J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2018 Oct;53(5):393-399. 10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.5.393.
Prolotherapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul Sacred Heart General Hospital, Seoul, Korea. msh124@paran.com
- KMID: 2424097
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.5.393
Abstract
- Prolotherapy is defined as "the rehabilitation of an incompetent structure such as ligament or tendon by induced proliferation of new cells" in the dictionary. It may include any treatment promoting the proliferation of new cells such as stem cell therapy. Traditionally, prolotherapy has been thought of as a method of strengthening a lax ligament by injecting various types of sclerosing or proliferant solutions which have commonly included hypertonic dextrose. And this therapy should involve the process of injecting solutions at the enthesis, where tendons and ligaments attach to the bone, to cause an inflammatory reaction. This inflammation initiates the regeneration and repair processes of the injured tissue in and around the joint to promote tissue proliferation and growth. Therefore, the method of prolotherapy includes the injection of small volumes of an irritant solution at painful ligament and tendon insertion sites over several treatment sessions. Because prolotherapy is a treatment modality that may provide a solution to a patient who complains of enthesopathic pain symptoms, it may be beneficial prior to long-term medication treatment or surgical intervention. Despite controversies over prolotherapy, its usage appears to be increasing gradually. This article discusses the current state of knowledge on prolotherapy and informs it to the physicians who manage the musculoskeletal pains.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
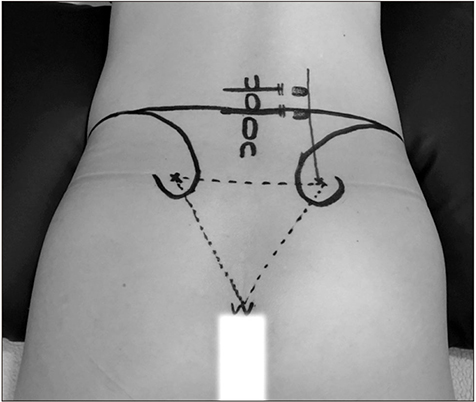
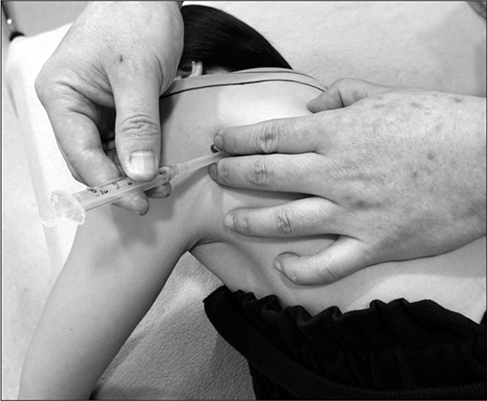
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
How Effective Is the Injection Therapy in Foot and Ankle Disorder?
Ha Heon Song
J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2021;25(1):10-16. doi: 10.14193/jkfas.2021.25.1.10.
Reference
-
1. Gove P. Webster's third new international dictionary, unabridged. Springfield: Merriam-Webster;2002.2. Moon SH. A trip to prolotherapy with doctor Moon. Seoul: Youngchang publishing Company;2016.3. Rabago D, Best TM, Beamsley M, Patterson J. A systematic review of prolotherapy for chronic musculoskeletal pain. Clin J Sport Med. 2005; 15:376–380.
Article4. Dorman TA. Prolotherapy: a survey. J Orthop Med. 1993; 15:49–50.
Article5. Banks AR. A rationale for prolotherapy. J Orthop Med. 1991; 13:54–59.6. Liu YK, Tipton CM, Matthes RD, Bedford TG, Maynard JA, Walmer HC. An in situ study of the influence of a sclerosing solution in rabbit medial collateral ligaments and its junction strength. Connect Tissue Res. 1983; 11:95–102.7. Hackett GS, Henderson DG. Joint stabilization; an experimental, histologic study with comments on the clinical application in ligament proliferation. Am J Surg. 1955; 89:968–973.8. Harrison ME. The biomechanical effects of prolotherapy on traumatized achilles tendons of male rats [thesis]. Utah: Brigham Young University;1995. 66.9. Klein RG, Dorman TA, Johnson CE. Proliferant injections for low back pain: histologic changes of injected ligaments and objective measurements of lumbar spine mobility before and after treatment. J Neurol Orthop Med Surg. 1989; 10:123–126.10. Kim SR, Stitik TP, Foye PM, Greenwald BD, Campagnolo DI. Critical review of prolotherapy for osteoarthritis, low back pain, and other musculoskeletal conditions: a physiatric perspective. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2004; 83:379–389.11. Hackett GS. Ligament and tendon relaxation treated by prolotherapy. Springfield: Thomas;1956.12. Scarpone M, Rabago DP, Zgierska A, Arbogast G, Snell E. The efficacy of prolotherapy for lateral epicondylosis: a pilot study. Clin J Sport Med. 2008; 18:248–254.
Article13. Rabago D, Lee KS, Ryan M, et al. Hypertonic dextrose and morrhuate sodium injections (prolotherapy) for lateral epicondylosis (tennis elbow): results of a single-blind, pilot-level, randomized controlled trial. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2013; 92:587–596.14. Topol GA, Reeves KD, Hassanein KM. Efficacy of dextrose prolotherapy in elite male kicking-sport athletes with chronic groin pain. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005; 86:697–702.
Article15. Maxwell NJ, Ryan MB, Taunton JE, Gillies JH, Wong AD. Sonographically guided intratendinous injection of hyperosmolar dextrose to treat chronic tendinosis of the Achilles tendon: a pilot study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 189:W215–W220.
Article16. Yelland MJ, Sweeting KR, Lyftogt JA, Ng SK, Scuffham PA, Evans KA. Prolotherapy injections and eccentric loading exercises for painful achilles tendinosis: a randomised trial. Br J Sports Med. 2011; 45:421–428.
Article17. Ryan MB, Wong AD, Gillies JH, Wong J, Taunton JE. Sonographically guided intratendinous injections of hyperosmolar dextrose/lidocaine: a pilot study for the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis. Br J Sports Med. 2009; 43:303–306.
Article18. Rabago D, Patterson JJ, Mundt M, et al. Dextrose prolotherapy for knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Ann Fam Med. 2013; 11:229–237.
Article19. Reeves KD, Hassanein K. Randomized prospective double-blind placebo-controlled study of dextrose prolotherapy for knee osteoarthritis with or without ACL laxity. Altern Ther Health Med. 2000; 6:68–74. 77–80.20. Reeves KD, Hassanein K. Randomized, prospective, placebo-controlled double-blind study of dextrose prolotherapy for osteoarthritic thumb and finger (DIP, PIP, and trapeziometacarpal) joints: evidence of clinical efficacy. J Altern Complement Med. 2000; 6:311–320.
Article21. Krstičević M, Jerić M, Došenović S, Jeličić Kadić A, Puljak L. Proliferative injection therapy for osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Int Orthop. 2017; 41:671–679.
Article22. Rabago D, Nourani B. Prolotherapy for osteoarthritis and tendinopathy: a descriptive review. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017; 19:34.
Article23. Mathews JA, Mills SB, Jenkins VM, et al. Back pain and sciatica: controlled trials of manipulation, traction, sclerosant and epidural injections. Br J Rheumatol. 1987; 26:416–423.
Article24. Ongley MJ, Klein RG, Dorman TA, Eek BC, Hubert LJ. A new approach to the treatment of chronic low back pain. Lancet. 1987; 2:143–146.
Article25. Klein RG, Eek BC, DeLong WB, Mooney V. A randomized double-blind trial of dextrose-glycerine-phenol injections for chronic, low back pain. J Spinal Disord. 1993; 6:23–33.
Article26. Dechow E, Davies RK, Carr AJ, Thompson PW. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of sclerosing injections in patients with chronic low back pain. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999; 38:1255–1259.
Article27. Yelland MJ, Glasziou PP, Bogduk N, Schluter PJ, McKernon M. Prolotherapy injections, saline injections, and exercises for chronic low-back pain: a randomized trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29:9–16.
Article28. Myers A. Prolotherapy treatment of low back pain and sciatica. Bull Hosp Joint Dis. 1961; 22:48–55.29. Dorman TA. Treatment for spinal pain arising in ligaments using prolotherapy: a retrospective survey. J Orthop Med. 1991; 13:13–19.30. Dorman TA. Whiplash injuries: treatment with prolotherapy and a new hypothesis. J Orthop Med. 1999; 21:13–21.
Article31. Schneider RC, Williams JJ, Liss L. Fatality after injection of sclerosing agent to precipitate fibro-osseous proliferation. J Am Med Assoc. 1959; 170:1768–1772.
Article32. Keplinger JE, Bucy PC. Paraplegia from treatment with sclerosing agents. Report of a case. JAMA. 1960; 173:1333–1335.33. Hunt WE, Baird WC. Complications following injection of sclerosing agent to precipitate fibro-osseous proliferation. J Neurosurg. 1961; 18:461–465.
Article34. Moon SH. Prolotherapy of lumbar spine. Stem Cell Regen Med. 2014; 1:42–48.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Prolotherapy on Shoulder Pain
- Effects of Prolotherapy on Knee Joint Pain due to Ligament Laxity
- A Systematic Review of Prolotherapy in Musculoskeletal Disease
- Effects of Prolotherapy on Chronic Musculoskeletal Disease
- The Effect of the Prolotherapy on the Injured Achilles Tendon in a Rat Model