Investig Clin Urol.
2016 Sep;57(5):324-329. 10.4111/icu.2016.57.5.324.
Clinical significance of preoperative thrombocytosis in patients who underwent radical nephrectomy for nonmetastatic renal cell carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. sph04@daum.net
- KMID: 2427010
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2016.57.5.324
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to examine the association of preoperative thrombocytosis with the prognosis of patients with nonmetastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
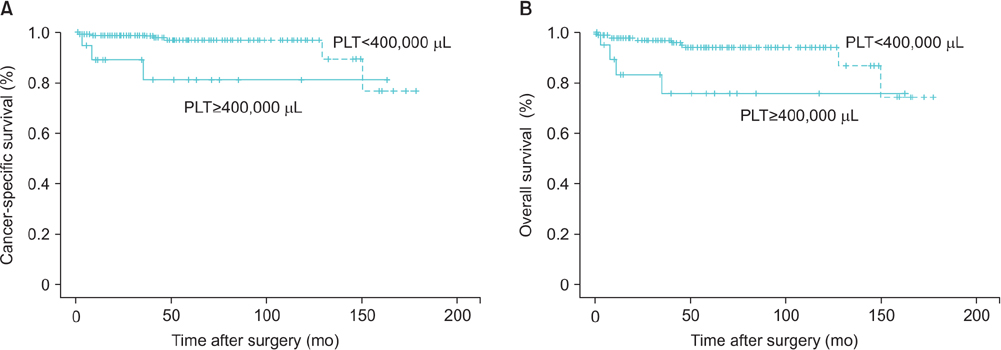
We conducted a retrospective analysis of 187 patients who underwent a radical nephrectomy for nonmetastatic RCC between July 1997 and June 2009. Thrombocytosis was defined as a platelet count≥400,000 µL, and patients were divided into 2 groups according to presence of preoperative thrombocytosis, and the cancer-specific survival rates and overall survival rates of the 2 groups after radical nephrectomy were compared.
RESULTS
The mean age of the patients was 56.0±11.7 years and the mean follow-up period was 59.3±42.1 months; there were 20 patients with preoperative thrombocytosis. Thirty patients developed metastases and 9 patients died during the follow-up period. In Kaplan-Meier analysis using a univariate log-rank test, both cancer-specific survival rate (p=0.013) and overall survival rate (p=0.012) showed significant association with preoperative thrombocytosis. Controlling for pathological TNM stage, Fuhrman grade and tumor diameter, the Cox proportional hazards model for cancer-specific survival rates showed that preoperative thrombocytosis was an independent prognostic factor (p=0.025).
CONCLUSIONS
Preoperative thrombocytosis was associated with poorer prognosis in patients with nonmetastatic RCC. Thus, preoperative platelet count may be clinically useful for risk stratification of patients undergoing surgery for nonmetastatic RCC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Carcinoma, Renal Cell/classification/pathology/*surgery
Female
Follow-Up Studies
Humans
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Kidney Neoplasms/complications/pathology/*surgery
Male
Middle Aged
Neoplasm Grading
Neoplasm Staging
Nephrectomy/*methods
Platelet Count
Prognosis
Retrospective Studies
Risk Assessment/methods
Thrombocytosis/blood/*etiology
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Down-regulation of transient receptor potential melastatin member 7 prevents migration and invasion of renal cell carcinoma cells via inactivation of the Src and Akt pathway
Yun-Sok Ha, Yeon-Yong Kim, Na Hee Yu, So Young Chun, Seock Hwan Choi, Jun Nyung Lee, Bum Soo Kim, Eun Sang Yoo, Tae Gyun Kwon
Investig Clin Urol. 2018;59(4):263-274. doi: 10.4111/icu.2018.59.4.263.
Reference
-
1. Lindblad P. Epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Scand J Surg. 2004; 93:88–96.2. Dekernion JB, Ramming KP, Smith RB. The natural history of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a computer analysis. J Urol. 1978; 120:148–152.3. Ljungberg B, Alamdari FI, Stenling R, Roos G. Prognostic significance of the Heidelberg classification of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 1999; 36:565–569.4. Van Brussel JP, Mickisch GH. Prognostic factors in renal cell and bladder cancer. BJU Int. 1999; 83:902–908.5. Ficarra V, Righetti R, Pilloni S, D'amico A, Maffei N, Novella G, et al. Prognostic factors in patients with renal cell carcinoma: retrospective analysis of 675 cases. Eur Urol. 2002; 41:190–198.6. Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Zincke H, Weaver AL, Blute ML. Comparisons of outcome and prognostic features among histologic subtypes of renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003; 27:612–624.7. Karakiewicz PI, Suardi N, Capitanio U, Jeldres C, Ficarra V, Cindolo L, et al. A preoperative prognostic model for patients treated with nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2009; 55:287–295.8. Saito K, Tatokoro M, Fujii Y, Iimura Y, Koga F, Kawakami S, et al. Impact of C-reactive protein kinetics on survival of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2009; 55:1145–1153.9. Griesshammer M, Bangerter M, Sauer T, Wennauer R, Bergmann L, Heimpel H. Aetiology and clinical significance of thrombocytosis: analysis of 732 patients with an elevated platelet count. J Intern Med. 1999; 245:295–300.10. Pedersen LM, Milman N. Prognostic significance of thrombocytosis in patients with primary lung cancer. Eur Respir J. 1996; 9:1826–1830.11. Hernandez E, Lavine M, Dunton CJ, Gracely E, Parker J. Poor prognosis associated with thrombocytosis in patients with cervical cancer. Cancer. 1992; 69:2975–2977.12. Zeimet AG, Marth C, Muller-Holzner E, Daxenbichler G, Dapunt O. Significance of thrombocytosis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994; 170:549–554.13. Bugada D, Allegri M, Lavand'homme P, De Kock M, Fanelli G. Inflammation-based scores: a new method for patient-targeted strategies and improved perioperative outcome in cancer patients. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:142425.14. Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz AG, Balch CM, Haller DG, editors. AJCC cancer staging manual. 6th ed. New York: Springer-Verlag;2002.15. Medina Lopez RA, Conde Sánchez JM, Congregado Ruiz CB, Gonzalez Resina R, Mármol Navarro S, Torrubia Romero FJ. Prognostic factors in renal cell carcinoma. Actas Urol Esp. 2009; 33:575–583.16. Ljungberg B, Cowan NC, Hanbury DC, Hora M, Kuczyk MA, Merseburger AS, et al. EAU guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: the 2010 update. Eur Urol. 2010; 58:398–406.17. Kontak JA, Campbell SC. Prognostic factors in renal cell carcinoma. Urol Clin North Am. 2003; 30:467–480.18. Fuhrman SA, Lasky LC, Limas C. Prognostic significance of morphologic parameters in renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1982; 6:655–663.19. Inoue K, Kohashikawa K, Suzuki S, Shimada M, Yoshida H. Prognostic significance of thrombocytosis in renal cell carcinoma patients. Int J Urol. 2004; 11:364–367.20. O'Keefe SC, Marshall FF, Issa MM, Harmon MP, Petros JA. Thrombocytosis is associated with a significant increase in the cancer specific death rate after radical nephrectomy. J Urol. 2002; 168(4 Pt 1):1378–1380.21. McDougal WS, Garnick MB. Clinical signs and symptoms of renal cell carcinoma. In : Vogelzang NJ, Scardino PT, Shipley WU, Coffey DS, editors. Comprehensive textbook of genitourinary oncology. 2nd ed. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2000. p. 111–128.22. Partin AW, Criley SR, Steiner MS, Hsieh K, Simons JW, Lumadue J, et al. Serum ferritin as a clinical marker for renal cell carcinoma: influence of tumor volume. Urology. 1995; 45:211–217.23. Erdemir F, Kilciler M, Bedir S, Ozgok Y, Coban H, Erten K. Clinical significance of platelet count in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Urol Int. 2007; 79:111–116.24. Westermark B, Heldin CH. Platelet-derived growth factor: structure, function and implications in normal and malignant cell growth. Acta Oncol. 1993; 32:101–105.25. Karpatkin S, Pearlstein E, Salk PL, Yogeeswaran G. Role of platelets in tumor cell metastases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981; 370:101–118.26. Wosnitzer M, Polland A, Hai Q, Hruby G, McKiernan J. Role of preoperative platelet level in clinical and pathological outcomes after surgery for renal cortical malignancies. BJU Int. 2011; 108:73–79.27. Brookman-May S, May M, Ficarra V, Kainz MC, Kampel-Kettner K, Kohlschreiber S, et al. Does preoperative platelet count and thrombocytosis play a prognostic role in patients undergoing nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma? Results of a comprehensive retrospective series. World J Urol. 2013; 31:1309–1316.28. Cho DS, Kim SJ, Lee SH, Ahn HS, Kim YS, Kim SI. Prognostic significance of preoperative C-reactive protein elevation and thrombocytosis in patients with non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Korean J Urol. 2011; 52:104–109.29. Gogus C, Baltaci S, Filiz E, Elhan A, Bedük Y. Significance of thrombocytosis for determining prognosis in patients with localized renal cell carcinoma. Urology. 2004; 63:447–450.30. Guthrie GJ, Charles KA, Roxburgh CS, Horgan PG, McMillan DC, Clarke SJ. The systemic inflammation-based neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: experience in patients with cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013; 88:218–230.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prognosis Associated with Thrombocytosis in Renal Cell Carcinoma
- A Case of Renal Cell Carcinoma with Hyperglycemia Corrected after Radical Nephrectomy
- Clinical Effect of Renal Angioinfarction in Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Significance of Thrombocytosis as a Prognostic Factor after Radical Nephrectomy in Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Prognostic Significance of Preoperative C-Reactive Protein Elevation and Thrombocytosis in Patients with Non-Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma