J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2010 May;51(5):779-783.
Valsalva Maneuver-induced Amaurosis Fugax
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. kimjy@cnu.ac.kr
- 2Institute for Medical Sciences, Chungnam National University Research, Daejeon, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report the case of a patient with amaurosis fugax that occurred following a Valsalva maneuver.
CASE SUMMARY
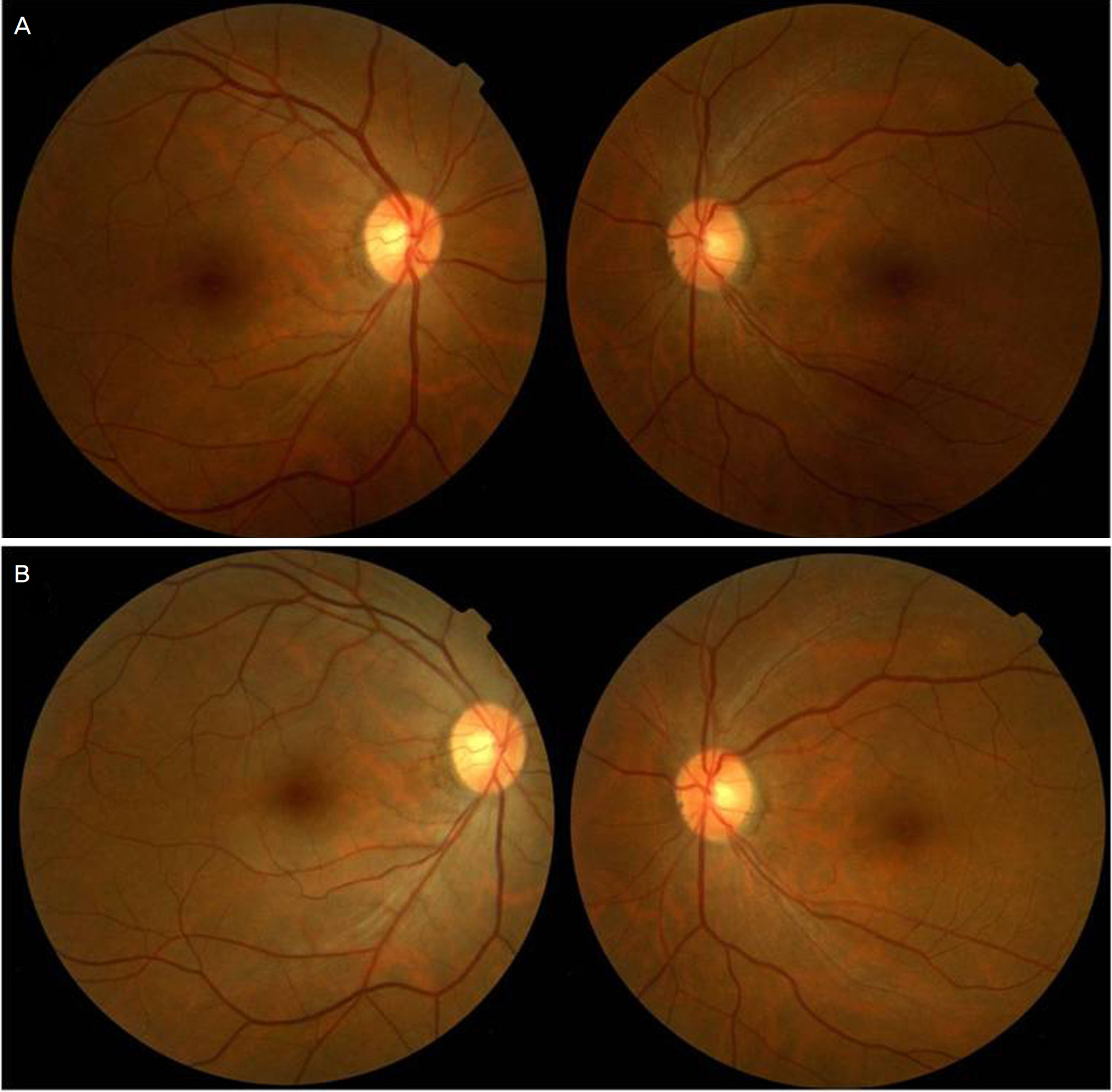
A 40-year-old man presented with amaurosis fugax of the right eye, which had occurred several times during the previous month. After coughing, the visual acuity of the right eye decreased temporarily during the first episode. Subsequently, any time a Valsalva maneuver, such as coughing, occurred, this symptom reappeared. Initially, this symptom persisted for five to ten minutes and occurred once or twice a day, but it gradually increased in frequency. The physical examination was normal, and his best corrected visual acuity was 20/20 bilaterally. Neither specific findings in the slit lamp examination nor abnormal findings in the fundus examination were detected. On fluorescein fundus angiography, no abnormal finding was observed before the symptom was triggered by a Valsalva maneuver, but after the symptom was triggered by coughing, the choroidal and retinal arterial phases were delayed. Hematological and neurological examinations, including magnetic resonance imaging, magnetic resonance angiography, and cerebral angiography, were all normal. Therefore, he was diagnosed with amaurosis fugax generated by a Valsalva maneuver.
CONCLUSIONS
In any patient who complains of amaurosis fugax repeatedly, as seen in this case, one must consider the possibility that it results from a Valsalva maneuver, after eliminating occlusive vascular diseases, such as carotid stenosis or atherosclerotic disease.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Gautier JC. Amaurosis fugax. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:426–8.
Article2. Miller FW, Santoro TJ. Nifedipine in the treatment of migraine abdominal and amaurosis fugax in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1984; 311:921.3. Shaw He Jr, Osher RH, Sith JL. Amaurosis fugax associated with SC hemoglobinopathy and lupus erythematosus. Am J Ophthalmol. 1979; 87:281–5.
Article4. Aasen J, Kerty E, Russell D, et al. Amaurosis fugax: clinical, Doppler, and angiographic findings. Acta Neurol Scand. 1988; 77:450–5.
Article5. Burger SK, Saul RF, Selhorst JB, Thurston SE. Transient monocular blindness caused by vasospasm. N Engl J Med. 1991; 325:870–3.
Article6. Jehn A, Dettwiler BF, Fleischhauer J, et al. Exercise-induced abdominal amaurosis fugax. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002; 120:220–2.7. Hsu HY, Chao AC, Chen YY, et al. Reflux of jugular and retrobulbar venous flow in transient monocular blindness. Ann Neurol. 2008; 63:247–53.
Article8. Amaurosis Fugax Study Group. Current management of amaurosis fugax. Stroke. 1990; 21:201–8.9. North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators. Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in abdominal patients with high-grade carotid stenosis. N Engl J Med. 1991; 325:870–3.10. Winterkorn JM, Kupersmith MJ, Wirtschafter JD, Forman S. Brief abdominal: treatment of vasospastic amaurosis fugax with calcium-channel blockers. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:396–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ocular and Systemic Manifestation of Amaurosis Fugax: Six-Year Observational Study
- Amaurosis Fugax Associated with Ipsilateral Internal Carotid Artery Agenesis
- Transient Visual Loss in Peripapillary Staphyloma
- An Effects of Repeated Valsalva Maneuver on Circulation of Normal Men
- Amaurosis Fugax Associated with Stenosis of the Intracranial Internal Carotid Artery: Successful Restoration of Ophthalmic Artery Flow by Stent Placement