J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2018 Oct;59(10):968-973. 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.10.968.
The Therapeutic Effect of Sclerocorneal Lens in Coexisting Corneal Ectasia and Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. sara514@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2422586
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2018.59.10.968
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We report short-term treatment effects of a mini-scleral lens in patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and corneal ectasia.
CASE SUMMARY
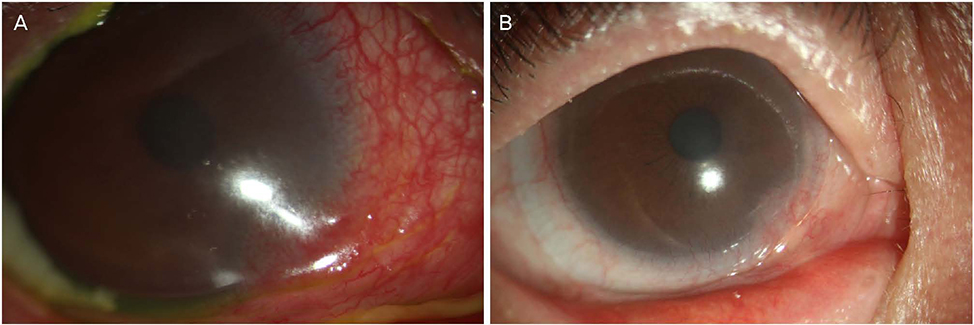
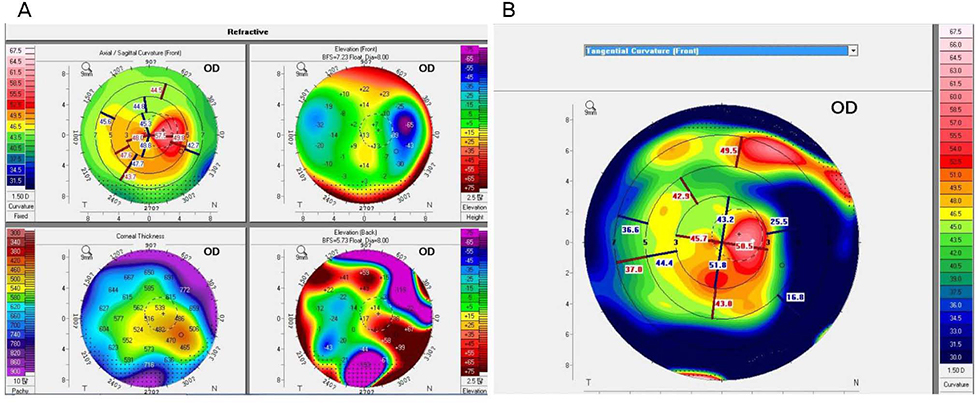
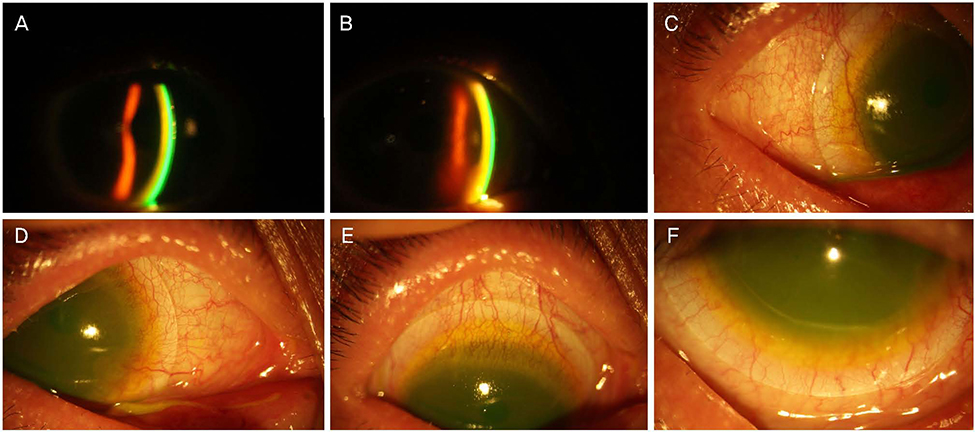
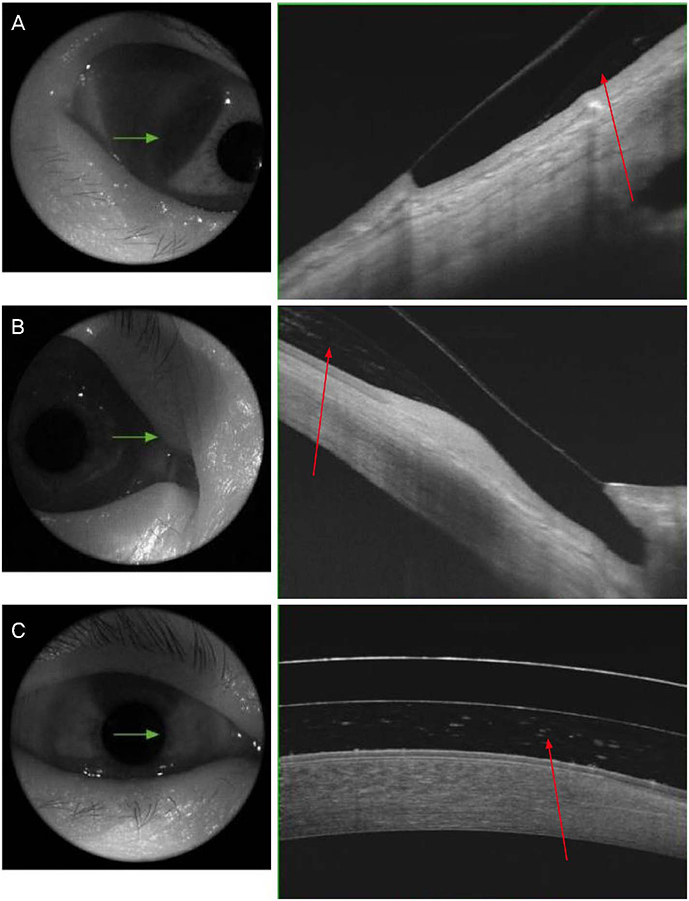
A 54-year-old female who had been diagnosed with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and keratoconus presented with persistent right eye pain and decreased visual acuity. Therapeutic lenses, topical antibiotic eye drops, and topical steroid eye drops were used; however the symptoms were not controlled, then the patient was treated with a mini-scleral contact lens in the right eye. At the time of the first visit to our hospital 17 years ago, and the best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) of the right eye was logMAR 0.22. However, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and corneal ectasia were severe and cataract surgery was considered because of worsening cataracts, but the patients refused this surgery. At the time, the BCVA of the right eye was then reduced to logMAR 1.10. On ophthalmic examination, there was conjunctival fibrosis and corneal neovascularization of the right eye. The symptoms were not managed with a using a therapeutic lens, and then the patient was prescribed a mini-scleral contact lens. After wearing the mini-scleral contact lens, the corneal and conjunctival neovascularization was reduced. After 6 months, the BCVA of the right eye improved to logMAR 0.60.
CONCLUSIONS
In patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and corneal ecstasia, mini-scleral contact lens can be considered as a useful treatment option for visual improvement and symptom control.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Andreanos KD, Hashemi K, Petrelli M, et al. Keratoconus treatment algorithm. Ophthalmol Ther. 2017; 6:245–262.
Article2. Lee JH, Park YM, Park YK, et al. Long-term effect and safety of contact lenses for keratoconus. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015; 56:1006–1011.
Article3. Rathi VM, Taneja M, Dumpati S, et al. Role of scleral contact lenses in management of coexisting keratoconus and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Cornea. 2017; 36:1267–1269.
Article4. Suh SY, Lee JH, Lee SU, et al. Fitting the miniscleral contact lens in patients with corneal abnormalities. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2016; 57:1699–1705.
Article5. Saeed HN, Kohanim S, Le HG, et al. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and corneal ectasia: management and a case for association. Am J Ophthalmol. 2016; 169:276–281.
Article6. Porcar E, Montalt JC, España-Gregori E, Peris-Martínez C. Corneo-scleral contact lenses in an uncommon case of keratoconus with high hyperopia and astigmatism. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2017; 40:351–356.
Article7. Yan P, Kapasi M, Conlon R, et al. Patient comfort and visual outcomes of mini-scleral contact lenses. Can J Ophthalmol. 2017; 52:69–73.
Article8. Schornack MM, Patel SV. Scleral lenses in the management of keratoconus. Eye Contact Lens. 2010; 36:39–44.
Article9. Kim S, Lee JS, Park YK, et al. Fitting miniscleral contact lenses in Korean patients with keratoconus. Clin Exp Optom. 2017; 100:375–379.
Article10. Carracedo G, Blanco MS, Martin-Gil A, et al. Short-term effect of scleral lens on the dry eye biomarkers in keratoconus. Optom Vis Sci. 2016; 93:150–157.
Article11. Dogru M, Karakaya H, Ozçetin H, et al. Tear function and ocular surface changes in keratoconus. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:1110–1118.
Article12. Di Pascuale MA, Espana EM, Liu DT, et al. Correlation of corneal complications with eyelid cicatricial pathologies in patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis syndrome. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:904–912.
Article13. McMonnies CW. Mechanisms of rubbing-related corneal trauma in keratoconus. Cornea. 2009; 28:607–615.
Article14. Sotozono C, Yamauchi N, Maeda S, Kinoshita S. Tear exchangeable limbal rigid contact lens for ocular sequelae resulting from Stevens-Johnson syndrome or Toxic epidermal necrolysis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2014; 158:983–993.
Article15. Yildiz EH, Erdurmus M, Elibol ES, et al. Contact lens impact on quality of life in keratoconus patients: rigid gas permeable versus soft silicone-hydrogel keratoconus lenses. Int J Ophthalmol. 2015; 8:1074–1077.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Stevens-Johnson's Syndrome
- Clinical Study of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
- A Case of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome in a Hypoxic Brain Injury Patient Treated with Carbamazepine
- Lamellar Graft of an Acellular, Preserved Human Cornea for Recurrent Anterior Granuloma in Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
- A Case of Secondary Milia Associated with Stevens-Johnson Syndrome