J Korean Fract Soc.
2017 Jul;30(3):137-141. 10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.3.137.
Atypical Fracture-Like Insufficiency Fracture of the Tibia with Prolonged Bisphosphonate Drug: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. hangugi@gmail.com
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2424122
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.3.137
Abstract
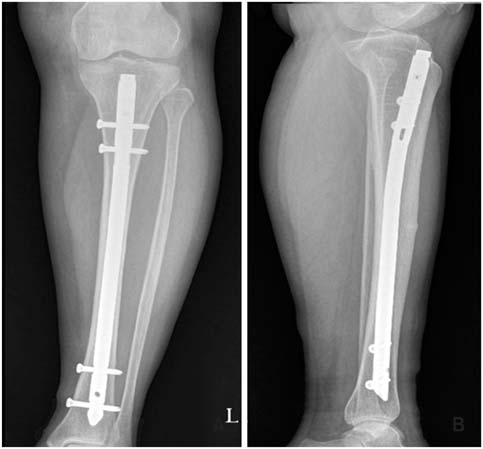
- Atypical femoral fracture related to a long-term bisphosphonate therapy has commonly been reported; however, a fracture at the site other than the femur has rarely been reported to date. Herein, we report a case of a patient on long-term bisphosphonate therapy who presented atypical tibial insufficiency fracture at the anterolateral aspect of diaphysis, without trauma. We, for the first time in Korea, present this case with a literature review.
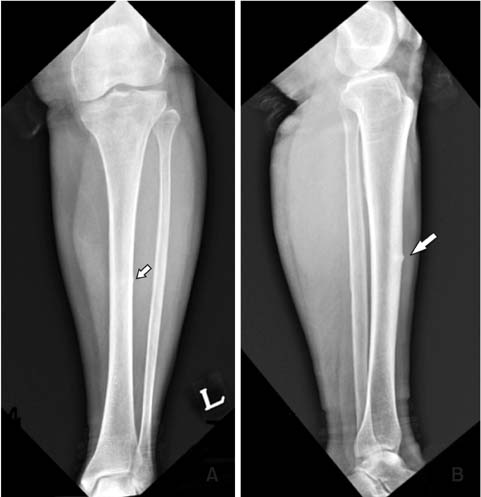
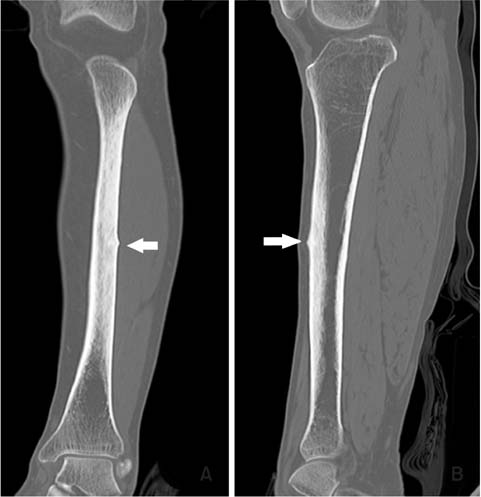
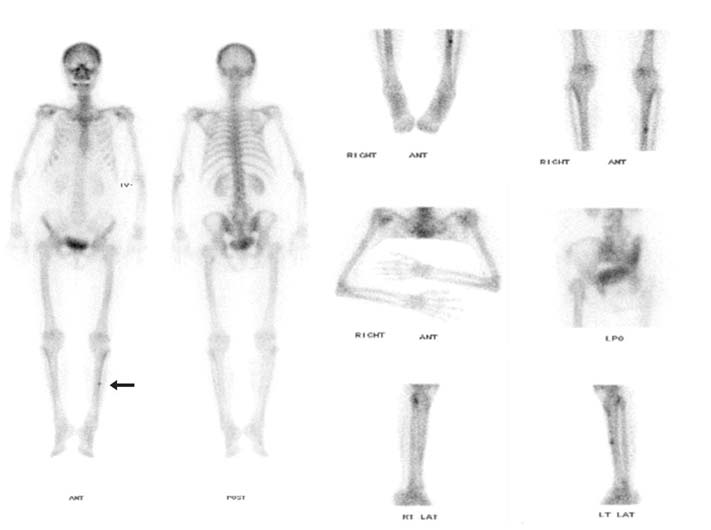
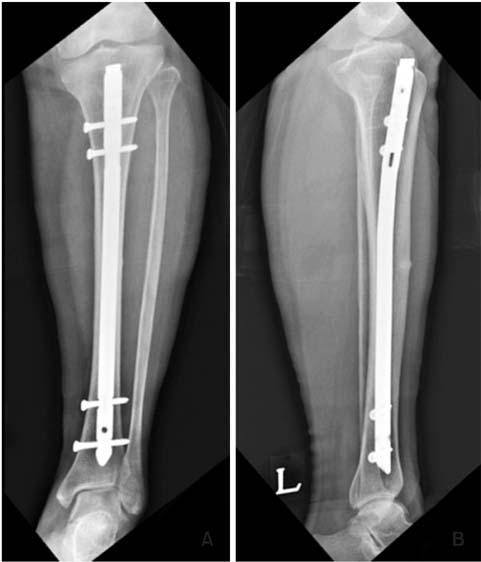
Figure
Reference
-
1. Park JM, Sung KS. Stress fractures of the tibia. Arthrosc Orthop Sports Med. 2015; 2:95–102.
Article2. Bone HG, Hosking D, Devogelaer JP, et al. Ten years' experience with alendronate for osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:1189–1199.
Article3. Shane E, Burr D, Abrahamsen B, et al. Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures: second report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res. 2014; 29:1–23.
Article4. Yang KH, Min BW, Ha YC. Atypical femoral fracture: 2015 position statement of the Korean Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Metab. 2015; 22:87–91.
Article5. Rogers MJ, Crockett JC, Coxon FP, Mönkkönen J. Biochemical and molecular mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates. Bone. 2011; 49:34–41.
Article6. Moon J, Bither N, Lee T. Atypical forearm fractures associated with long-term use of bisphosphonate. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013; 133:889–892.
Article7. Beals RK, Cook RD. Stress fractures of the anterior tibial diaphysis. Orthopedics. 1991; 14:869–875.
Article8. Bissonnette L, April PM, Dumais R, Boire G, Roux S. Atypical fracture of the tibial diaphysis associated with bisphosphonate therapy: a case report. Bone. 2013; 56:406–409.
Article9. Odvina CV, Levy S, Rao S, Zerwekh JE, Rao DS. Unusual mid-shaft fractures during long-term bisphosphonate therapy. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2010; 72:161–168.
Article10. Breglia MD, Carter JD. Atypical insufficiency fracture of the tibia associated with long-term bisphosphonate therapy. J Clin Rheumatol. 2010; 16:76–78.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Insufficiency Fracture of Ipsilateral Femur Neck in Patient Treated with Long Term Bisphosphonate Treatment: A Case Report
- Insufficiency Fracture of Simultaneously Bilateral Femur Neck in Patient Treated with Long-Term Bisphosphonate Treatment - A Case Report -
- Ulnar Insufficiency Fractures in Patients on Prolonged Bisphosphonate Therapy: A Case Report
- Atypical Fracture of the Proximal Shaft of the Ulna Associated with Prolonged Bisphosphonate Therapy
- Atypical femoral neck fracture after prolonged bisphosphonate therapy