J Korean Acad Nurs.
2017 Feb;47(1):1-13. 10.4040/jkan.2017.47.1.1.
Effects of a Cognitive Training Program on Cognitive Function and Activities of Daily Living in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, U1 University, Yeongdong, Korea.
- 2College of Nursing, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. msjung@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2425932
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.1.1
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of a cognitive training program on neurocognitive task performance and activities of daily living (ADL) in patients who had a stroke.
METHODS
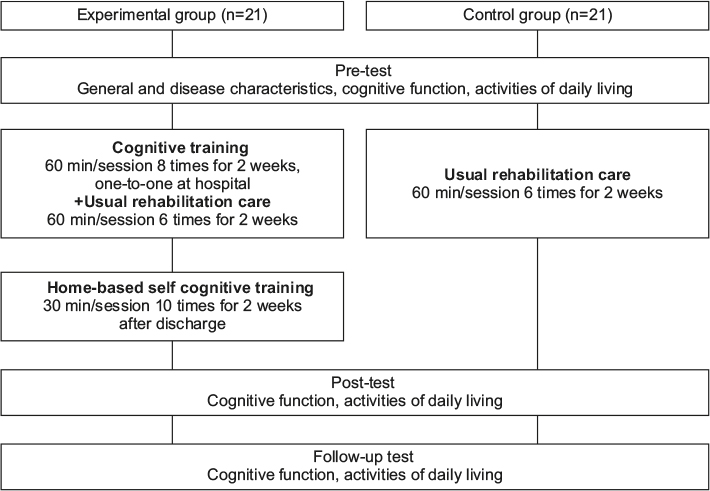
The research design for this study was a nonequivalent control group non-synchronized design. Patients were assigned to the experimental (n=21) or control group (n=21). The experimental group received a 4-week cognitive training program and usual care (i.e., rehabilitation service), while the control was received usual care only. Cognitive function was measured with a standardized neurocognitive test battery and ADL was assessed at baseline and one and two months after completion of the intervention. Repeated measures ANOVA was used to determine changes in cognitive function and ADL over 2 months.
RESULTS
The interaction of group and time was significant indicating that the experimental group showed improvement in attention, visuospatial function, verbal memory, and executive function compared to the control group which had a sustained or gradual decrease in test performance. A significant group by time interaction in instrumental ADL was also found between the experimental group with gradual improvement and the control group showing no noticeable change.
CONCLUSION
Findings show that the cognitive training program developed in this study is beneficial in restoring cognitive function and improving ADL in patients following a stroke. Further study is needed to investigate the long-term relationship between cognitive training participation and cognitive improvement and effective functioning in daily living.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effects of Group Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy on the Nurses’ Job Stress, Burnout, Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment and Turnover Intention
Hye-Lyun Kim, Sook-Hee Yoon
J Korean Acad Nurs. 2018;48(4):432-442. doi: 10.4040/jkan.2018.48.4.432.
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization. International classification of disease-10. Geneva, CH: Author;2007.2. Hong KS, Bang OY, Kang DW, Yu KH, Bae HJ, Lee JS, et al. Stroke statistics in Korea: Part I. Epidemiology and risk factors: A report from the Korean stroke society and clinical research center for stroke. J Stroke. 2013; 15(1):2–20. DOI: 10.5853/jos.2013.15.1.2.3. Statistics Korea. 2012 annual report on the cause of death statistics [Internet]. Daejeon: Author;2013. cited 2013 July 20. Available from: http://kostat.go.kr/portal/korea/kor_nw/2/6/2/index.board?bmode=read&bSeq=&aSeq=308559&pageNo=1&rowNum=10&navCount=10&currPg=&sTarget=title&sTxt=.4. Lawrence ES, Coshall C, Dundas R, Stewart J, Rudd AG, Howard R, et al. Estimates of the prevalence of acute stroke impairments and disability in a multiethnic population. Stroke. 2001; 32(6):1279–1284. DOI: 10.1161/01.STR.32.6.1279.5. Patel MD, Coshall C, Rudd AG, Wolfe CD. Cognitive impairment after stroke: Clinical determinants and its associations with long-term stroke outcomes. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002; 50(4):700–706. DOI: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2002.50165.x.6. Roth EJ, Lovell L, Harvey RL, Heinemann AW, Semik P, Diaz S. Incidence of and risk factors for medical complications during stroke rehabilitation. Stroke. 2001; 32(2):523–529. DOI: 10.1161/01.STR.32.2.523.7. Oros RI, Popescu CA, Iova CA, Mihancea P, Iova SO. The impact of cognitive impairment after stroke on activities of daily living. Hum Vet Med. 2016; 8(1):41–44.8. Sadek JR, Stricker N, Adair JC, Haaland KY. Performancebased everyday functioning after stroke: Relationship with IADL questionnaire and neurocognitive performance. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2011; 17(5):832–840. DOI: 10.1017/s1355617711000841.9. Tatemichi TK, Desmond DW, Stern Y, Paik M, Sano M, Bagiella E. Cognitive impairment after stroke: Frequency, patterns, and relationship to functional abilities. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1994; 57(2):202–207. DOI: 10.1136/jnnp.57.2.202.10. Kim YH. Principle of neurorehabilitation. J Korean Soc Clin Neurophysiol. 2001; 3(2):223–228.11. Rakic P. Neurogenesis in adult primate neocortex: An evaluation of the evidence. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002; 3(1):65–71. DOI: 10.1038/nrn700.12. Uylings HB, Kuypers K, Diamond MC, Veltman WA. Effects of differential environments on plasticity of dendrites of cortical pyramidal neurons in adult rats. Exp Neurol. 1978; 62(3):658–677. DOI: 10.1016/0014-4886(78)90276-5.13. Cicerone KD, Dahlberg C, Kalmar K, Langenbahn DM, Malec JF, Bergquist TF, et al. Evidence-based cognitive rehabilitation: Recommendations for clinical practice. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2000; 81(12):1596–1615. DOI: 10.1053/apmr.2000.19240.14. Lee HR, Kim JY, Han DS. A survey on the cognitive rehabilitation of occupational therapy in Korea. J Korean Soc Occup Ther. 2012; 20(2):73–84.15. Cho YN, Jung JH, Kim HK. A study on cognitive dysfunctions of stroke patients. J Korean Soc Cogn Rehabil. 2012; 1(1):37–50.16. Min DL. Current status and future demand for rehabilitation in stroke patients after discharge [master's thesis]. Seoul: Yonsei University;2003.17. Kim HJ, Yang YS, Choi KH, Kim TY. The effect of computer-based cognitive training program on cognition. Dement Neurocognitive Disord. 2013; 12(4):87–93. DOI: 10.12779/dnd.2013.12.4.87.18. Kang Y, Jang S, Na DL. Seoul neuropsychological screening battery (SNSB-II). 2nd ed. Seoul: Human Brain Research & Consulting Co.;2012.19. Jung HY, Park BK, Shin HS, Kang YK, Pyun SB, Paik NJ, et al. Development of the Korean version of modified barthel index (K-MBI): Multi-center study for subjects with stroke. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2007; 31(3):283–297.20. Kang SJ, Choi SH, Lee BH, Kwon JC, Na DL, Han SH, et al. The reliability and validity of the Korean instrumental activities of daily living (K-IADL). J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2002; 20(1):8–14.21. Kim BR, Chun MH, Kim LS, Park JY. Effect of virtual reality on cognition in stroke patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2011; 35(4):450–459. DOI: 10.5535/arm.2011.35.4.450.22. Cho YN, Kim HK, Kwon HC. The effects of computerized cognitive rehabilitation on cognitive function in elderly post-stroke patients. J Spec Educ Rehabil Sci. 2012; 51(4):261–278.23. Lin ZC, Tao J, Gao YL, Yin DZ, Chen AZ, Chen LD. Analysis of central mechanism of cognitive training on cognitive impairment after stroke: Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Int Med Res. 2014; 42(3):659–668. DOI: 10.1177/0300060513505809.24. Pulvermüller F, Neininger B, Elbert T, Mohr B, Rockstroh B, Koebbel P, et al. Constraint-induced therapy of chronic aphasia after stroke. Stroke. 2001; 32(7):1621–1626. DOI: 10.1161/01.STR.32.7.1621.25. Kim YG. The effects of Korean computer-based cognitive rehabilitation program (CoTras) for the cognition and ADL in stroke. J Korean Soc Occup Ther. 2011; 19(3):75–88.26. Field A. Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS statistics. 4th ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage;2013.27. Shams L, Seitz AR. Benefits of multisensory learning. Trends Cogn Sci. 2008; 12(11):411–417. DOI: 10.1016/j.tics.2008.07.006.28. Lezak MD. Neuropsychological assessment. 3rd ed. New York, NY: Oxford University Press;1995.29. Marshall GA, Rentz DM, Frey MT, Locascio JJ, Johnson KA, Sperling RA. Executive function and instrumental activities of daily living in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011; 7(3):300–308. DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2010.04.005.30. Willis SL, Tennstedt SL, Marsiske M, Ball K, Elias J, Koepke KM, et al. Long-term effects of cognitive training on everyday functional outcomes in older adults. JAMA. 2006; 296(23):2805–2814. DOI: 10.1001/jama.296.23.2805.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Cognitive Rehabilitation Program on Cognitive Function, Depression, and Activities of Daily Living among Patients with Strokes
- The Impacts of Cognitive Function, Disease Severity, and Disability on Ability to Perform Activities of Daily Living after Stroke
- Effectiveness of Cognitive Training to Instrumental Activities of Daily Living in Community-Dwelling Elderly
- Effects of activities of daily living-based dual-task training on upper extremity function, cognitive function, and quality of life in stroke patients
- Development and Evaluation of a Community based Multifaceted Cognitive Training Program for the Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairment