescott HC, Langa KM, Liu V, Escobar GJ, Iwashyna TJ. Increased 1-year healthcare use in survivors of severe sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014; 190:62–69. PMID: 24872085.
Article6. Hofhuis JG, Spronk PE, van Stel HF, Schrijvers GJ, Rommes JH, Bakker J. The impact of critical illness on perceived health-related quality of life during ICU treatment, hospital stay, and after hospital discharge: a long-term follow-up study. Chest. 2008; 133:377–385. PMID: 17925419.7. Cuthbertson BH, Roughton S, Jenkinson D, Maclennan G, Vale L. Quality of life in the five years after intensive care: a cohort study. Crit Care. 2010; 14:R6. PMID: 20089197.
Article8. Herridge MS, Tansey CM, Matté A, Tomlinson G, Diaz-Granados N, Cooper A, et al. Functional disability 5 years after acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:1293–1304. PMID: 21470008.
Article9. Calvo-Ayala E, Khan BA, Farber MO, Ely EW, Boustani MA. Interventions to improve the physical function of ICU survivors: a systematic review. Chest. 2013; 144:1469–1480. PMID: 23949645.10. Delaney CP, Zutshi M, Senagore AJ, Remzi FH, Hammel J, Fazio VW. Prospective, randomized, controlled trial between a pathway of controlled rehabilitation with early ambulation and diet and traditional postoperative care after laparotomy and intestinal resection. Dis Colon Rectum. 2003; 46:851–859. PMID: 12847356.
Article11. Chiang LL, Wang LY, Wu CP, Wu HD, Wu YT. Effects of physical training on functional status in patients with prolonged mechanical ventilation. Phys Ther. 2006; 86:1271–1281. PMID: 16959675.
Article12. Burtin C, Clerckx B, Robbeets C, Ferdinande P, Langer D, Troosters T, et al. Early exercise in critically ill patients enhances short-term functional recovery. Crit Care Med. 2009; 37:2499–2505. PMID: 19623052.
Article13. Schweickert WD, Pohlman MC, Pohlman AS, Nigos C, Pawlik AJ, Esbrook CL, et al. Early physical and occupational therapy in mechanically ventilated, critically ill patients: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2009; 373:1874–1882. PMID: 19446324.
Article14. Kayambu G, Boots R, Paratz J. Physical therapy for the critically ill in the ICU: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care Med. 2013; 41:1543–1554. PMID: 23528802.15. Callahan LA, Supinski GS. Sepsis-induced myopathy. Crit Care Med. 2009; 37(10 Suppl):S354–S367. PMID: 20046121.
Article16. Sossdorf M, Fischer J, Meyer S, Dahlke K, Wissuwa B, Seidel C, et al. Physical exercise induces specific adaptations resulting in reduced organ injury and mortality during severe polymicrobial sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2013; 41:e246–e255. PMID: 23887230.
Article17. Sossdorf M, Otto GP, Menge K, Claus RA, Lösche W, Kabisch B, et al. Potential effect of physiotherapeutic treatment on mortality rate in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: a retrospective cohort analysis. J Crit Care. 2013; 28:954–958. PMID: 23958242.
Article18. de Araújo CC, Silva JD, Samary CS, Guimarães IH, Marques PS, Oliveira GP, et al. Regular and moderate exercise before experimental sepsis reduces the risk of lung and distal organ injury. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012; 112:1206–1214. PMID: 22267391.
Article19. Chen HI, Hsieh SY, Yang FL, Hsu YH, Lin CC. Exercise training attenuates septic responses in conscious rats. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007; 39:435–442. PMID: 17473769.
Article20. Kayambu G, Boots R, Paratz J. Early physical rehabilitation in intensive care patients with sepsis syndromes: a pilot randomised controlled trial. Intensive Care Med. 2015; 41:865–874. PMID: 25851383.
Article21. Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit Care Med. 2013; 41:580–637. PMID: 23353941.
Article22. Kayambu G, Boots RJ, Paratz JD. Early rehabilitation in sepsis: a prospective randomised controlled trial investigating functional and physiological outcomes The i-PERFORM Trial (Protocol Article). BMC Anesthesiol. 2011; 11:21. PMID: 22035174.
Article23. Anderson K, Aito S, Atkins M, Biering-Sørensen F, Charlifue S, Curt A, et al. Functional recovery measures for spinal cord injury: an evidence-based review for clinical practice and research. J Spinal Cord Med. 2008; 31:133–144. PMID: 18581660.
Article24. Granger CV, Cotter AC, Hamilton BB, Fiedler RC, Hens MM. Functional assessment scales: a study of persons with multiple sclerosis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1990; 71:870–875. PMID: 2222154.25. Granger CV, Cotter AC, Hamilton BB, Fiedler RC. Functional assessment scales: a study of persons after stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1993; 74:133–138. PMID: 8431095.26. Shah S, Vanclay F, Cooper B. Improving the sensitivity of the Barthel Index for stroke rehabilitation. J Clin Epidemiol. 1989; 42:703–709. PMID: 2760661.
Article27. Keith RA, Granger CV, Hamilton BB, Sherwin FS. The functional independence measure: a new tool for rehabilitation. Adv Clin Rehabil. 1987; 1:6–18. PMID: 3503663.28. Lawton MP, Brody EM. Assessment of older people: self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Gerontologist. 1969; 9:179–186. PMID: 5349366.
Article29. Kazis LE, Anderson JJ, Meenan RF. Effect sizes for interpreting changes in health status. Med Care. 1989; 27(3 Suppl):S178–S189. PMID: 2646488.
Article30. Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985; 13:818–829. PMID: 3928249.31. Chiavone PA, Sens YA. Evaluation of APACHE II system among intensive care patients at a teaching hospital. Sao Paulo Med J. 2003; 121:53–57. PMID: 12870050.
Article32. Wong DT, Crofts SL, Gomez M, McGuire GP, Byrick RJ. Evaluation of predictive ability of APACHE II system and hospital outcome in Canadian intensive care unit patients. Crit Care Med. 1995; 23:1177–1183. PMID: 7600824.
Article33. Houlden H, Edwards M, McNeil J, Greenwood R. Use of the Barthel Index and the Functional Independence Measure during early inpatient rehabilitation after single incident brain injury. Clin Rehabil. 2006; 20:153–159. PMID: 16541936.
Article34. Song JE, Kim MH, Jeong WY, Jung IY, Oh DH, Kim YC, et al. Mortality risk factors for patients with septic shock after implementation of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign Bundles. Infect Chemother. 2016; 48:199–208. PMID: 27659434.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Clinical Analysis of the Corelation Between the Postreplanted Edema & the Late Functional Recovery
- Sepsis, Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock in the Elderly
- Comparison of Functional Recovery Status according to Rehabilitation Therapy in Stroke Patients
- The Effects of Tracheostomy for the Functional Outcomes of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Patients
- Effects of Therapeutic Exercise on Patients with Osteoarthritis of Knee