Yonsei Med J.
2017 Mar;58(2):370-379. 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.2.370.
Long Pentraxin 3 as a Predictive Marker of Mortality in Severe Septic Patients Who Received Successful Early Goal-Directed Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shhan74@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Infectious Diseases, Hongik Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2427126
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2017.58.2.370
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Pentraxin 3 (PTX3) has been suggested to be a prognostic marker of mortality in severe sepsis. Currently, there are limited data on biomarkers including PTX3 that can be used to predict mortality in severe sepsis patients who have undergone successful initial resuscitation through early goal-directed therapy (EGDT).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
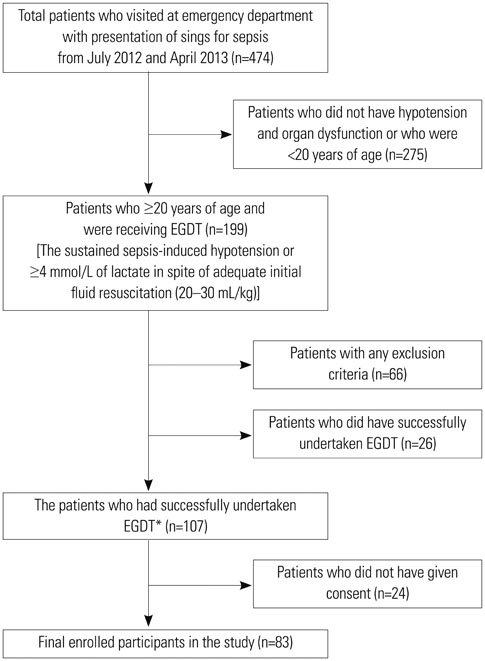
A prospective cohort study was conducted among 83 severe sepsis patients with fulfillment of all EGDT components and the achievement of final goal. Plasma PTX3 levels were measured by sandwich ELISA on hospital day (HD) 0, 3, and 7. The data for procalcitonin, C-reactive protein and delta neutrophil index were collected by electric medical record. The primary outcome was 28-day all-cause mortality.
RESULTS
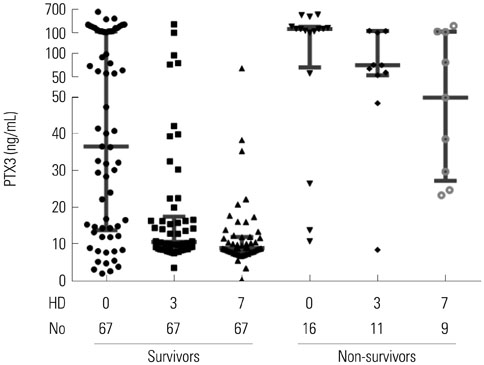
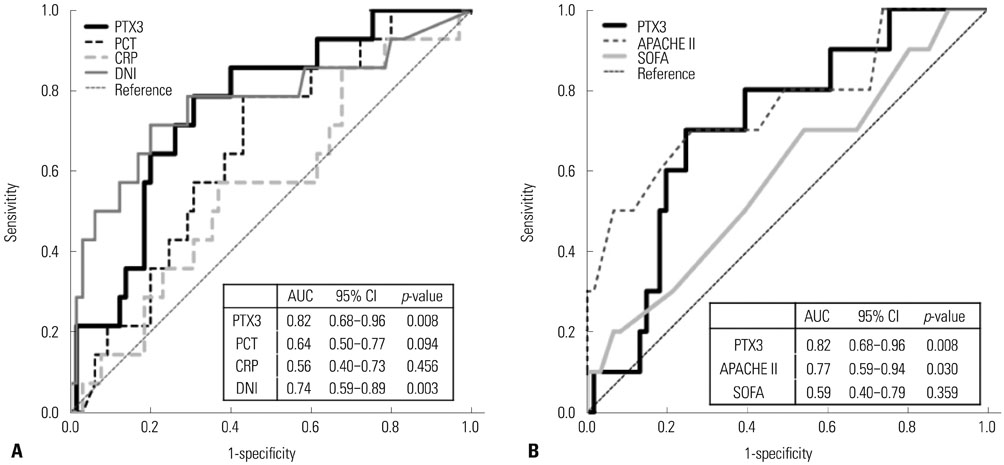
28-day all-cause mortality was 19.3% and the median (interquartile range) APHCH II score of total patients was 16 (13-19). The non-survivors (n=16) had significantly higher PTX3 level at HD 0 [201.4 (56.9-268.6) ng/mL vs. 36.5 (13.7-145.3) ng/mL, p=0.008]. PTX3 had largest AUC(ROC) value for the prediction of mortality among PTX3, procalcitonin, delta neutrophil index, CRP and APACHE II/SOFA sore at HD 0 [0.819, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.677-0.961, p=0.008]. The most valid cut-off level of PTX3 at HD 0 was 140.28 ng/mL (sensitivity 66.7%, specificity 73.8%). The PTX3 and procalcitonin at HD 0 showed strong correlation (r=0.675, p<0.001). However, PTX3 at HD 0 was the only independent predictive marker in Cox's proportional hazards model (≥140 ng/mL; hazard rate 7.16, 95% CI 2.46-15.85, p=0.001).
CONCLUSION
PTX3 at HD 0 could be a powerful predictive biomarker of 28-day all-cause mortality in severe septic patients who have undergone successful EGDT.
MeSH Terms
-
APACHE
Aged
Biomarkers/blood
C-Reactive Protein/*analysis/metabolism
Calcitonin/blood
Cause of Death
Female
Humans
Leukocyte Count
Male
Middle Aged
Neutrophils
Organ Dysfunction Scores
Prognosis
Proportional Hazards Models
Prospective Studies
ROC Curve
Reference Standards
Sensitivity and Specificity
Sepsis/blood/*mortality
Serum Amyloid P-Component/*analysis
Time Factors
Biomarkers
Serum Amyloid P-Component
Calcitonin
C-Reactive Protein
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
An Update on Sepsis Biomarkers
Mi-Hee Kim, Jung-Hyun Choi
Infect Chemother. 2020;52(1):1-18. doi: 10.3947/ic.2020.52.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Bottazzi B, Garlanda C, Cotena A, Moalli F, Jaillon S, Deban L, et al. The long pentraxin PTX3 as a prototypic humoral pattern recognition receptor: interplay with cellular innate immunity. Immunol Rev. 2009; 227:9–18.
Article2. Hasday JD, Bascom R, Costa JJ, Fitzgerald T, Dubin W. Bacterial endotoxin is an active component of cigarette smoke. Chest. 1999; 115:829–835.
Article3. Breviario F, d'Aniello EM, Golay J, Peri G, Bottazzi B, Bairoch A, et al. Interleukin-1-inducible genes in endothelial cells. Cloning of a new gene related to C-reactive protein and serum amyloid P component. J Biol Chem. 1992; 267:22190–22197.
Article4. Introna M, Alles VV, Castellano M, Picardi G, De Gioia L, Bottazzai B, et al. Cloning of mouse PTX3, a new member of the pentraxin gene family expressed at extrahepatic sites. Blood. 1996; 87:1862–1872.
Article5. Vincent JL, Rello J, Marshall J, Silva E, Anzueto A, Martin CD, et al. International study of the prevalence and outcomes of infection in intensive care units. JAMA. 2009; 302:2323–2329.
Article6. Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock, 2012. Intensive Care Med. 2013; 39:165–228.
Article7. Lee K, Chang Y, Song K, Park YY, Huh JW, Hong SB, et al. Associations between single nucleotide polymorphisms of high mobility group box 1 protein and clinical outcomes in Korean sepsis patients. Yonsei Med J. 2016; 57:111–117.
Article8. Schulte W, Bernhagen J, Bucala R. Cytokines in sepsis: potent immunoregulators and potential therapeutic targets--an updated view. Mediators Inflamm. 2013; 2013:165974.
Article9. Huttunen R, Aittoniemi J. New concepts in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of bacteremia and sepsis. J Infect. 2011; 63:407–419.
Article10. Mauri T, Coppadoro A, Bellani G, Bombino M, Patroniti N, Peri G, et al. Pentraxin 3 in acute respiratory distress syndrome: an early marker of severity. Crit Care Med. 2008; 36:2302–2308.
Article11. Muller B, Peri G, Doni A, Torri V, Landmann R, Bottazzi B, et al. Circulating levels of the long pentraxin PTX3 correlate with severity of infection in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 2001; 29:1404–1407.
Article12. Uusitalo-Seppälä R, Huttunen R, Aittoniemi J, Koskinen P, Leino A, Vahlberg T, et al. Pentraxin 3 (PTX3) is associated with severe sepsis and fatal disease in emergency room patients with suspected infection: a prospective cohort study. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e53661.
Article13. Bastrup-Birk S, Skjoedt MO, Munthe-Fog L, Strom JJ, Ma YJ, Garred P. Pentraxin-3 serum levels are associated with disease severity and mortality in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e73119.
Article14. Kunes P, Holubcova Z, Kolackova M, Krejsek J. Pentraxin 3 (PTX 3): an endogenous modulator of the inflammatory response. Mediators Inflamm. 2012; 2012:920517.15. Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J, Parker MM, Jaeschke R, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Crit Care Med. 2008; 36:296–327.
Article16. Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E, Angus D, Cook D, et al. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Intensive Care Med. 2003; 29:530–538.
Article17. Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, Ressler J, Muzzin A, Knoblich B, et al. Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345:1368–1377.
Article18. Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987; 40:373–383.
Article19. Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, De Mendonça A, Bruining H, et al. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996; 22:707–710.
Article20. Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985; 13:818–829.21. Kang CI, Kim SH, Kim HB, Park SW, Choe YJ, Oh MD, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia: risk factors for mortality and influence of delayed receipt of effective antimicrobial therapy on clinical outcome. Clin Infect Dis. 2003; 37:745–751.
Article22. Khwaja A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract. 2012; 120:c179–c184.
Article23. Lee WM, Stravitz RT, Larson AM. Introduction to the revised American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Position Paper on acute liver failure 2011. Hepatology. 2012; 55:965–967.
Article24. Nahm CH, Choi JW, Lee J. Delta neutrophil index in automated immature granulocyte counts for assessing disease severity of patients with sepsis. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2008; 38:241–246.25. Huh JW, Choi HS, Lim CM, Koh Y, Oh YM, Shim TS, et al. Low-dose hydrocortisone treatment for patients with septic shock: a pilot study comparing 3days with 7days. Respirology. 2011; 16:1088–1095.
Article26. Dellinger RP, Carlet JM, Masur H, Gerlach H, Calandra T, Cohen J, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2004; 32:858–873.
Article27. Boyd JC. Mathematical tools for demonstrating the clinical usefulness of biochemical markers. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1997; 227:46–63.
Article28. Vänskä M, Koivula I, Hämäläinen S, Pulkki K, Nousiainen T, Jantunen E, et al. High pentraxin 3 level predicts septic shock and bacteremia at the onset of febrile neutropenia after intensive chemotherapy of hematologic patients. Haematologica. 2011; 96:1385–1389.
Article29. Mauri T, Bellani G, Patroniti N, Coppadoro A, Peri G, Cuccovillo I, et al. Persisting high levels of plasma pentraxin 3 over the first days after severe sepsis and septic shock onset are associated with mortality. Intensive Care Med. 2010; 36:621–629.
Article30. Lin Q, Fu F, Shen L, Zhu B. Pentraxin 3 in the assessment of ventilator-associated pneumonia: an early marker of severity. Heart Lung. 2013; 42:139–145.
Article31. Huttunen R, Hurme M, Aittoniemi J, Huhtala H, Vuento R, Laine J, et al. High plasma level of long pentraxin 3 (PTX3) is associated with fatal disease in bacteremic patients: a prospective cohort study. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e17653.
Article32. Wagenaar JF, Goris MG, Gasem MH, Isbandrio B, Moalli F, Mantovani A, et al. Long pentraxin PTX3 is associated with mortality and disease severity in severe Leptospirosis. J Infect. 2009; 58:425–432.
Article33. Sprong T, Peri G, Neeleman C, Mantovani A, Signorini S, van der Meer JW, et al. Pentraxin 3 and C-reactive protein in severe meningococcal disease. Shock. 2009; 31:28–32.
Article34. Kao SJ, Yang HW, Tsao SM, Cheng CW, Bien MY, Yu MC, et al. Plasma long pentraxin 3 (PTX3) concentration is a novel marker of disease activity in patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013; 51:907–913.
Article35. Vincent JL, Beumier M. Diagnostic and prognostic markers in sepsis. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2013; 11:265–275.
Article36. Seok Y, Choi JR, Kim J, Kim YK, Lee J, Song J, et al. Delta neutrophil index: a promising diagnostic and prognostic marker for sepsis. Shock. 2012; 37:242–246.37. Park BH, Kang YA, Park MS, Jung WJ, Lee SH, Lee SK, et al. Delta neutrophil index as an early marker of disease severity in critically ill patients with sepsis. BMC Infect Dis. 2011; 11:299.
Article38. Kim CH, Park JT, Kim EJ, Han JH, Han JS, Choi JY, et al. An increase in red blood cell distribution width from baseline predicts mortality in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. Crit Care. 2013; 17:R282.
Article39. Jo YH, Kim K, Lee JH, Kang C, Kim T, Park HM, et al. Red cell distribution width is a prognostic factor in severe sepsis and septic shock. Am J Emerg Med. 2013; 31:545–548.
Article40. Cunha C, Aversa F, Lacerda JF, Busca A, Kurzai O, Grube M, et al. Genetic PTX3 deficiency and aspergillosis in stem-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2014; 370:421–432.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Update of Sepsis: Recent Evidences about Early Goal Directed Therapy
- The Effect of Early Goal-directed Therapy Protocol Implementation on the Prognosis of Patients with Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock in the Emergency Department
- The Efficacy of Early Goal-directed Therapy in Septic Shock Patients in the Emergency Department: Severe Sepsis Campaign
- Management of sepsis
- Hypoalbuminemia, Low Base Excess Values, and Tachypnea Predict 28-Day Mortality in Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Patients in the Emergency Department