Different Responses in Induction of Allergen Specific Immunoglobulin G4 and IgE-Blocking Factors for Three Mite Subcutaneous Immunotherapy Products
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Allergy and Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. parkjw@yuhs.ac
- 2Institute of Allergy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Ajou Medical School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 4Department of Dermatology & Cutaneous Biology Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Brain Korea 21 PLUS Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2427161
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2016.57.6.1427
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Specific immunoglobulin G4 (sIgG4) and immunoglobulin E (IgE)-blocking factors produced by subcutaneous immunotherapy (SCIT) play a critical role in the induction of allergen tolerance. However, comparative studies of available SCIT reagents on the induction of sIgG4 are limited. We compared increases in sIgG4 for three different house dust mite (HDM) SCIT reagents.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
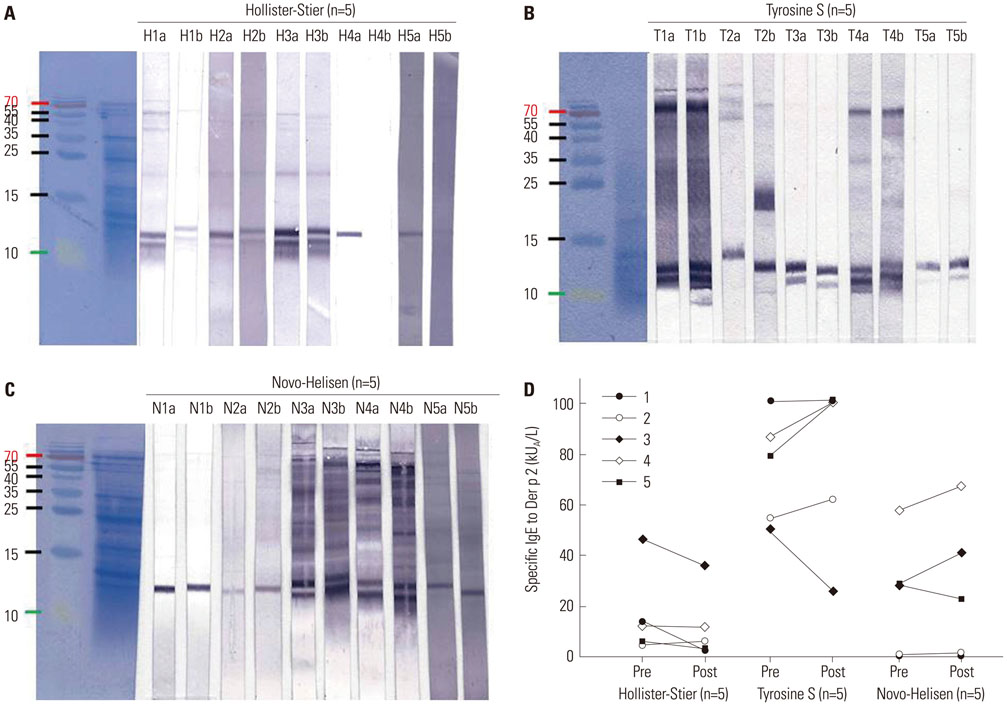
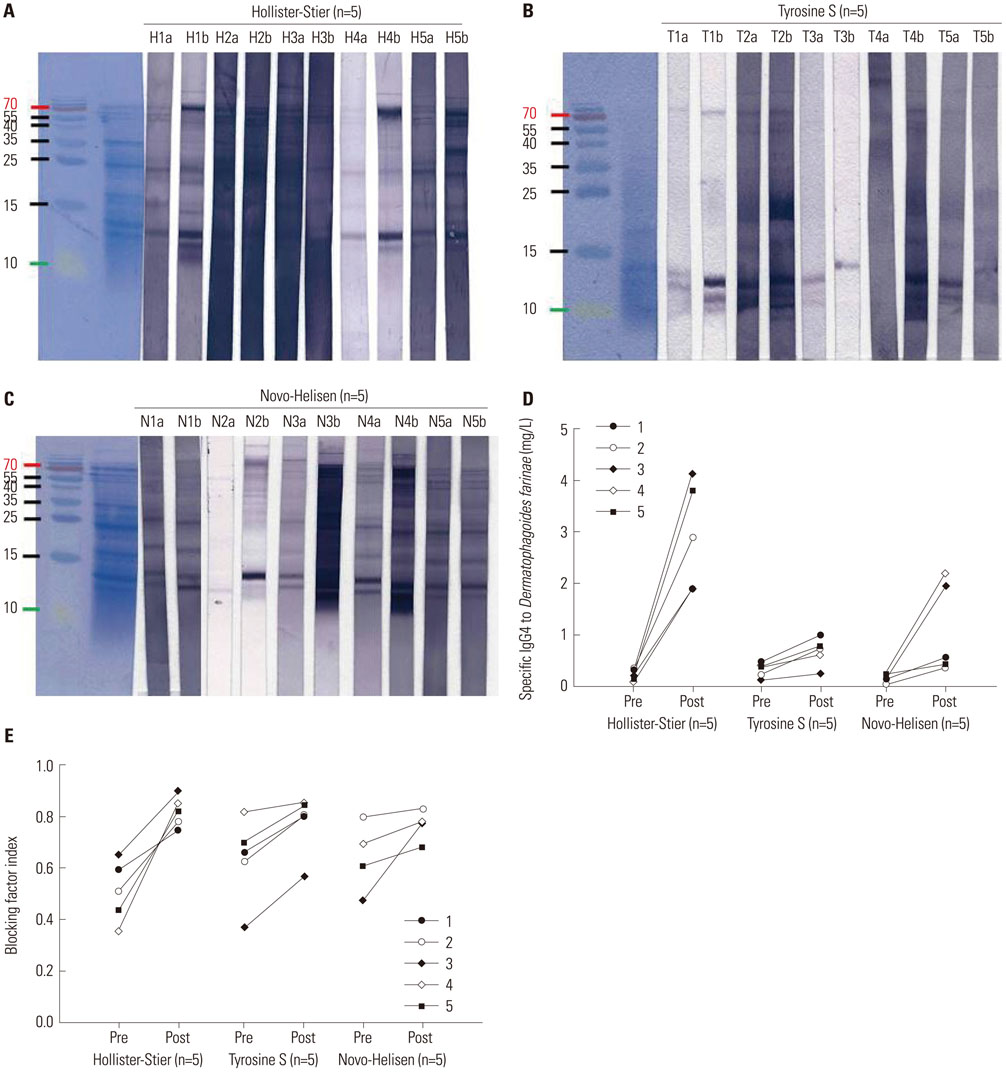
Seventy-two HDM sensitized allergic patients were enrolled and classified into four groups: 1) control (n=27), 2) SCIT with Hollister-Stier® (n=19), 3) Tyrosine S® (n=16), and 4) Novo-Helisen® (n=10). Levels of specific IgE (sIgE), sIgG4, and IgE blocking factor to Dermatophagoides farinae (D. farinae) were measured using ImmunoCAP (sIgE, sIgG4) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (IgE-blocking factors). Levels were measured before and 13.9±6.6 months after the SCIT. The allergen specificity and the induction levels of sIgE and sIgG4 were confirmed by immunoblot analysis.
RESULTS
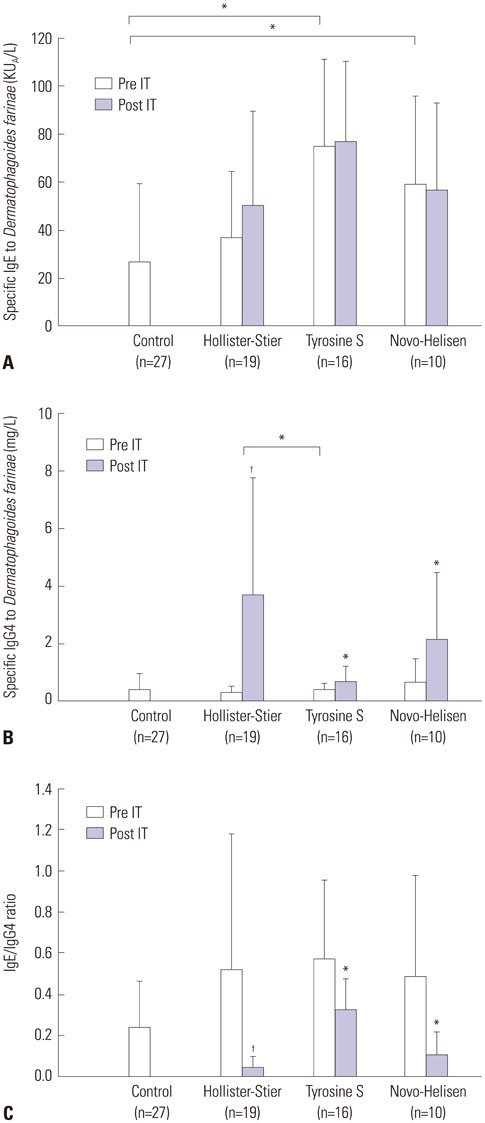
After SCIT, sIgG4 levels to D. farinae increased significantly; however, the increases differed significantly among the SCIT groups (p<0.001). Specific IgG4 levels to D. farinae were highest in Hollister-Stier® (3.7±4.1 mg/L), followed by Novo-Helisen® (2.2±2.3 mg/L) and Tyrosine S® (0.7±0.5 mg/L). In addition, patients who were administered using Hollister-Stier® showed the most significant decrease in IgE/IgG4 ratio (p<0.001) and increase in blocking factor (p=0.009). Finally, according to IgE immunoblot results, the Hollister-Stier® group showed the most significant attenuation of IgE binding patterns among others.
CONCLUSION
Currently available SCIT reagents induce different levels of specific IgG4, IgE/IgG4 ratio, and IgE-blocking factor.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Allergens/administration & dosage/*immunology
Animals
Antibody Specificity/immunology
Antigens, Dermatophagoides
*Antigens, Neoplasm
Dermatitis, Atopic/blood/*immunology/*therapy
Desensitization, Immunologic/*methods
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Female
Humans
Immunoglobulin E/blood/*immunology
Immunoglobulin G/blood/*immunology
Injections, Subcutaneous
Male
Mites/*immunology
Pyroglyphidae/immunology
Treatment Outcome
Young Adult
Allergens
Antigens, Dermatophagoides
Antigens, Neoplasm
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulin E
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Safety and Utility of Rush Immunotherapy with Aqueous Allergen Extracts for Treatment of Respiratory Allergies
Ji-Ho Lee, Jae-Hwa Choi, Keun-Bae Jeong, Seok Jeong Lee, Myoung Kyu Lee, Won-Yeon Lee, Suk Joong Yong, Sang-Ha Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;36(3):e18. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e18.Safety of Ultra-rush Schedule of Subcutaneous Allergen Immunotherapy With House Dust Mite Extract Conducted in an Outpatient Clinic in Patients With Atopic Dermatitis and Allergic Rhinitis
So-Hee Lee, Myoung-Eun Kim, Yoo Seob Shin, Young-Min Ye, Hae-Sim Park, Dong-Ho Nahm
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019;11(6):846-855. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.6.846.Allergen standardization
Jung-Won Park, Kyoung Yong Jeong
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(4):191-196. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.4.191.
Reference
-
1. Kim SH, Shin SY, Lee KH, Kim SW, Cho JS. Long-term effects of specific allergen immunotherapy against house dust mites in polysensitized patients with allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:535–540.
Article2. Burks AW, Calderon MA, Casale T, Cox L, Demoly P, Jutel M, et al. Update on allergy immunotherapy: American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology/European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology/PRACTALL consensus report. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:1288.e3–1296.e3.
Article3. Jutel M, Kosowska A, Smolinska S. Allergen immunotherapy: past, present, and future. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2016; 8:191–197.
Article4. Bae JM, Choi YY, Park CO, Chung KY, Lee KH. Efficacy of allergen-specific immunotherapy for atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 132:110–117.
Article5. Lee J, Lee H, Noh S, Bae BG, Shin JU, Park CO, et al. Retrospective analysis on the effects of house dust mite specific immunotherapy for more than 3 years in atopic dermatitis. Yonsei Med J. 2016; 57:393–398.
Article6. Lee J, Park CO, Lee KH. Specific immunotherapy in atopic dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015; 7:221–229.
Article7. Jutel M, Akdis CA. Immunological mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy. Allergy. 2011; 66:725–732.
Article8. Akdis CA, Akdis M. Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy and immune tolerance to allergens. World Allergy Organ J. 2015; 8:17.
Article9. Didier A, Campo P, Moreno F, Durand-Perdriel F, Marin A, Chartier A. Dose-dependent immunological responses after a 6-month course of sublingual house dust mite immunotherapy in patients with allergic rhinitis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2015; 168:182–192.
Article10. Panizo C, Cimarra M, González-Mancebo E, Vega A, Senent C, Martín S. In vivo and in vitro immunological changes induced by a short course of grass allergy immunotherapy tablets. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2010; 20:454–462.11. Shamji MH, Ljørring C, Francis JN, Calderon MA, Larché M, Kimber I, et al. Functional rather than immunoreactive levels of IgG4 correlate closely with clinical response to grass pollen immunotherapy. Allergy. 2012; 67:217–226.
Article12. Cox L, Jacobsen L. Comparison of allergen immunotherapy practice patterns in the United States and Europe. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2009; 103:451–459.
Article13. Jeong KY, Choi SY, Lee JH, Lee IY, Yong TS, Lee JS, et al. Standardization of house dust mite extracts in Korea. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:346–350.
Article14. Möbs C, Ipsen H, Mayer L, Slotosch C, Petersen A, Würtzen PA, et al. Birch pollen immunotherapy results in long-term loss of Bet v 1-specific TH2 responses, transient TR1 activation, and synthesis of IgE-blocking antibodies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 130:1108.e6–1116.e6.
Article15. Cox L, Esch RE, Corbett M, Hankin C, Nelson M, Plunkett G. Allergen immunotherapy practice in the United States: guidelines, measures, and outcomes. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011; 107:289–299.
Article16. Larenas-Linnemann D, Cox LS. Immunotherapy and Allergy Diagnostics Committee of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. European allergen extract units and potency: review of available information. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008; 100:137–145.
Article17. Calderón M, Cardona V, Demoly P. EAACI 100 Years of Immunotherapy Experts Panel. One hundred years of allergen immunotherapy European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology celebration: review of unanswered questions. Allergy. 2012; 67:462–476.
Article18. Fernández-Caldas E. Towards a more complete standardization of mite allergen extracts. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013; 160:1–3.
Article19. Goikoetxea MJ, Sanz ML, García BE, Mayorga C, Longo N, Gamboa PM, et al. Recommendations for the use of in vitro methods to detect specific immunoglobulin E: are they comparable? J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2013; 23:448–454.20. Wollmann E, Lupinek C, Kundi M, Selb R, Niederberger V, Valenta R. Reduction in allergen-specific IgE binding as measured by microarray: a possible surrogate marker for effects of specific immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015; 136:806.e7–809.e7.21. Ferreira F, Wolf M, Wallner M. Molecular approach to allergy diagnosis and therapy. Yonsei Med J. 2014; 55:839–852.
Article22. Ree HI, Jeon SH, Lee IY, Hong CS, Lee DK. Fauna and geographical distribution of house dust mites in Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 1997; 35:9–17.
Article23. Park HJ, Lee JH, Park KH, Ann HW, Jin MN, Choi SY, et al. A nationwide survey of inhalant allergens sensitization and levels of indoor major allergens in Korea. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:222–227.
Article24. Jeong KY, Park JW, Hong CS. House dust mite allergy in Korea: the most important inhalant allergen in current and future. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:313–325.
Article25. Johannessen BR, Skov LK, Kastrup JS, Kristensen O, Bolwig C, Larsen JN, et al. Structure of the house dust mite allergen Der f 2: implications for function and molecular basis of IgE cross-reactivity. FEBS Lett. 2005; 579:1208–1212.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The early changes of humoral immune response after rush immunotherapy with Dermatophagoides farinae (D.f) and Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (D.p) in house dust mite sensitive asthmatic children
- Two Cases of Atopic Dermatitis Improved by Combination Treatment of Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy and Histamine-Immunoglobulin Complex
- Update in the Mechanisms of Allergen-Specific Immunotheraphy
- New approaches to immunotherapy in house dust mite allergy
- The Effects of Nonspecific IgE and IgG Antibodies on Basophil Histamine Release mediated by Specific IgE Antibodies