Healthc Inform Res.
2017 Jan;23(1):67-73. 10.4258/hir.2017.23.1.67.
Cost-Effective Mobile-Based Healthcare System for Managing Total Joint Arthroplasty Follow-Up
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research and Innovation Department, OpenIT, Heraklion, Greece. bitsaki@tsl.gr
- 2Department of Orthopaedics and Trauma Surgery, University of Duisburg-Essen, Essen, Germany.
- KMID: 2368987
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2017.23.1.67
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
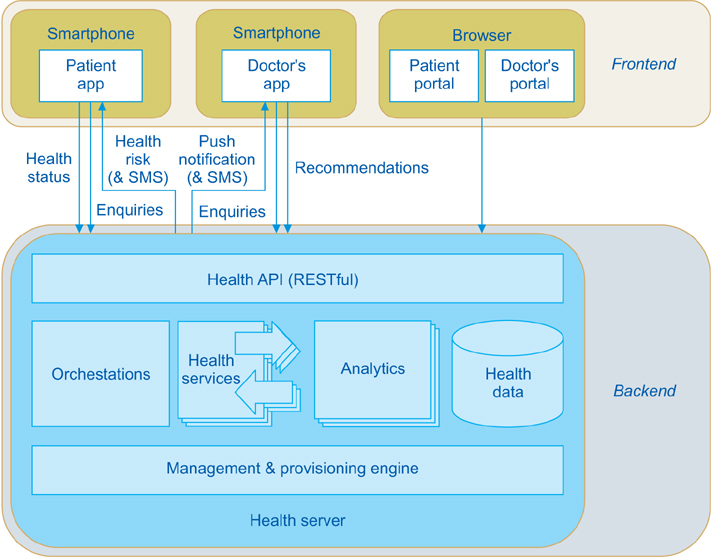
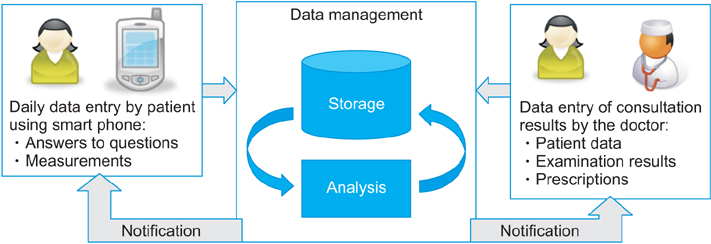
Long-term follow-up care after total joint arthroplasty is essential to evaluate hip and knee arthroplasty outcomes, to provide information to physicians and improve arthroplasty performance, and to improve patients' health condition. In this paper, we aim to improve the communication between arthroplasty patients and physicians and to reduce the cost of follow-up controls based on mobile application technologies and cloud computing.
METHODS
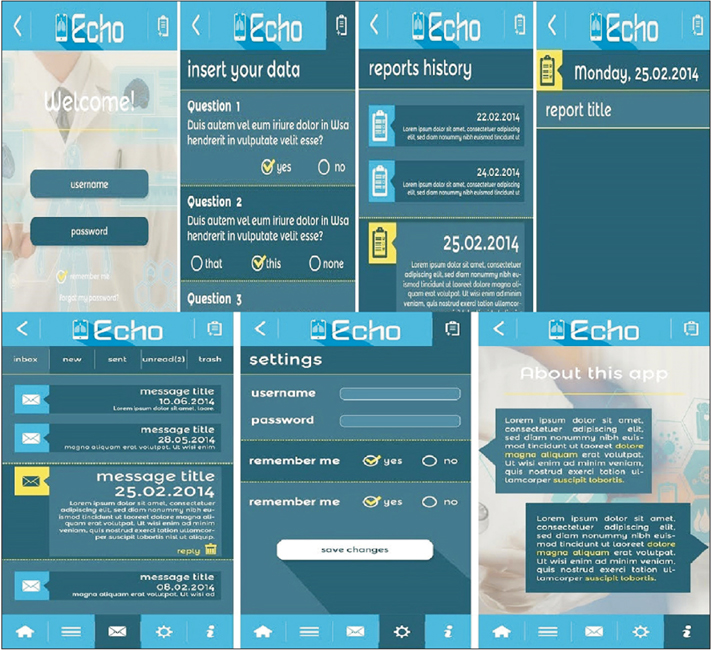
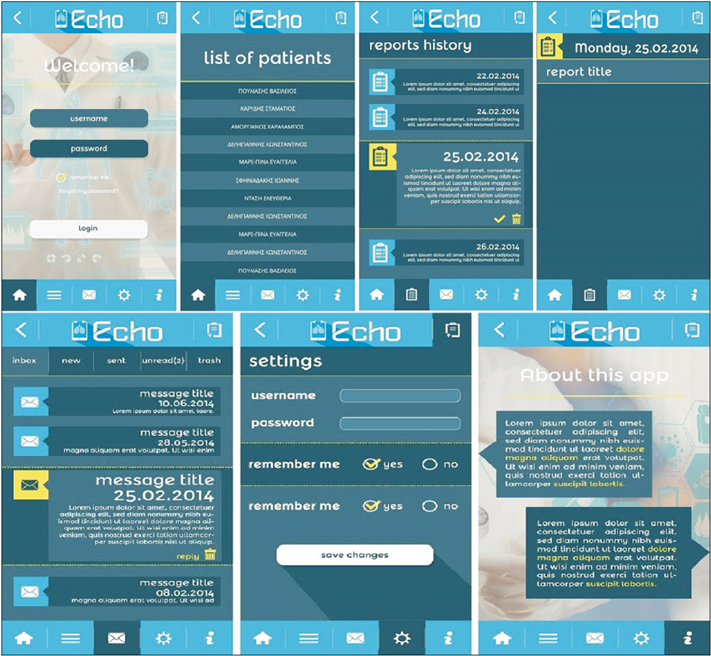
We propose a mobile-based healthcare system that provides cost-effective follow-up controls for primary arthroplasty patients through questions about symptoms in the replaced joint, questionnaires (WOMAC and SF-36v2) and the radiological examination of knee or hip joint. We also perform a cost analysis for a set of 423 patients that were treated in the University Clinic for Orthopedics in Essen-Werden.
RESULTS
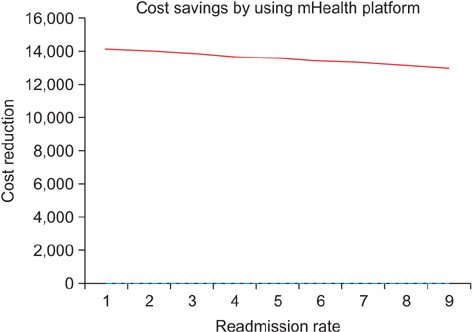
The estimation of healthcare costs shows significant cost savings (a reduction of 63.67% for readmission rate 5%) in both the University Clinic for Orthopedics in Essen-Werden and the state of North Rhine-Westphalia when the mobile-based healthcare system is applied.
CONCLUSIONS
We propose a mHealth system to reduce the cost of follow-up assessments of arthroplasty patients through evaluation of diagnosis, self-monitoring, and regular review of their health status.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Arthroplasty*
Arthroplasty, Replacement
Arthroplasty, Replacement, Knee
Cloud Computing
Cost Savings
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Costs and Cost Analysis
Database Management Systems
Delivery of Health Care*
Diagnosis
Follow-Up Studies*
Health Care Costs
Hip
Hip Joint
Humans
Joints*
Knee
Mobile Applications
Orthopedics
Telemedicine
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, Mowat F, Halpern M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89(4):780–785.
Article2. Haddad FS, Ashby E, Konangamparambath S. Should follow-up of patients with arthroplasties be carried out by general practitioners? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007; 89(9):1133–1134.
Article3. Lavernia CJ. Cost-effectiveness of early surgical intervention in silent osteolysis. J Arthroplasty. 1998; 13(3):277–279.
Article4. Lindahl H, Oden A, Garellick G, Malchau H. The excess mortality due to periprosthetic femur fracture: a study from the Swedish national hip arthroplasty register. Bone. 2007; 40(5):1294–1298.
Article5. Hacking C, Weinrauch P, Whitehouse SL, Crawford RW, Donnelly WJ. Is there a need for routine follow-up after primary total hip arthroplasty? ANZ J Surg. 2010; 80(10):737–740.
Article6. Maru M, Auyeung J, Irwin L. Primary total hip replacement follow-up study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2005; 15(4):286–288.
Article7. Lieberman JR, Leger RR, Tao JC, Clohisy JC, Meneghini RM. Total hip arthroplasty surveillance: when do we see our patients postoperatively? J Arthroplasty. 2011; 26(8):1161–1164.
Article8. Teeny SM, York SC, Mesko JW, Rea RE. Long-term follow-up care recommendations after total hip and knee arthroplasty: results of the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons' member survey. J Arthroplasty. 2003; 18(8):954–962.
Article9. Sharareh B, Schwarzkopf R. Effectiveness of telemedical applications in postoperative follow-up after total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29(5):918–922.e1.
Article10. British Orthopaedic Association. Primary total hip replacement: a guide to good practice. London: British Orthopaedic Association;2006.11. British Orthopaedic Association. Knee replacement: a guide to good practice. London: British Orthopaedic Association;1999.12. Bitsaki M, Koutras C, Koutras G, Leymann F, Steimle F, Wagner S, et al. ChronicOnline: Implementing a mHealth solution for monitoring and early alerting in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Health Informatics J. 2016; 04. 21. [Epub]. DOI: 10.1177/1460458216641480.
Article13. Wood G, Naudie D, MacDonald S, McCalden R, Bourne R. An electronic clinic for arthroplasty follow-up: a pilot study. Can J Surg. 2011; 54(6):381–386.
Article14. Marsh J, Bryant D, MacDonald SJ, Naudie D, Remtulla A, McCalden R, et al. Are patients satisfied with a web-based followup after total joint arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; 472(6):1972–1981.
Article15. Jeong YW, Kim JA. Development of computer-tailored education program for patients with total hip replacement. Healthc Inform Res. 2014; 20(4):258–265.
Article16. Milani P, Coccetta CA, Rabini A, Sciarra T, Massazza G, Ferriero G. Mobile smartphone applications for body position measurement in rehabilitation: a review of goniometric tools. PM R. 2014; 6(11):1038–1043.
Article17. Graham D, Suzuki A, Reitz C, Saxena A, Kuo J, Tetsworth K. Measurement of rotational deformity: using a smartphone application is more accurate than conventional methods. ANZ J Surg. 2013; 83(12):937–941.
Article18. Peters FM, Greeff R, Goldstein N, Frey CT. Improving acetabular cup orientation in total hip arthroplasty by using smartphone technology. J Arthroplasty. 2012; 27(7):1324–1330.
Article19. Hawi N, Kabbani AR, O'Loughlin P, Krettek C, Citak M, Liodakis E. Intraoperative measurement of femoral antetorsion using the anterior cortical angle method: a novel use for smartphones. Int J Med Robot. 2013; 9(1):29–35.
Article20. Roberts N, Bradley B, Williams D. Use of SMS and tablet computer improves the electronic collection of elective orthopaedic patient reported outcome measures. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2014; 96(5):348–351.
Article21. Bellamy N. Osteoarthritis: an evaluative index for clinical trials [master's thesis]. Hamilton, Canada: McMaster University;1982.22. Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I: Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992; 30(6):473–483.23. Official population of Nordrhein-Westfalen [Internet]. Dusseldorf: IT.NRW.com;c2015. cited at 2017 Jan 3. Available from: https://www.it.nrw.de/presse/pressemitteilungen/2015/pres_241_15.html.24. Wengler A, Nimptsch U, Mansky T. Hip and knee replacement in Germany and the USA: analysis of individual inpatient data from German and US hospitals for the years 2005 to 2011. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2014; 111(23-24):407–416.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Mobile-Bearing and Fixed-Bearing Designs in High Flexion Total Knee Arthroplasty: Using a Navigation System
- Economic Burden of Periprosthetic Joint Infection Following Primary Total Knee Replacement in a Developing Country
- Three Concurrent Periprosthetic Joint Infections: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Mobile bearing joint in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Comparison of the Mobile-bearing and Fixed-bearing Designs for High Flexion Total Knee Arthroplasty