Ann Lab Med.
2019 Mar;39(2):214-217. 10.3343/alm.2019.39.2.214.
Simultaneous Detection of Clostridioides difficile Glutamate Dehydrogenase and Toxin A/B: Comparison of the C. DIFF QUIK CHEK COMPLETE and RIDASCREEN Assays
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. micro.lee@samsung.comm, pmhhj77@gmail.com
- KMID: 2425979
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2019.39.2.214
Abstract
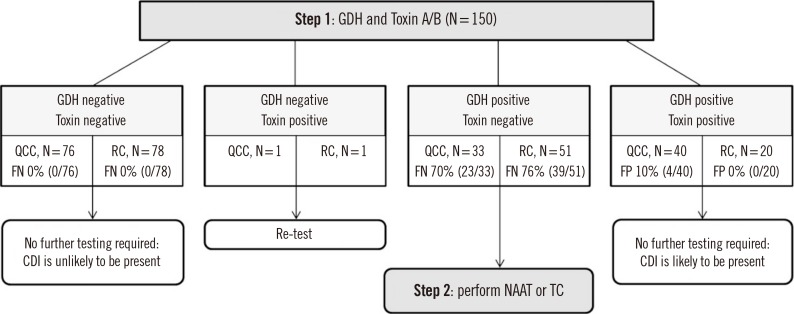
- Various commercial assays have recently been developed for detecting glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) and/or toxin A/B to diagnose Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI). We compared the performance of two assays for the simultaneous detection of C. difficile GDH and toxin A/B, using 150 stool samples: C. DIFF QUIK CHEK COMPLETE (QCC; TechLab, Blacksburg, VA, USA) and RIDASCREEN Clostridium difficile GDH (RC-GDH) and Toxin A/B (RC-Toxin A/B; R-Biopharm, Darmstadt, Germany). For GDH detection, QCC and RC-GDH showed satisfactory sensitivity (95.7% and 94.3%, respectively) and specificity (92.5% and 93.8%, respectively) compared with C. difficile culture. For toxin A/B detection, QCC showed higher sensitivity than RC-Toxin A/B (60.0% vs 33.3%, P < 0.001) compared with toxigenic C. difficile culture. When the results of QCC or RC-GDH+RC-Toxin A/B were used as the first step of a two-step algorithm for diagnosing CDI, QCC permitted more accurate discrimination than RC of positive or negative results for CDI (77.3% and 65.3%, respectively). QCC is useful for the simultaneous detection of C. difficile GDH and toxin A/B as a part of the two-step algorithm for diagnosing CDI.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Makristathis A, Zeller I, Mitteregger D, Kundi M, Hirschl AM. Comprehensive evaluation of chemiluminescent immunoassays for the laboratory diagnosis of Clostridium difficile infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2017; 36:1253–1259. PMID: 28181032.2. Shin BM, Yoo SM, Shin WC. Evaluation of Xpert C. difficile, BD MAX Cdiff, IMDx C. difficile for Abbott m2000, and Illumigene C. difficile assays for direct detection of toxigenic Clostridium difficile in stool specimens. Ann Lab Med. 2016; 36:131–137. PMID: 26709260.3. Mori N, Takahashi T. Characteristics and immunological roles of surface layer proteins in Clostridium difficile. Ann Lab Med. 2018; 38:189–195. PMID: 29401552.4. Planche T, Wilcox M. Reference assays for Clostridium difficile infection: one or two gold standards? J Clin Pathol. 2011; 64:1–5. PMID: 21118850.5. Debast SB, Bauer MP, Kuijper EJ. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases: update of the treatment guidance document for Clostridium difficile infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014; 20:1–26.6. Crobach MJ, Planche T, Eckert C, Barbut F, Terveer EM, Dekkers OM, et al. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases: update of the diagnostic guidance document for Clostridium difficile infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016; 22:S63–S81. PMID: 27460910.7. McDonald LC, Gerding DN, Johnson S, Bakken JS, Carroll KC, Coffin SE, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for Clostridium difficile infection in adults and children: 2017 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA). Clin Infect Dis. 2018; 66:987–994. PMID: 29562266.8. Park KS, Ki CS, Lee NY. Isolation and identification of Clostridium difficile using ChromID C. difficile medium combined with Gram staining and PRO disc testing: a proposal for a simple culture process. Ann Lab Med. 2015; 35:404–409. PMID: 26131411.9. Terhes G, Urbán E, Sóki J, Hamid KA, Nagy E. Community-acquired Clostridium difficile diarrhea caused by binary toxin, toxin A, and toxin B gene-positive isolates in Hungary. J Clin Microbiol. 2004; 42:4316–4318. PMID: 15365032.10. Lemee L, Dhalluin A, Testelin S, Mattrat MA, Maillard K, Lemeland JF, et al. Multiplex PCR targeting tpi (triose phosphate isomerase), tcdA (Toxin A), and tcdB (Toxin B) genes for toxigenic culture of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 2004; 42:5710–5714. PMID: 15583303.11. Kato H, Kato N, Watanabe K, Iwai N, Nakamura H, Yamamoto T, et al. Identification of toxin A-negative, toxin B-positive Clostridium difficile by PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 1998; 36:2178–2182. PMID: 9665986.12. Vanpoucke H, De Baere T, Claeys G, Vaneechoutte M, Verschraegen G. Evaluation of six commercial assays for the rapid detection of Clostridium difficile toxin and/or antigen in stool specimens. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2001; 7:55–64. PMID: 11298143.13. Chung HS, Lee M. Evaluation of the performance of C. DIFF QUIK CHEK COMPLETE and its usefulness in a hospital setting with a high prevalence of Clostridium difficile infection. J Investig Med. 2017; 65:88–92.14. Swindells J, Brenwald N, Reading N, Oppenheim B. Evaluation of diagnostic tests for Clostridium difficile infection. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:606–608. PMID: 20032256.15. Ota KV, McGowan KL. Clostridium difficile testing algorithms using glutamate dehydrogenase antigen and C. difficile toxin enzyme immunoassays with C. difficile nucleic acid amplification testing increase diagnostic yield in a tertiary pediatric population. J Clin Microbiol. 2012; 50:1185–1188. PMID: 22259201.16. Mattner F, Winterfeld I, Mattner L. Diagnosing toxigenic Clostridium difficile: new confidence bounds show culturing increases sensitivity of the toxin A/B enzyme immunoassay and refute gold standards. Scand J Infect Dis. 2012; 44:578–585. PMID: 22404319.17. Eastwood K, Else P, Charlett A, Wilcox M. Comparison of nine commercially available Clostridium difficile toxin detection assays, a real-time PCR assay for C. difficile tcdB, and a glutamate dehydrogenase detection assay to cytotoxin testing and cytotoxigenic culture methods. J Clin Microbiol. 2009; 47:3211–3217. PMID: 19710274.18. Toltzis P, Nerandzic MM, Saade E, O'Riordan MA, Smathers S, Zaoutis T, et al. High proportion of false-positive Clostridium difficile enzyme immunoassays for toxin A and B in pediatric patients. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2012; 33:175–179. PMID: 22227987.19. Cohen SH, Gerding DN, Johnson S, Kelly CP, Loo VG, McDonald LC, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for Clostridium difficile infection in adults: 2010 update by the society for healthcare epidemiology of America (SHEA) and the infectious diseases society of America (IDSA). Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2010; 31:431–455. PMID: 20307191.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnostic Algorithm for the Rapid and CostEffective Detection of Clostridioides difficile Infection: Comparison between C. DIFF QUIK CHEK COMPLETE and VIDAS GDH & Toxin Assay
- Comparison of Simultaneous Use of C. DIFF QUIK CHEK and VIDAS C. difficile Toxin A&B to detect C. difficile in Fecal Specimen
- Evaluation of a Rapid Membrane Enzyme Immunoassay for the Simultaneous Detection of Glutamate Dehydrogenase and Toxin for the Diagnosis of Clostridium difficile Infection
- Evaluation of Rapid Assay (Tox A/B Quik Chek) for the Detection of Clostridium difficile Toxins A and B
- Laboratory diagnosis of Clostridioides difficile infection: guidelines and status of practice in Korea