Korean J Ophthalmol.
2018 Dec;32(6):433-437. 10.3341/kjo.2017.0124.
Clinical Results of Anti-adhesion Adjuvants after Endonasal Dacryocystorhinostomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Uijeongbu, Korea.
- 2Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yswoph@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2427956
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2017.0124
Abstract
- PURPOSE
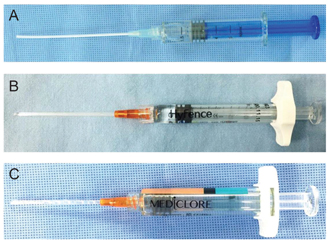
Various absorbable anti-adhesion agents have been used to prevent postoperative synechia formation after endonasal surgery. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the anti-adhesion effects of HyFence and Mediclore after endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) compared to a mixed solution of hyaluronic acid and sodium carboxymethylcellulose (Guardix-Sol).
METHODS
In this retrospective study, endonasal DCR and silicone tube intubation were performed on 198 eyes of 151 patients. Three different anti-adhesion adjuvants were applied to the osteotomy site in the nasal cavity after standard endonasal DCR procedures. The subjects were classified into three respective groups: group A (71 eyes, Guardix-Sol 1.5 g), group B (89 eyes, HyFence 1.5 mL), and group C (38 eyes, Mediclore 1 cc). The three groups were evaluated by asking patients about subjective symptoms and by performing lacrimal irrigation tests and endoscopic examinations.
RESULTS
There were no statistically significant differences in age, sex, timing of tube removal, or follow-up period among the three groups. There were no statistically significant differences in success rates among the three groups (p = 0.990, 91.5% [65 / 71], 92.1% [82 / 89], and 92.1% [35 / 38], respectively).
CONCLUSIONS
HyFence and Mediclore are safe and effective adjunctive modalities following endonasal DCR compared to Guardix-Sol. Therefore, these agents can be considered good alternatives to Guardix-Sol to increase the success rate of endonasal DCR in treating patients with poor prognosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. McDonogh M, Meiring JH. Endoscopic transnasal dacryocystorhinostomy. J Laryngol Otol. 1989; 103:585–587.
Article2. Zilelioglu G, Ugurbas SH, Anadolu Y, et al. Adjunctive use of mitomycin C on endoscopic lacrimal surgery. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998; 82:63–66.3. Choi YJ, Hwang SJ, Lee TS. Short-term clinical results of amniotic membrane application to endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:384–389.
Article4. Cukurova I, Caner Mercan G, Cetinkaya E, et al. Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy: outcomes using mucosal f lap preserving technique. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013; 270:1661–1666.5. Onerci M, Orhan M, Ogretmenoglu O, Irkec M. Long-term results and reasons for failure of intranasal endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy. Acta Otolaryngol. 2000; 120:319–322.6. Kim JH, Lee JH, Yoon JH, et al. Antiadhesive effect of the mixed solution of sodium hyaluronate and sodium carboxymethylcellulose after endoscopic sinus surgery. Am J Rhinol. 2007; 21:95–99.
Article7. Chang C, Hong SM, Cho JH, et al. A randomized, multi-center, single blind, active-controlled, matched pairs clinical study to evaluate prevention of adhesion formation and safety of HyFence in patients after endoscopic sinus surgery. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2014; 7:30–35.
Article8. Song KJ, Lee HM, Lee EJ, et al. Anti-adhesive effect of a thermosensitive poloxamer applied after the removal of nasal packing in endoscopic sinus surgery: a randomised multicentre clinical trial. Clin Otolaryngol. 2013; 38:225–230.
Article9. Elkins TE, Bury RJ, Ritter JL, et al. Adhesion prevention by solutions of sodium carboxymethylcellulose in the rat. I. Fertil Steril. 1984; 41:926–928.
Article10. Oh TH, Paik JS, Yang SW. Results of the mixed solution of hyaluronate and sodium carboxymethylcellulose in endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010; 51:159–163.
Article11. Kimmelman CP, Edelstein DR, Cheng HJ. Sepragel sinus (hylan B) as a postsurgical dressing for endoscopic sinus surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001; 125:603–608.
Article12. Gago LA, Saed GM, Chauhan S, et al. Seprafilm (modified hyaluronic acid and carboxymethylcellulose) acts as a physical barrier. Fertil Steril. 2003; 80:612–616.
Article13. Kwon SW, Seo YW, Cho YA. Antiadhesive effect of the mixed solution of hyaluronate and sodium carboxymethylcellulose after strabismus surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:145–150.
Article14. Kwon SK, Ryu YJ, Kim DW, et al. Prevention of anterior glottis web with hyaluronic acid derivatives in rabbit model. Laryngoscope. 2016; 126:2320–2324.
Article15. Ferland R, Mulani D, Campbell PK. Evaluation of a sprayable polyethylene glycol adhesion barrier in a porcine efficacy model. Hum Reprod. 2001; 16:2718–2723.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Effect of the Mixed Solution of Sodium Hyaluronate and Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose After Endonasal Dacryocystorhinostomy
- Clinical Application of Polyether Ester Urethane in Endonasal Dacryocystorhinostomy
- Clinical Outcomes of Endonasal Dacryocystorhinostomy with Canalicular Trephination in Canalicular Obstruction
- Clinical Effecd of Endonasal Lacrimal Surgery
- Success Rate of Endonasal Dacryocystorhinostomy Based on the Location of the Lacrimal Sac