Hip Pelvis.
2018 Dec;30(4):226-232. 10.5371/hp.2018.30.4.226.
Risk Factors of Neuropathic Pain after Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Saga University, Saga, Japan. epc9719@yahoo.co.jp
- KMID: 2427926
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.4.226
Abstract
- PURPOSE
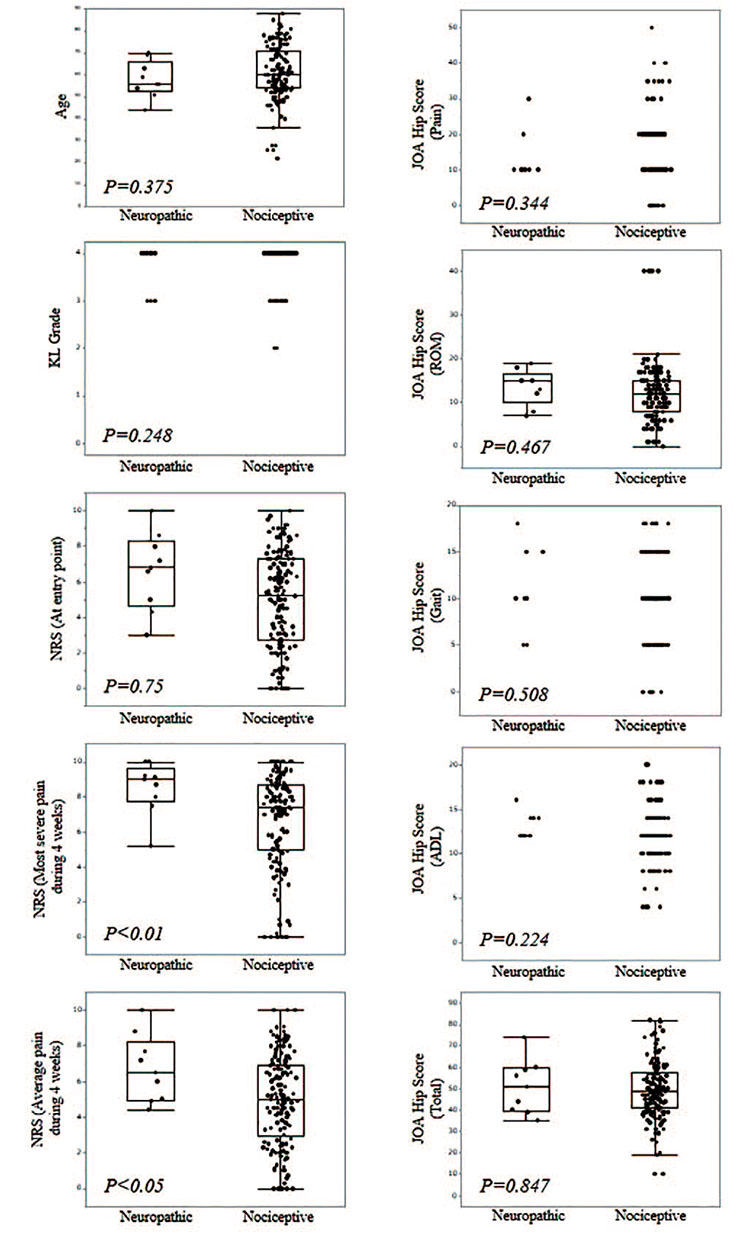
Pain caused by osteoarthritis is primarily nociceptive pain; however, it is considered that a component of this pain is due to neuropathic pain (NP). We investigated the effects of total hip arthroplasty (THA) in patients with NP diagnosed by the PainDETECT questionnaire.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
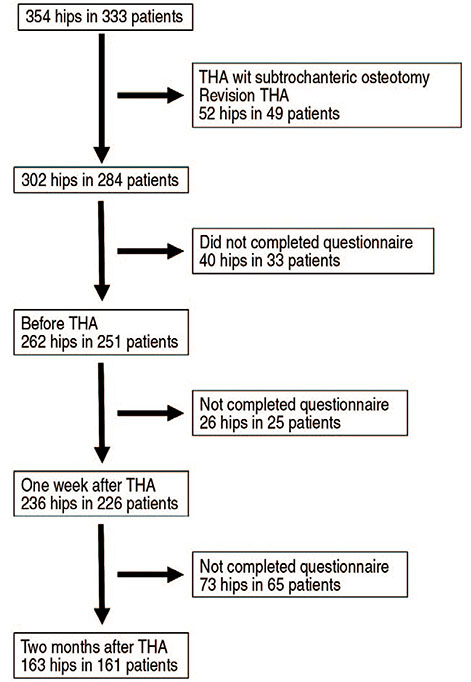
One hundred sixty-three hips (161 patients) were evaluated. All patients were asked to complete the PainDETECT questionnaire based on their experience with NP, and clinical scores were evaluated using the Japanese Orthopaedic Association (JOA) Hip Score before and after THA.
RESULTS
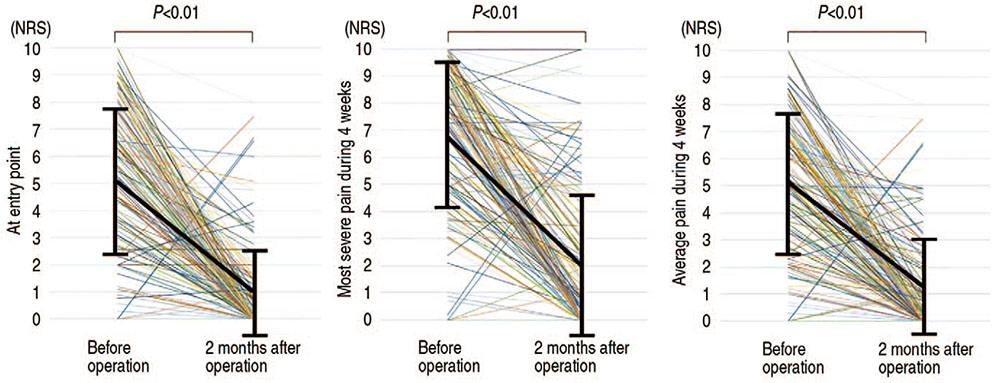
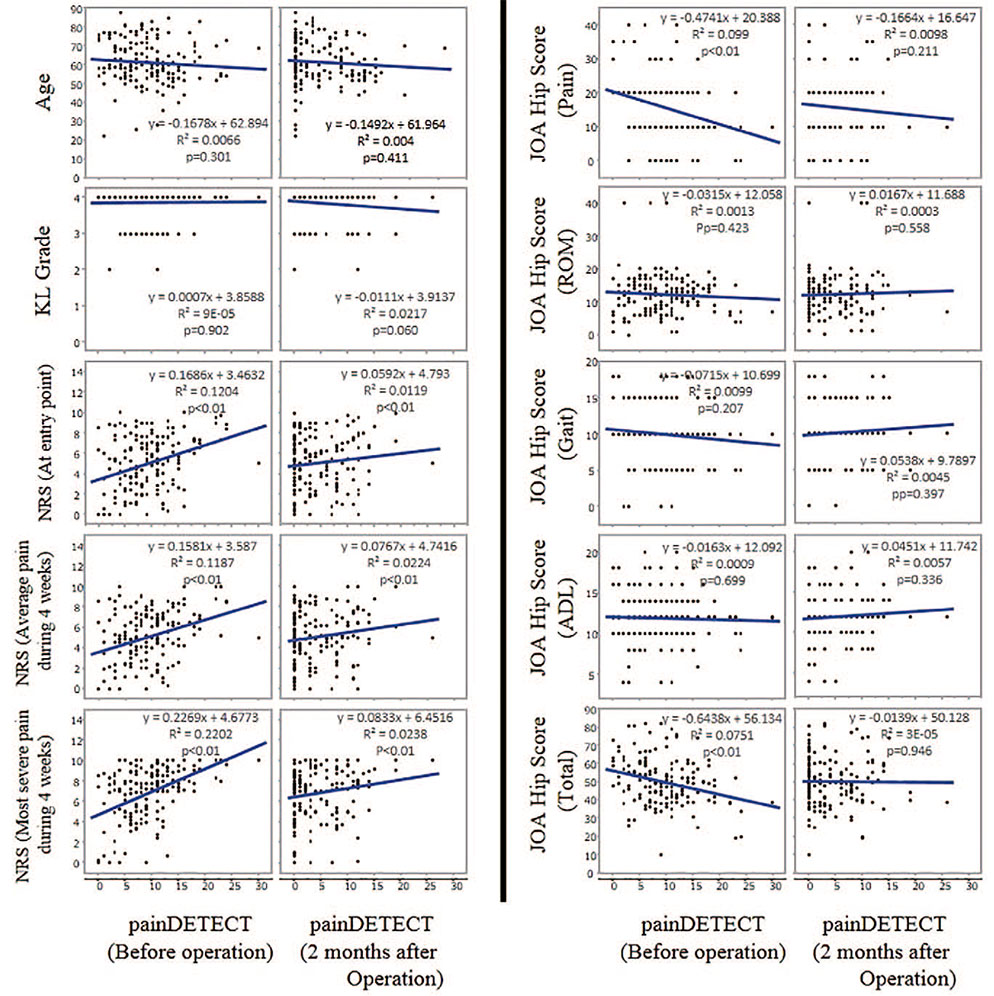
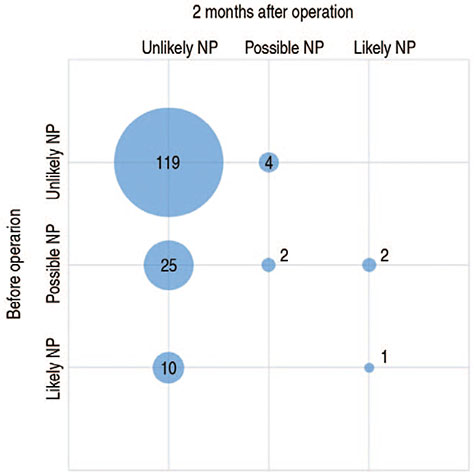
The patients of 24.5% reported NP before THA; 5.5% reported NP 2 months after THA. Prior to THA, there was no significant correlation between the PainDETECT score and the radiographic severity; however, there was a significant correlation between the PainDETECT score and JOA score. NP at 2 months after THA was not significantly correlated with pain scores at 1 week after THA; however, a significant correlation was observed between the preoperative pain score and NP at 2 months after THA.
CONCLUSION
THA was useful for relieving nociceptive pain and for relieving NP in patients with hip osteoarthritis. Preoperative pain was a risk factor for NP after THA. Controlling preoperative pain may be effective for reducing postoperative NP.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sharma L, Kapoor D, Issa S. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: an update. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2006; 18:147–156.
Article2. Jensen MP, Dworkin RH, Gammaitoni AR, Olaleye DO, Oleka N, Galer BS. Assessment of pain quality in chronic neuropathic and nociceptive pain clinical trials with the neuropathic pain scale. J Pain. 2005; 6:98–106.
Article3. Siddall PJ, McClelland JM, Rutkowski SB, Cousins MJ. A longitudinal study of the prevalence and characteristics of pain in the first 5 years following spinal cord injury. Pain. 2003; 103:249–257.
Article4. Dimitroulas T, Duarte RV, Behura A, Kitas GD, Raphael JH. Neuropathic pain in osteoarthritis: a review of pathophysiological mechanisms and implications for treatment. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014; 44:145–154.
Article5. Freynhagen R, Baron R, Gockel U, Tölle TR. painDETECT: a new screening questionnaire to identify neuropathic components in patients with back pain. Curr Med Res Opin. 2006; 22:1911–1920.
Article6. Hochman JR, French MR, Bermingham SL, Hawker GA. The nerve of osteoarthritis pain. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010; 62:1019–1023.
Article7. Shigemura T, Ohtori S, Kishida S, et al. Neuropathic pain in patients with osteoarthritis of hip joint. Eur Orhtop Traumatol. 2011; 2:73.
Article8. Ohtori S, Orita S, Yamashita M, et al. Existence of a neuropathic pain component in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Yonsei Med J. 2012; 53:801–805.
Article9. Charnley J. Arthroplasty of the hip. A new operation. Lancet. 1961; 1:1129–1132.
Article10. Sonohata M, Tajima T, Kitajima M, et al. Total hip arthroplasty combined with double-chevron subtrochanteric osteotomy. J Orthop Sci. 2012; 17:382–389.
Article11. Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957; 16:494–502.
Article12. Schaible HG. Mechanisms of chronic pain in osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2012; 14:549–556.
Article13. Bouhassira D, Lantéri-Minet M, Attal N, Laurent B, Touboul C. Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the general population. Pain. 2008; 136:380–387.
Article14. Hochman JR, Davis AM, Elkayam J, Gagliese L, Hawker GA. Neuropathic pain symptoms on the modified painDETECT correlate with signs of central sensitization in knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013; 21:1236–1242.
Article15. Gwilym SE, Oag HC, Tracey I, Carr AJ. Evidence that central sensitisation is present in patients with shoulder impingement syndrome and influences the outcome after surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011; 93:498–502.
Article16. Sofat N, Ejindu V, Kiely P. What makes osteoarthritis painful? The evidence for local and central pain processing. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011; 50:2157–2165.
Article17. Tawfic Q, Kumar K, Pirani Z, Armstrong K. Prevention of chronic post-surgical pain: the importance of early identification of risk factors. J Anesth. 2017; 31:424–431.
Article18. Macrae WA. Chronic post-surgical pain: 10 years on. Br J Anaesth. 2008; 101:77–86.
Article19. Dworkin RH, O'Connor AB, Backonja M, et al. Pharmacologic management of neuropathic pain: evidence-based recommendations. Pain. 2007; 132:237–251.
Article20. Attal N, Cruccu G, Baron R, et al. EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision. Eur J Neurol. 2010; 17:1113–e88.
Article21. Tan T, Barry P, Reken S, Baker M. Guideline Development Group. Pharmacological management of neuropathic pain in non-specialist settings: summary of NICE guidance. BMJ. 2010; 340:c1079.
Article22. Werner MU, Kongsgaard UE. I. Defining persistent postsurgical pain: is an update required? Br J Anaesth. 2014; 113:1–4.
Article