J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2018 Nov;61(6):669-679. 10.3340/jkns.2017.0295.
Activin A/BMP2 Chimera (AB204) Exhibits Better Spinal Bone Fusion Properties than rhBMP2
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. nsyoon@gmail.com
- 2Protein Engineering Laboratory, joint Center for Biosciences at Songdo Global University, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Cham Teun Teun Research Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Physiology, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 5Structural Biology Laboratory, The Salk Institute for Biological Studies, La Jolla, CA, USA.
- KMID: 2428108
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2017.0295
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
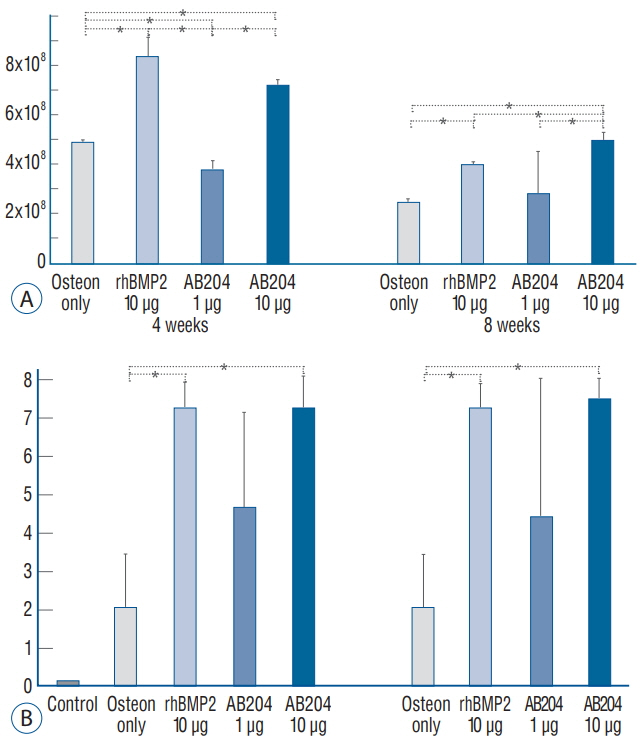
To compare the spinal bone fusion properties of activin A/BMP2 chimera (AB204) with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein (rhBMP2) using a rat posterolateral spinal fusion model.
METHODS
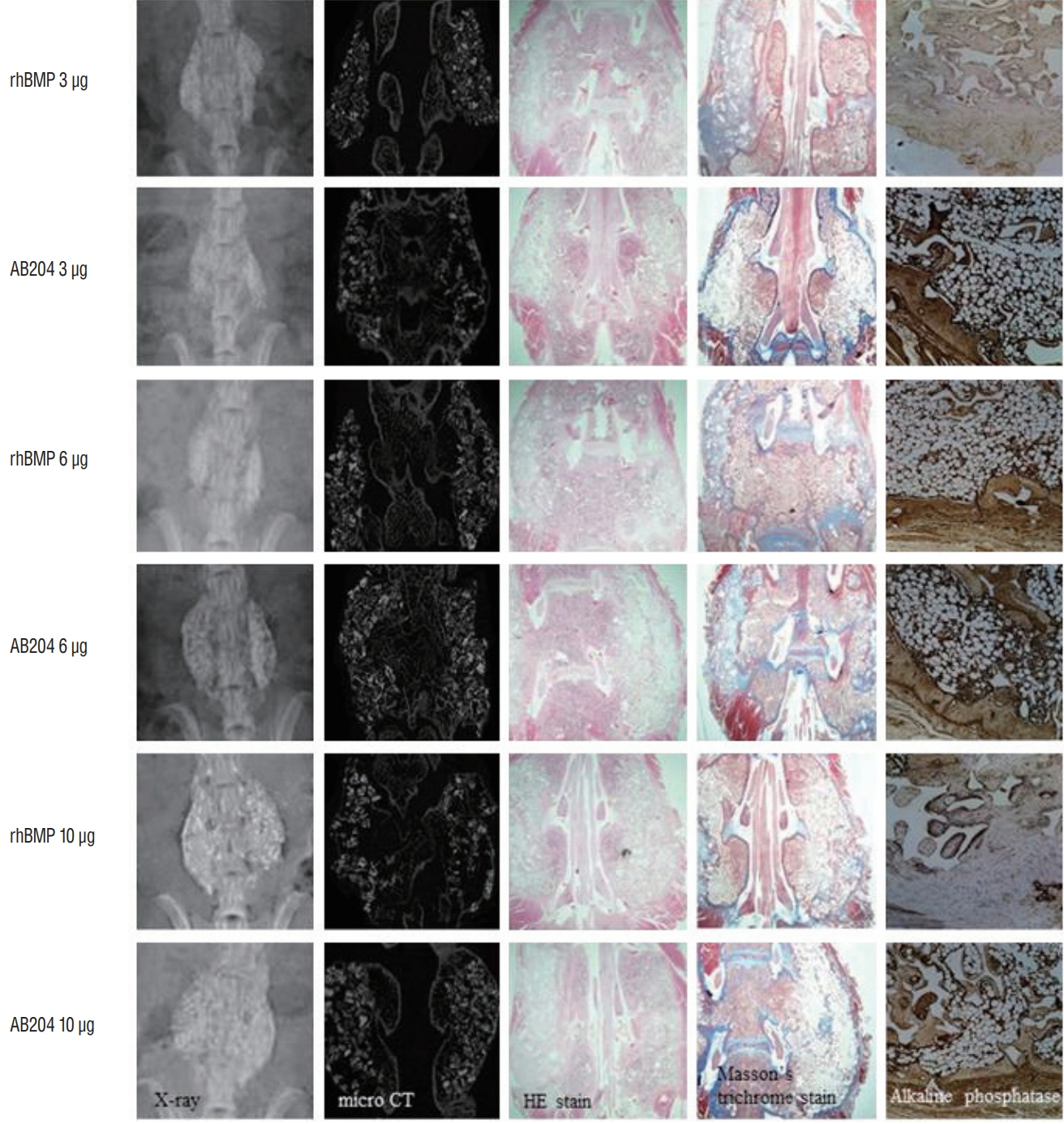
The study was designed to compare the effects and property at different dosages of AB204 and rhBMP2 on spinal bone fusion. Sixty-one male Sprague-Dawley rats underwent posterolateral lumbar spinal fusion using one of nine treatments during the study, that is, sham; osteon only; 3.0 μg, 6.0 μg, or 10.0 μg of rhBMP2 with osteon; and 1.0 μg, 3.0 μg, 6.0 μg, or 10.0 μg of AB204 with osteon. The effects and property on spinal bone fusion was calculated at 4 and 8 weeks after treatment using the scores of physical palpation, simple radiograph, micro-computed tomography, and immunohistochemistry.
RESULTS
Bone fusion scores were significantly higher for 10.0 μg AB204 and 10.0 μg rhBMP2 than for osteon only or 1.0 μg AB204. AB204 exhibited more prolonged osteoblastic activity than rhBMP2. Bone fusion properties of AB204 were similar with the properties of rhBMP2 at doses of 6.0 and 10.0 μg, but, the properties of AB204 at doses of 3.0 μg exhibited better than the properties of rhBMP2 at doses of 3.0 μg.
CONCLUSION
AB204 chimeras could to be more potent for treating spinal bone fusion than rhBMP2 substitutes with increased osteoblastic activity for over a longer period.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Allendorph GP, Read JD, Kawakami Y, Kelber JA, Isaacs MJ, Choe S. Designer TGFβ superfamily ligands with diversified functionality. PLoS One. 6:e26402. 2011.
Article2. Allendorph GP, Vale WW, Choe S. Structure of the ternary signaling complex of a TGF-β superfamily member. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 103:7643–7648. 2006.
Article3. Bhatt RA, Rozental TD. Bone graft substitutes. Hand Clin. 28:457–468. 2012.
Article4. Brown MA, Zhao Q, Baker KA, Naik C, Chen C, Pukac L, et al. Crystal structure of BMP-9 and functional interactions with pro-region and receptors. J Biol Chem. 280:25111–25118. 2005.
Article5. Campana V, Milano G, Pagano E, Barba M, Cicione C, Salonna G, et al. Bone substitutes in orthopaedic surgery: From basic science to clinical practice. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 25:2445–2461. 2014.
Article6. Chen Y, Bhushan A, Vale W. Smad8 mediates the signaling of the ALK-2 [corrected] receptor serine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 94:12938–12943. 1997.7. Derynck R, Miyazono K. The tgf-[beta] family. CSHL Press. 50:29–43. 2008.8. Gray PC, Greenwald J, Blount AL, Kunitake KS, Donaldson CJ, Choe S, et al. Identification of a binding site on the type ii activin receptor for activin and inhibin. J Biol Chem. 275:3206–3212. 2000.
Article9. Greenwald J, Groppe J, Gray P, Wiater E, Kwiatkowski W, Vale W, et al. The BMP7/actrii extracellular domain complex provides new insights into the cooperative nature of receptor assembly. Mol Cell. 11:605–617. 2003.
Article10. Greenwald J, Vega ME, Allendorph GP, Fischer WH, Vale W, Choe S. A flexible activin explains the membrane-dependent cooperative assembly of TGF-β family receptors. Mol Cell. 15:485–489. 2004.
Article11. Han X, Zhang W, Gu J, Zhao H, Ni L, Han J, et al. Accelerated posterolateral spinal fusion by collagen scaffolds modified with engineered collagen-binding human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in rats. PLoS One. 9:e98480. 2014.
Article12. Joseph V, Rampersaud YR. Heterotopic bone formation with the use of rhBMP2 in posterior minimal access interbody fusion: a CT analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 32:2885–2890. 2007.
Article13. Kamiya N, Ye L, Kobayashi T, Mochida Y, Yamauchi M, Kronenberg HM, et al. BMP signaling negatively regulates bone mass through sclerostin by inhibiting the canonical Wnt pathway. Development. 135:3801–3811. 2008.
Article14. Koenig BB, Cook JS, Wolsing DH, Ting J, Tiesman JP, Correa PE, et al. Characterization and cloning of a receptor for BMP-2 and BMP-4 from NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 14:5961–5974. 1994.
Article15. Latzman JM, Kong L, Liu C, Samadani U. Administration of human recombinant bone morphogenetic protein-2 for spine fusion may be associated with transient postoperative renal insufficiency. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 35:E231–E237. 2010.
Article16. Lu J, Bhargav D, Wei AQ, Diwan A. Posterolateral intertransverse spinal fusion possible in osteoporotic rats with BMP-7 in a higher dose delivered on a composite carrier. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 33:242–249. 2008.
Article17. Weis-Garcia F. Serine/threonine kinase receptors: mediators of transforming growth factor beta family signals. Cancer Surv. 27:41–64. 1996.18. Mesfin A, Buchowski JM, Zebala LP, Bakhsh WR, Aronson AB, Fogelson JL, et al. High-dose rhBMP-2 for adults: major and minor complications: a study of 502 spine cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 95:1546–1553. 2013.19. Miron R, Zhang Y. Osteoinduction: a review of old concepts with new standards. J Dent Res. 91:736–744. 2012.20. Miyazaki M, Morishita Y, He W, Hu M, Sintuu C, Hymanson HJ, et al. A porcine collagen-derived matrix as a carrier for recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 enhances spinal fusion in rats. Spine J. 9:22–30. 2009.
Article21. Nishimura R, Kato Y, Chen D, Harris SE, Mundy GR, Yoneda T. Smad5 and DPC4 are key molecules in mediating BMP-2-induced osteoblastic differentiation of the pluripotent mesenchymal precursor cell line C2C12. J Biol Chem. 273:1872–1879. 1998.
Article22. Park BH, Song KJ, Yoon SJ, Park HS, Jang KY, Zhou L, et al. Acceleration of spinal fusion using COMP-angiopoietin 1 with allografting in a rat model. Bone. 49:447–454. 2011.
Article23. Pimenta L, Marchi L, Oliveira L, Coutinho E, Amaral R. A prospective, randomized, controlled trial comparing radiographic and clinical outcomes between stand-alone lateral interbody lumbar fusion with either silicate calcium phosphate or rh-BMP2. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 74:343–350. 2013.
Article24. Pryor LS, Gage E, Langevin C-J, Herrera F, Breithaupt AD, Gordon CR, et al. Review of bone substitutes. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2:151–160. 2009.
Article25. Schlickewei W, Schlickewei C. The use of bone substitutes in the treatment of bone defects-the clinical view and history. Macromol Symp. 253:10–23. 2007.
Article26. ten Dijke P, Franzén P, Yamashita H, Ichijo H, Heldin CH, Miyazono K. Serine/threonine kinase receptors. Prog Growth Factor Res. 5:55–72. 1994.
Article27. Thompson TB, Woodruff TK, Jardetzky TS. Structures of an ActRiiB: activin A complex reveal a novel binding mode for TGF-β ligand: receptor interactions. EMBO J. 22:1555–1566. 2003.
Article28. Wang JC, Kanim LE, Yoo S, Campbell PA, Berk AJ, Lieberman JR. Effect of regional gene therapy with bone morphogenetic protein-2-producing bone marrow cells on spinal fusion in rats. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 85-A:905–911. 2003.
Article29. Yoon BH, Esquivies L, Ahn C, Gray PC, Ye Sk, Kwiatkowski W, et al. An activin A/BMP2 chimera, AB204, displays bone-healing properties superior to those of BMP2. J Bone Miner Res. 29:1950–1959. 2014.
Article30. Zhu W, Rawlins BA, Boachie-Adjei O, Myers ER, Arimizu J, Choi E, et al. Combined bone morphogenetic protein-2 and -7 gene transfer enhances osteoblastic differentiation and spine fusion in a rodent model. J Bone Miner Res. 19:2021–2032. 2004.
Article31. Zimmerman C, Mathews L. Activin receptors: Cellular signalling by receptor serine kinases. Macromol Symp. 253:10–23. 2007.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bone Generation Following Repeated Administration of Recombinant Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2
- Spinal Fusion with B.O.P.(Biocompatible Osteoconductive Polymer)
- Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Sustained Delivery by Hydrogels with Microspheres Repairs Rabbit Mandibular Defects
- Exogenous Stimulation of Human Intervertebral Disc Cells in 3-Dimensional Alginate Bead Culture With BMP2 and L51P: Cytocompatibility and Effects on Cell Phenotype
- Local Bone versus Autogenous Iliac Bone Graft for Posterolateral Lumbar Fusion in the Same Patient