Clin Orthop Surg.
2018 Dec;10(4):398-406. 10.4055/cios.2018.10.4.398.
Preoperative Serum Albumin Levels Predict Treatment Cost in Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA.
- 2School of Dental Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA. akamath@post.harvard.edu
- KMID: 2426523
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.4.398
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Hypoalbuminemia (serum albumin < 3.5 g/dL) is associated with increased morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty (THA) and total knee arthroplasty (TKA). However, costs associated with hypoalbuminemia remain unknown. This study investigated the effect of serum albumin on direct treatment costs, length of stay (LOS), and readmissions for primary and revision THA and TKA patients.
METHODS
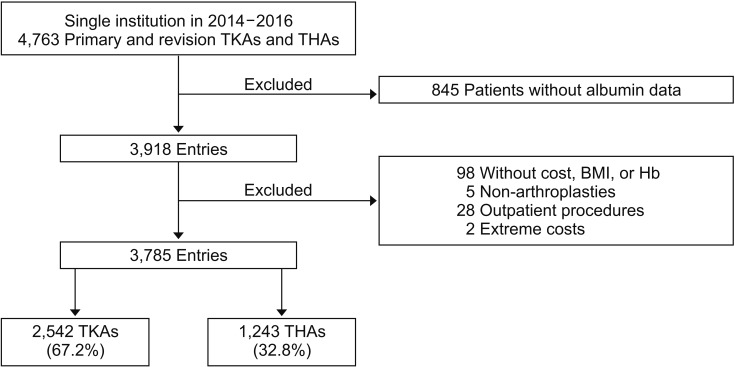
All adult patients at a single institution undergoing primary or revision THA or TKA between January 2014 and December 2016 were retrospectively reviewed. Patients were stratified by preoperative serum albumin level. The primary outcome was total direct costs at index hospitalization. Secondary outcomes included LOS and readmission within 30 days. Multivariable regressions were utilized to adjust for demographics and comorbidities.
RESULTS
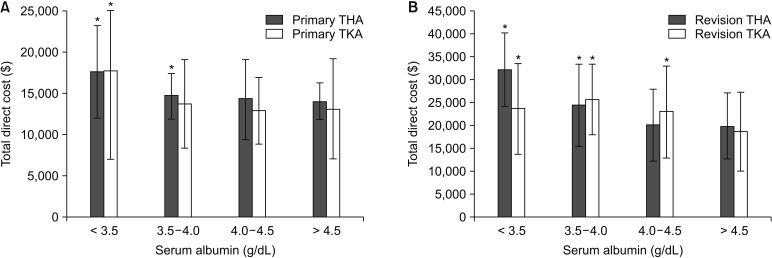
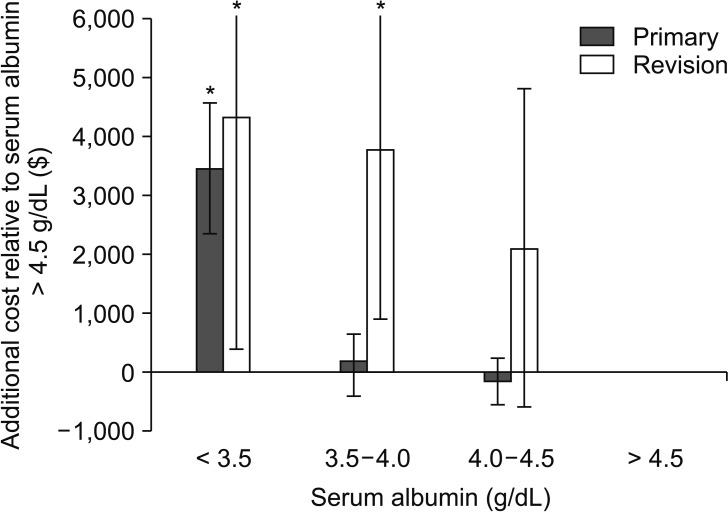
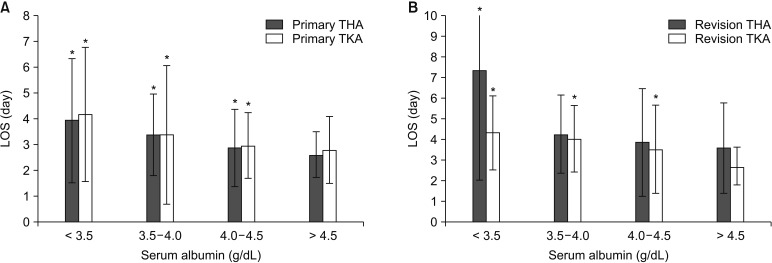
Of 3,785 patients, 114 (3.0%) had hypoalbuminemia. After adjustment, hypoalbuminemia was associated with a 16.2% increase in costs (β = 0.162; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.112 to 0.213; p < 0.001), representing an average cost increase of $3,383 (95% CI, $2,281 to $4,485) relative to costs for serum albumin > 4.5 g/dL. The increased total costs were significantly higher in revision ($4,322, p = 0.034) than in primary ($3,446, p < 0.001) procedures. In adjusted regression, each 1.0 g/dL increase in serum albumin yielded a 6.6% reduction in costs (β = −0.066; 95% CI, −0.090 to −0.042]; p < 0.001), for average savings of $1,282 (95% CI, $759 to $1,806) per unit albumin. Adjusted regressions demonstrated that a 1-point increase in serum albumin reduced readmissions by 53% (odds ratio, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.31-0.73; p = 0.001) and LOS by 0.6 days (β = −0.60; 95% CI, −0.76 to −0.44; p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Hypoalbuminemia is associated with increased total direct costs, LOS, and readmissions following primary and revision THA and TKA. Future efforts to predict and address total costs should take into consideration the patient's preoperative serum albumin levels.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wolford ML, Palso K, Bercovitz A. Hospitalization for total hip replacement among inpatients aged 45 and over: United States, 2000–2010. NCHS Data Brief. 2015; (186):1–8.2. Ellsworth B, Kamath AF. Malnutrition and total joint arthroplasty. J Nat Sci. 2016; 2(3):e179. PMID: 27376151.3. Cross MB, Yi PH, Thomas CF, Garcia J, Della Valle CJ. Evaluation of malnutrition in orthopaedic surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014; 22(3):193–199. PMID: 24603829.
Article4. Bohl DD, Shen MR, Kayupov E, Della Valle CJ. Hypoalbuminemia independently predicts surgical site infection, pneumonia, length of stay, and readmission after total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016; 31(1):15–21. PMID: 26427941.
Article5. Huang R, Greenky M, Kerr GJ, Austin MS, Parvizi J. The effect of malnutrition on patients undergoing elective joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28(8 Suppl):21–24. PMID: 23993346.
Article6. Busher JT. Serum albumin and globulin. In : Walker HK, Hall WD, Hurst JW, editors. Clinical methods: the history, physical, and laboratory examinations. Boston, MA: Butterworths;1990. p. 497–499.7. Inacio MC, Paxton EW, Fisher D, Li RA, Barber TC, Singh JA. Bariatric surgery prior to total joint arthroplasty may not provide dramatic improvements in post-arthroplasty surgical outcomes. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29(7):1359–1364. PMID: 24674730.
Article8. Fu MC, McLawhorn AS, Padgett DE, Cross MB. Hypoalbuminemia is a better predictor than obesity of complications after total knee arthroplasty: a propensity score-adjusted observational analysis. HSS J. 2017; 13(1):66–74. PMID: 28167877.
Article9. Kamath AF, Nelson CL, Elkassabany N, Guo Z, Liu J. Low albumin is a risk factor for complications after revision total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2017; 30(3):269–275. PMID: 27362927.
Article10. Courtney PM, Rozell JC, Melnic CM, Sheth NP, Nelson CL. Effect of malnutrition and morbid obesity on complication rates following primary total joint arthroplasty. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2016; 25(2):99–104. PMID: 27518294.11. Walls JD, Abraham D, Nelson CL, Kamath AF, Elkassabany NM, Liu J. Hypoalbuminemia more than morbid obesity is an independent predictor of complications after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30(12):2290–2295. PMID: 26148837.
Article12. Jensen JE, Jensen TG, Smith TK, Johnston DA, Dudrick SJ. Nutrition in orthopaedic surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982; 64(9):1263–1272. PMID: 7142234.
Article13. Nussenbaum FD, Rodriguez-Quintana D, Fish SM, Green DM, Cahill CW. Implementation of preoperative screening criteria lowers infection and complication rates following elective total hip arthroplasty and total knee arthroplasty in a veteran population. J Arthroplasty. 2018; 33(1):10–13. PMID: 28838614.
Article14. Bozic KJ, Ward L, Vail TP, Maze M. Bundled payments in total joint arthroplasty: targeting opportunities for quality improvement and cost reduction. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; 472(1):188–193. PMID: 23649225.
Article15. Bosco JA 3rd, Karkenny AJ, Hutzler LH, Slover JD, Iorio R. Cost burden of 30-day readmissions following Medicare total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29(5):903–905. PMID: 24332969.
Article16. Clair AJ, Evangelista PJ, Lajam CM, Slover JD, Bosco JA, Iorio R. Cost analysis of total joint arthroplasty readmissions in a bundled payment care improvement initiative. J Arthroplasty. 2016; 31(9):1862–1865. PMID: 27105556.
Article17. Clement RC, Derman PB, Graham DS, et al. Risk factors, causes, and the economic implications of unplanned readmissions following total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28(8 Suppl):7–10.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Total Elbow Arthroplasty for the Fracture of Elbow Arthrodesis Site: A Case Report
- Geometric Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Case Report
- Total Hip Arthroplasty for Ankylosed Hip
- Repeated Periprosthethic Femoral Fracture in a Below Knee Amputee with Ipsilateral Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Case Report
- Cost-Effective Mobile-Based Healthcare System for Managing Total Joint Arthroplasty Follow-Up