J Vet Sci.
2018 Nov;19(6):850-854. 10.4142/jvs.2018.19.6.850.
Novel reassortants of clade 2.3.4.4 H5N6 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses possessing genetic heterogeneity in South Korea in late 2017
- Affiliations
-
- 1Avian Influenza Research & Diagnostic Division, Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, Gimcheon 39660, Korea. leeyj700@korea.kr
- KMID: 2427035
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2018.19.6.850
Abstract
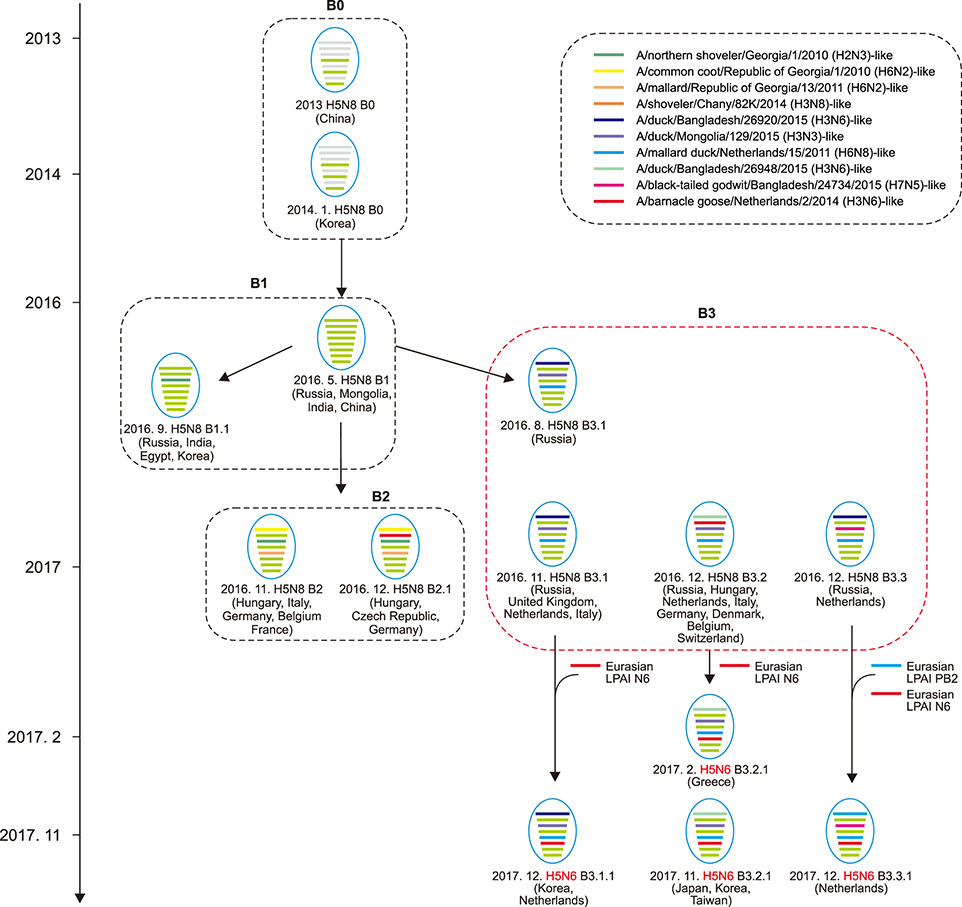
- Novel H5N6 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses (HPAIVs) were isolated from duck farms and migratory bird habitats in South Korea in November to December 2017. Genetic analysis demonstrated that at least two genotypes of H5N6 were generated through reassortment between clade 2.3.4.4 H5N8 HPAIVs and Eurasian low pathogenic avian influenza virus in migratory birds in late 2017, suggesting frequent reassortment of clade 2.3.4.4 H5 HPAIVs and highlighting the need for systematic surveillance in Eurasian breeding grounds.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Beerens N, Heutink R, Bergervoet SA, Harders F, Bossers A, Koch G. Multiple reassorted viruses as cause of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N8) virus epidemic, the Netherlands, 2016. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017; 23:1974–1981.
Article2. Claes F, Morzaria SP, Donis RO. Emergence and dissemination of clade 2.3.4.4 H5Nx influenza viruses—how is the Asian HPAI H5 lineage maintained. Curr Opin Virol. 2016; 16:158–163.
Article3. Drummond AJ, Suchard MA, Xie D, Rambaut A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol Biol Evol. 2012; 29:1969–1973.
Article4. Eagles D, Siregar ES, Dung DH, Weaver J, Wong F, Daniels P. H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza in Southeast Asia. Rev Sci Tech. 2009; 28:341–348.
Article5. Kwon JH, Lee DH, Swayne DE, Noh JY, Yuk SS, Erdene-Ochir TO, Hong WT, Jeong JH, Jeong S, Gwon GB, Song CS. Highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N8) viruses reintroduced into South Korea by migratory waterfowl, 2014–2015. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016; 22:507–510.
Article6. Lee DH, Bahl J, Torchetti MK, Killian ML, Ip HS, DeLiberto TJ, Swayne DE. Highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses and generation of novel reassortants, United States, 2014–2015. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016; 22:1283–1285.
Article7. Lee DH, Sharshov K, Swayne DE, Kurskaya O, Sobolev I, Kabilov M, Alekseev A, Irza V, Shestopalov A. Novel reassortant clade 2.3.4.4 avian influenza A(H5N8) virus in wild aquatic birds, Russia, 2016. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017; 23:359–360.
Article8. Lee EK, Lee YN, Kye SJ, Lewis NS, Brown IH, Sagong M, Heo GB, Kang YM, Cho HK, Kang HM, Cheon SH, Lee M, Park BK, Kim YJ, Lee YJ. Characterization of a novel reassortant H5N6 highly pathogenic avian influenza virus clade 2.3.4.4 in Korea, 2017. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2018; 7:103.
Article9. Lee EK, Song BM, Lee YN, Heo GB, Bae YC, Joh SJ, Park SC, Choi KS, Lee HJ, Jang I, Kang MS, Jeong OM, Choi BK, Lee SM, Jeong SC, Park BK, Lee HS, Lee YJ. Multiple novel H5N6 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses, South Korea, 2016. Infect Genet Evol. 2017; 51:21–23.
Article10. Mitnaul LJ, Matrosovich MN, Castrucci MR, Tuzikov AB, Bovin NV, Kobasa D, Kawaoka Y. Balanced hemagglutinin and neuraminidase activities are critical for efficient replication of influenza A virus. J Virol. 2000; 74:6015–6020.
Article11. Neverov AD, Kryazhimskiy S, Plotkin JB, Bazykin GA. Coordinated evolution of influenza A surface proteins. PLoS Genet. 2015; 11:e1005404.
Article12. Saito T, Tanikawa T, Uchida Y, Takemae N, Kanehira K, Tsunekuni R. Intracontinental and intercontinental dissemination of Asian H5 highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (clade 2.3.4.4) in the winter of 2014–2015. Rev Med Virol. 2015; 25:388–405.
Article13. Takemae N, Tsunekuni R, Sharshov K, Tanikawa T, Uchida Y, Ito H, Soda K, Usui T, Sobolev I, Shestopalov A, Yamaguchi T, Mine J, Ito T, Saito T. Five distinct reassortants of H5N6 highly pathogenic avian influenza A viruses affected Japan during the winter of 2016-2017. Virology. 2017; 512:8–20.
Article14. Wang G, Deng G, Shi J, Luo W, Zhang G, Zhang Q, Liu L, Jiang Y, Li C, Sriwilaijaroen N, Hiramatsu H, Suzuki Y, Kawaoka Y, Chen H. H6 influenza viruses pose a potential threat to human health. J Virol. 2014; 88:3953–3964.
Article15. Wei K, Chen Y, Xie D. Genome-scale evolution and phylodynamics of H5N1 influenza virus in China during 1996-2012. Vet Microbiol. 2013; 167:383–393.
Article16. Zhao K, Gu M, Zhong L, Duan Z, Zhang Y, Zhu Y, Zhao G, Zhao M, Chen Z, Hu S, Liu W, Liu X, Peng D, Liu X. Characterization of three H5N5 and one H5N8 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses in China. Vet Microbiol. 2013; 163:351–357.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent outbreaks of highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses in South Korea
- Evolution, global spread, and pathogenicity of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5Nx clade 2.3.4.4
- Pathogenicity of clade 2.3.4.4 H5N6 highly pathogenic avian influenza virus in three chicken breeds from South Korea in 2016/2017
- Novel reassortant 2.3.4.4B H5N6 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses circulating among wild, domestic birds in Xinjiang, Northwest China
- Surveillance of wild birds for avian influenza virus in Korea