Ann Lab Med.
2014 May;34(3):235-239. 10.3343/alm.2014.34.3.235.
Evaluation of a Rapid Membrane Enzyme Immunoassay for the Simultaneous Detection of Glutamate Dehydrogenase and Toxin for the Diagnosis of Clostridium difficile Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kscpjsh@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1791926
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2014.34.3.235
Abstract
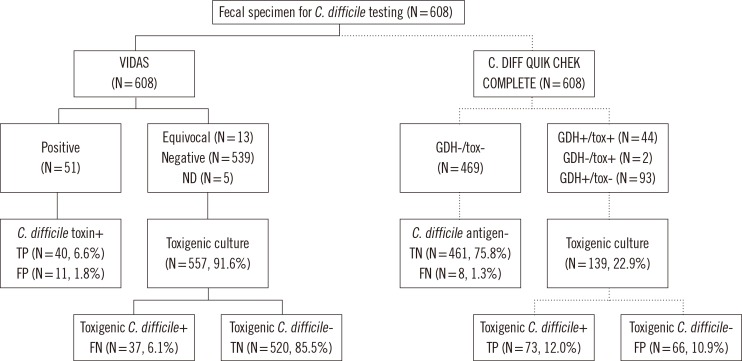
- We evaluated the new C. DIFF QUIK CHEK COMPLETE (CD COMPLETE; TechLab, USA), which is a rapid membrane enzyme immunoassay that uses a combination of glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) antigen and toxin A and B detection. A total of 608 consecutive loose stool specimens collected from the patients with suspected Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) from August to December 2012 were subjected to the CD COMPLETE and VIDAS Clostridium difficile A & B (VIDAS CDAB; bioMerieux, France). Their performances were compared with a toxigenic culture as a reference. Stool specimens that were culture-negative and CD COMPLETE- or VIDAS CDAB-positive were analyzed by using an enrichment procedure. In comparison to the toxigenic cultures, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive values (PPV), and negative predictive values (NPV) were 63.6%, 98.0%, 76.1%, and 96.4%, respectively, for the CD COMPLETE-toxin and 75.5%, 97.4%, 72.5%, and 97.8%, respectively, for the VIDAS CDAB. In comparison to the enriched C. difficile cultures, the sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV for the CD COMPLETE-GDH were 91.0%, 92.4%, 70.5%, and 98.1%, respectively. The CD COMPLETE is a reliable method for the diagnosis of CDI and provides greater sensitivity than toxin enzyme immunoassay alone. Furthermore, the CD COMPLETE-GDH has advantages over direct culture in detecting C. difficile.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Bacterial Proteins/*analysis
Bacterial Toxins/*analysis
Clostridium Infections/*diagnosis/microbiology
Clostridium difficile/enzymology/*isolation & purification/metabolism
Enterotoxins/*analysis
Feces/microbiology
Glutamate Dehydrogenase/*analysis
Humans
*Immunoenzyme Techniques
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic
Sensitivity and Specificity
Bacterial Proteins
Bacterial Toxins
Enterotoxins
Glutamate Dehydrogenase
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kelly CP, LaMont JT. Clostridium difficile-more difficult than ever. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:1932–1940. PMID: 18971494.2. Ticehurst JR, Aird DZ, Dam LM, Borek AP, Hargrove JT, Carroll KC. Effective detection of toxigenic Clostridium difficile by a two-step algorithm including tests for antigen and cytotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 2006; 44:1145–1149. PMID: 16517916.3. Eastwood K, Else P, Charlett A, Wilcox M. Comparison of nine commercially available Clostridium difficile toxin detection assays, a real-time PCR assay for C. difficile tcdB, and a glutamate dehydrogenase detection assay to cytotoxin testing and cytotoxigenic culture methods. J Clin Microbiol. 2009; 47:3211–3217. PMID: 19710274.4. Culbreath K, Ager E, Nemeyer RJ, Kerr A, Gilligan PH. Evolution of testing algorithms at a university hospital for detection of Clostridium infections. J Clin Microbiol. 2012; 50:3073–3076. PMID: 22718938.5. Bauer MP, Kuijper EJ, van Dissel JT. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID): treatment guidance document for Clostridium difficile infection (CDI). Clin Microbiol Infect. 2009; 15:1067–1079. PMID: 19929973.6. Bruins MJ, Verbeek E, Wallinga JA, Bruijnesteijn van Coppenraet LE, Kuijper EJ, Bloembergen P. Evaluation of three enzyme immunoassays and a loop-mediated isothermal amplification test for the laboratory diagnosis of Clostridium difficile infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012; 31:3035–3039. PMID: 22706512.7. Swindells J, Brenwald N, Reading N, Oppenheim B. Evaluation of diagnostic tests for Clostridium difficile infection. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:606–608. PMID: 20032256.8. Crobach MJ, Dekkers OM, Wilcox MH, Kuijper EJ. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID): data review and recommendations for diagnosing Clostridium difficile-infection (CDI). Clin Microbiol Infect. 2009; 15:1053–1066. PMID: 19929972.9. Surawicz CM, Brandt LJ, Binion DG, Ananthakrishnan AN, Curry SR, Gilligan PH, et al. Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of Clostridium difficile infections. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108:478–498. PMID: 23439232.10. Terhes G, Urbán E, Sóki J, Hamid KA, Nagy E. Community-acquired Clostridium difficile diarrhea caused by binary toxin, toxin A, and toxin B gene-positive isolates in Hungary. J Clin Microbiol. 2004; 42:4316–4318. PMID: 15365032.11. Spigaglia P. Comparative analysis of Clostridium difficile clinical isolates belonging to different genetic lineages and time periods. J Med Microbiol. 2004; 53:1129–1136. PMID: 15496392.12. O'Neill GL, Ogunsola FT, Brazier JS, Duerden BI. Modification of a PCR ribotyping method for application as a routine typing scheme for Clostridium difficile. Anaerobe. 1996; 2:205–209.13. Barbut F, Monot M, Rousseau A, Cavelot S, Simon T, Burghoffer B, et al. Rapid diagnosis of Clostridium difficile infection by multiplex real-time PCR. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011; 30:1279–1285. PMID: 21487764.14. Kim H, Jeong SH, Kim M, Lee Y, Lee K. Detection of Clostridium difficile toxin A/B genes by multiplex real-time PCR for the diagnosis of C. difficile infection. J Med Microbiol. 2012; 61:274–277. PMID: 21959205.15. Arroyo LG, Rousseau J, Willey BM, Low DE, Staempfli H, McGeer A, et al. Use of a selective enrichment broth to recover Clostridium difficile from stool swabs stored under different conditions. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:5341–5343. PMID: 16208013.16. Reller ME, Lema CA, Perl TM, Cai M, Ross TL, Speck KA, et al. Yield of stool culture with isolate toxin testing versus a two-step algorithm including stool toxin testing for detection of toxigenic Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 45:3601–3605. PMID: 17804652.17. Shetty N, Wren MW, Coen PG. The role of glutamate dehydrogenase for the detection of Clostridium difficile in faecal samples: a meta-analysis. J Hosp Infect. 2011; 77:1–6. PMID: 21145132.18. Karre T, Sloan L, Patel R, Mandrekar J, Rosenblatt J. Comparison of two commercial molecular assays to a laboratory-developed molecular assay for diagnosis of Clostridium difficile infection. J Clin Microbiol. 2011; 49:725–727. PMID: 21123537.19. Tenover FC, Novak-Weekley S, Woods CW, Peterson LR, Davis T, Schreckenberger P, et al. Impact of strain type on detection of toxigenic Clostridium difficile: comparison of molecular diagnostic and enzyme immunoassay approaches. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:3719–3724. PMID: 20702676.20. Goldenberg SD, Gumban M, Hall A, Patel A, French GL. Lack of effect of strain type on detection of toxigenic Clostridium difficile by glutamate dehydrogenase and polymerase chain reaction. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011; 70:417–419. PMID: 21683272.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Simultaneous Detection of Clostridioides difficile Glutamate Dehydrogenase and Toxin A/B: Comparison of the C. DIFF QUIK CHEK COMPLETE and RIDASCREEN Assays
- Comparison of Simultaneous Use of C. DIFF QUIK CHEK and VIDAS C. difficile Toxin A&B to detect C. difficile in Fecal Specimen
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Clostridium difficile Infection in Korea: The First National Survey
- Diagnosis of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea
- Evaluation of Rapid Assay (Tox A/B Quik Chek) for the Detection of Clostridium difficile Toxins A and B