J Korean Acad Nurs.
2018 Oct;48(5):497-505. 10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.497.
Improving Empathy in Nursing Students: A Comparative Longitudinal Study of Two Curricula
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing, School of Nursing, Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Retired, Ankara, Turkey.
- 2Department of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing, Gulhane School of Nursing, University of Health Sciences, Etlik Ankara, Turkey. emine.oksuz@sbu.edu.tr
- 3Department of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing, School of Nursing, Koc University, Istanbul, Turkey.
- KMID: 2424357
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.497
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study aimed to examine changes of empathy levels of nursing student in two different curricula structures, one called "traditional" and the other called "integrated" curricula. The study was a longitudinal design to follow a cohort of nursing students to examine the magnitude of changes in empathy in their education years.
METHODS
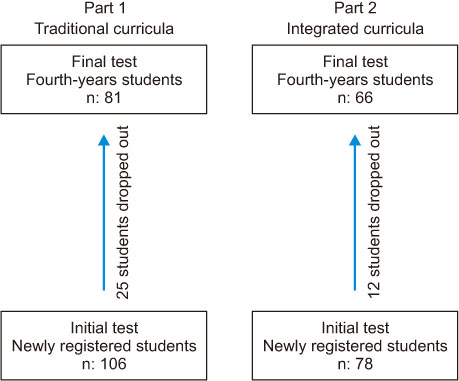
The study was conducted in a public school of nursing giving a baccalaureate degree, which had a fundamental change in their curricula. In all, 81 students from the traditional curricula and 66 students from the integrated curricula completed the study, and data from a total of 147 students were analyzed between 2003 and 2008. The Empathic Communication Skills Scale and the Empathic Tendency Scale were given to the students in the beginning of their freshman year and at the end of the fourth year just before graduation.
RESULTS
Although both of the curricula were seemed effective at improving empathic skills of students, especially the scores of students who completed the integrated curricula were higher than the scores of the other group attending the traditional curricula (p < .05). However, the empathic tendency scores of students in both curricula decreased at the end of fourth year.
CONCLUSION
Although undergraduate nursing curricula either traditional or integrated improved empathic skills, it seemed that integrated curricula were more effective than traditional curricula in increasing empathic skills. The more hours and more experiential methods contributed to improved empathy. The decrease in empathic tendency requires further attention of educators and nurse managers.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ak M, Cinar O, Sutcigil L, Congologlu ED, Haciomeroglu B, Canbaz H, et al. Communication skills training for emergency nurses. Int J Med Sci. 2011; 8(5):397–401. DOI: 10.7150/ijms.8.397.
Article2. López-Pérez B, Ambrona T, Gregory J, Stocks E, Oceja L. Feeling at hospitals: Perspective-taking, empathy and personal distress among professional nurses and nursing students. Nurse Educ Today. 2013; 33(4):334–338. DOI: 10.1016/j.nedt.2013.01.010.
Article3. Dökmen Ü. A new measurement model of the empathy and developing empathy by using psychodrama. J Educ Fac Ankara Univ. 1988; 21(1-2):155–190.4. Hojat M, Vergare MJ, Maxwell K, Brainard G, Herrine SK, Isenberg GA, et al. The devil is in the third year: A longitudinal study of erosion of empathy in medical school. Acad Med. 2009; 84(9):1182–1191. DOI: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181b17e55.
Article5. Pazar B, Demiralp M, Erer İ. The communication skills and the empathic tendency levels of nursing students: A cross-sectional study. Contemp Nurse. 2017; 53(3):368–377. DOI: 10.1080/10376178.2017.1359101.
Article6. Cunico L, Sartori R, Marognolli O, Meneghini AM. Developing empathy in nursing students: A cohort longitudinal study. J Clin Nurs. 2012; 21(13-14):2016–2025. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2012.04105.x.
Article7. Ward J, Cody J, Schaal M, Hojat M. The empathy enigma: An empirical study of decline in empathy among undergraduate nursing students. J Prof Nurs. 2012; 28(1):34–40. DOI: 10.1016/j.profnurs.2011.10.007.
Article8. Williams B, Brown T, Boyle M, McKenna L, Palermo C, Etherington J. Levels of empathy in undergraduate emergency health, nursing, and midwifery students: A longitudinal study. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2014; 5:299–306. DOI: 10.2147/AMEP.S66681.
Article9. Brunero S, Lamont S, Coates M. A review of empathy education in nursing. Nurs Inq. 2010; 17(1):65–74. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1800.2009.00482.x.
Article10. McKenna L, Boyle M, Brown T, Williams B, Molloy A, Lewis B, et al. Levels of empathy in undergraduate nursing students. Int J Nurs Pract. 2012; 18(3):246–251. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-172X.2012.02035.x.
Article11. Ozcan CT, Oflaz F, Cicek HS. Empathy: The effects of undergraduate nursing education in Turkey. Int Nurs Rev. 2010; 57(4):493–499. DOI: 10.1111/j.1466-7657.2010.00832.x.
Article12. Goodwin J, Deady R. The art of mental health practice: The role of drama in developing empathy. Perspect Psychiatr Care. 2013; 49(2):126–134. DOI: 10.1111/ppc.12004.
Article13. Richardson C, Percy M, Hughes J. Nursing therapeutics: Teaching student nurses care, compassion and empathy. Nurse Educ Today. 2015; 35(5):e1–e5. DOI: 10.1016/j.nedt.2015.01.016.
Article14. Ortabağ T, Tosun N, Bebiş H, Yava A, Sütçü Çiçek H, Akbayrak N. The other side of the bed: The experiences of first class nursing school students hospitalized for training purposes. Gülhane Med J. 2010; 52(3):189–197.15. Kaya H. Nursing education to improve global health. Int J Hum Sci. 2010; 7(1):360–365.16. Ozcan CT, Oflaz F, Bakir B. The effect of a structured empathy course on the students of a medical and a nursing school. Int Nurs Rev. 2012; 59(4):532–538. DOI: 10.1111/j.1466-7657.2012.01019.x.
Article17. Lovan SR, Wilson M. Comparing empathy levels in students at the beginning and end of a nursing program. Int J Hum Caring. 2012; 16(3):28–33.
Article18. Bagnasco A, Pagnucci N, Tolotti A, Rosa F, Torre G, Sasso L. The role of simulation in developing communication and gestural skills in medical students. BMC Med Educ. 2014; 14(1):106. DOI: 10.1186/1472-6920-14-106.
Article19. Briggs CL, Fox L, Abell CH. The influence of film on the empathy ratings of nursing students. Int J Hum Caring. 2012; 16(2):59–63.
Article20. Chen D, Lew R, Hershman W, Orlander J. A cross-sectional measurement of medical student empathy. J Gen Intern Med. 2007; 22(10):1434–1438. DOI: 10.1007/s11606-007-0298-x.
Article21. Williams B, Boyle M, Fielder C. Empathetic attitudes of undergraduate paramedic and nursing students towards four medical conditions: A three-year longitudinal study. Nurse Educ Today. 2015; 35(2):e14–e18. DOI: 10.1016/j.nedt.2014.12.007.
Article22. Hojat M, Vergare M, Isenberg G, Cohen M, Spandorfer J. Underlying construct of empathy, optimism, and burnout in medical students. Int J Med Educ. 2015; 6:12–16. DOI: 10.5116/ijme.54c3.60cd.
Article23. Tei S, Becker C, Kawada R, Fujino J, Jankowski KF, Sugihara G, et al. Can we predict burnout severity from empathy-related brain activity? Transl Psychiatry. 2014; 4:e393. DOI: 10.1038/tp.2014.34.
Article24. Ledoux K. Understanding compassion fatigue: Understanding compassion. J Adv Nurs. 2015; 71(9):2041–2050. DOI: 10.1111/jan.12686.
Article25. Gibbons C. Stress, coping and burn-out in nursing students. Int J Nurs Stud. 2010; 47(10):1299–1309. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2010.02.015.
Article26. Gibbons C, Dempster M, Moutray M. Stress, coping and satisfaction in nursing students. J Adv Nurs. 2011; 67(3):621–632. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2010.05495.x.
Article27. Arieli D. Emotional work and diversity in clinical placements of nursing students. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2013; 45(2):192–201. DOI: 10.1111/jnu.12020.
Article28. Ward J. The empathy enigma: Does it still exist? Comparison of empathy using students and standardized actors. Nurse Educ. 2016; 41(3):134–138. DOI: 10.1097/NNE.0000000000000236.29. Haley B, Heo S, Wright P, Barone C, Rettigantid MR, Anders M. Effects of using an advancing care excellence for seniors simulation scenario on nursing student empathy: A randomized controlled trial. Clin Simul Nurs. 2017; 13(10):511–519. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecns.2017.06.003.
Article30. Bas-Sarmiento P, Fernández-Gutiérrez M, Baena-Baños M, Romero-Sánchez JM. Efficacy of empathy training in nursing students: A quasi-experimental study. Nurse Educ Today. 2017; 59:59–65. DOI: 10.1016/j.nedt.2017.08.012.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors influencing nursing students' empathy
- Relations on Self-esteem, Empathy and Interpersonal Relationship for Reinforcing Competence in Communication of Nursing Students
- Changes in Empathy of Nursing College Students: A Cohort Longitudinal Study
- Mediating Effect of Cultural Competence between Cultural Empathy and Nursing Professionalism in Nursing Students
- The Effects of Empathy on Interpersonal Relationship through the Mediating Effect of Ego-resilience in Nursing Students