Investig Clin Urol.
2016 Sep;57(5):364-366. 10.4111/icu.2016.57.5.364.
Preperitoneal placement of an inflatable penile prosthesis reservoir for postoperative erectile dysfunction after radical cystoprostatectomy with orthotopic neobladder
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. jspaick@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Urology, Seoul Metropolitan Government-Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2427016
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2016.57.5.364
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To describe a case of safe placement of an inflatable penile prosthesis reservoir for postoperative erectile dysfunction (ED) with a history of radical cystoprostatectomy with an orthotopic Studer neobladder.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
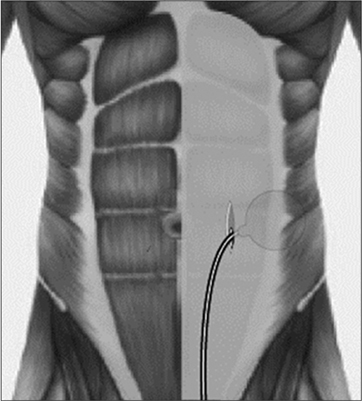
A 55-year-old bladder cancer patient, who underwent radical cystoprostatectomy with orthotopic Studer neobladder 2 years prior, suffered from postoperative ED. A 3-piece inflatable penile prosthesis was implanted via a penoscrotal incision. The alternative reservoir placement began with a longitudinal 4-cm incision, which was 2 finger-breaths to the left and lateral to the umbilicus. Thereafter, the anterior and posterior rectus sheaths were dissected and incised. Then, the transversalis fascia entering into the preperitoneal space was incised, followed by circumferential sweeping using the forefinger, and, finally, placement of a 100 mL 'flat' reservoir. The reservoir was filled with 65 mL saline and then evaluated for back pressure. The reservoir tubing exited through the defect of the rectus sheaths and tunneled through the abdominal fat into the penoscrotal wound.
RESULTS
Total operative time was 105 minutes, and the estimated blood loss was minimal. The patient was discharged at postoperative day 1 and experienced no perioperative complications. At the 6-month follow-up, there was no abdominal bulging from the preperitoneal reservoir, and the reservoir was not palpable.
CONCLUSIONS
The preperitoneal placement of the flat reservoir at the level of the umbilicus is a safe and acceptable surgical technique for postoperative ED after radical cystoprostatectomy with orthotopic neobladder.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Garber BB, Morris A. Intravesical penile implant reservoir: case report, literature review, and strategies for prevention. Int J Impot Res. 2013; 25:41–44.2. Al-Enezi A, Al-Khadhari S, Al-Shaiji TF. Three-piece inflatable penile prosthesis: surgical techniques and pitfalls. J Surg Tech Case Rep. 2011; 3:76–83.3. Perito PE, Wilson SK. Traditional (retroperitoneal) and abdominal wall (ectopic) reservoir placement. J Sex Med. 2011; 8:656–659.4. Morey AF, Cefalu CA, Hudak SJ. High submuscular placement of urologic prosthetic balloons and reservoirs via transscrotal approach. J Sex Med. 2013; 10:603–610.5. Hartman RJ Jr, Helfand BT, McVary KT. Outcomes of lateral retroperitoneal reservoir placement of three-piece penile prosthesis in patients following radical prostatectomy. Int J Impot Res. 2010; 22:279–283.6. Harper WM 4th. Low lithotomy patient positioning for penile prosthesis implantation. J Sex Med. 2010; 7:2320–2323.7. Tran CN, Boncher N, Montague DK, Angermeier KW. Erosion of inflatable penile prosthesis reservoir into neobladder. J Sex Med. 2013; 10:2343–2346.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Convenience of infrapubic approach in inflatable penile prosthetic implantation
- Experience of Mentor Inflatable Penile Prosthesis for Erectile Impotence
- Complications of Penile Prosthesis Implantation
- Urinary Incontinence Could Be Controlled by an Inflatable Penile Prosthesis
- Evolution of penile prosthetic devices