J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2018 Mar;20(1):40-46. 10.7461/jcen.2018.20.1.40.
Usefulness of Middle Meningeal Embolization to Prevent Recurrent Spontaneous Chronic Subdural Hemorrhage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea. c99867@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2422559
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2018.20.1.40
Abstract
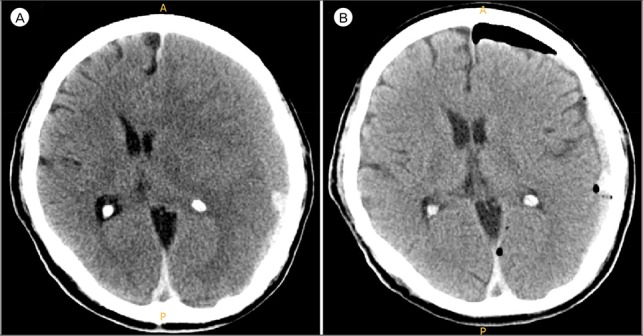
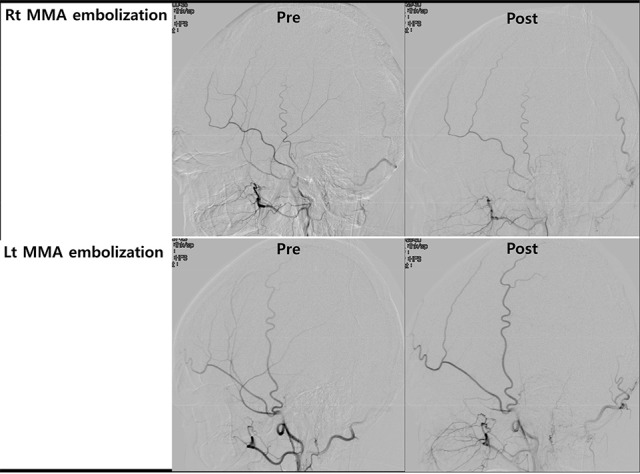
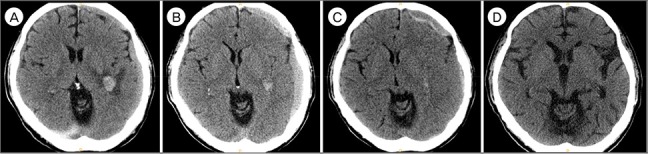
- Spontaneous chronic subdural hematoma (SDH) is a rare condition that could develop in association with hematologic disease. A 66-year-old male developed a chronic SDH as an initial manifestation of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML). He experienced recurrent chronic subdural hemorrhage and newly developed intracerebral hemorrhage. Considering the scheduled long-term chemotherapy, bilateral middle meningeal artery (MMA) embolization was performed to prevent recurrence of subdural hemorrhage. Although pancytopenia occurred during the 7 months' follow-up period, residual chronic subdural hemorrhage was absorbed without recurrence. To our best knowledge, this is the first report of CMML with spontaneous chronic SDH. MMA embolization is potentially a useful and safe treatment option in the challenging clinical situations with underlying pathologies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Middle meningeal artery embolization to treat progressive epidural hematoma: a case report
Tae Joon Park, Sang Pyung Lee, Jinwook Baek, Kyoungsoo Ryou, Seong Hwan Kim
J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2020;22(1):20-25. doi: 10.7461/jcen.2020.22.1.20.
Reference
-
1. Abdulhamid MM, Li YM, Hall WA. Spontaneous acute subdural hematoma as the initial manifestation of chronic myeloid leukemia. J Neurooncol. 2011; 2. 101(3):513–516. PMID: 20582615.
Article2. Adès L, Sekeres MA, Wolfromm A, Teichman ML, Tiu RV, Itzykson R, et al. Predictive factors of response and survival among chronic myelomonocytic leukemia patients treated with azacitidine. Leuk Res. 2013; 6. 37(6):609–613. PMID: 23415110.
Article3. Braun T, Itzykson R, Renneville A, de Renzis B, Dreyfus F, Laribi K, et al. Molecular predictors of response to decitabine in advanced chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: a phase 2 trial. Blood. 2011; 10. 06. 118(14):3824–3831. PMID: 21828134.
Article4. Bromberg JE, Vandertop WP, Jansen GH. Recurrent subdural haematoma as the primary and sole manifestation of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Neurosurg. 1998; 8. 12(4):373–376. PMID: 10070435.5. Cambier N, Wattel E, Menot M, Guerci A, Chomienne C, Fenaux P. All-trans retinoic acid in adult chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: results of a pilot study. Leukemia. 1996; 7. 10(7):1164–1167. PMID: 8683997.6. Comănescu A, Roşca E, Bota M, Ninulescu G. Chronic subdural hematoma in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia and dural metastatic infiltration. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2008; 10. 49(2):259–262. PMID: 18516337.7. Feldman EJ, Cortes J, DeAngelo D, Holyoake T, Simonsson B, O'Brien SG, et al. On the use of lonafarnib in myelodysplastic syndrome and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2008; 9. 22(9):1707–1711. PMID: 18548095.
Article8. Ichimura S, Horiguchi T, Inoue S, Yoshida K. Nontraumatic acute subdural hematoma associated with the myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2012; 1. 3(1):98–99. PMID: 22346213.
Article9. Khaladkar SM, Thakkar DK, Jantre MN, Kulkarni VM, Singh A. Chronic subdural hematoma-unsual cause of headache in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with high-dose imatinib mesylate: a rare case report with review of literature. Med J DY Patil Univ. 2015; May-Jun. 8(3):411–413.
Article10. Kim MS, Lee DH, Lee YR, Kim DK, Bae SH, Hwang JY, et al. A case of subdural hematoma in patient with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with high-dose imatinib mesylate. Korean J Hematol. 2010; 3. 45(1):73–75. PMID: 21120168.
Article11. Laumer R. Implantation of a reservoir for refractory chronic subdural hematoma. Neurosurgery. 2002; 3. 50(3):672.
Article12. Lee KS. History of chronic subdural hematoma. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2015; 10. 11(2):27–34. PMID: 27169062.
Article13. Mandai S, Sakurai M, Matsumoto Y. Middle meningeal artery embolization for refractory chronic subdural hematoma. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2000; 10. 93(4):686–688. PMID: 11014549.14. McDermott M, Fleming RJ, Vanderlinden GR, Tucker WS. Spontaneous arterial subdural hematoma. Neurosurgery. 1984; 1. 14(1):13–18. PMID: 6694787.
Article15. Mino M, Nishimura S, Hori E, Kohama M, Yonezawa S, Midorikawa H, et al. Efficacy of middle meningeal artery embolization in the treatment of refractory chronic subdural hematoma. Surg Neurol Int. 2010; 12. 13. 1:78. PMID: 21206540.
Article16. O'Brien SG, Guilhot F, Larson RA, Gathmann I, Baccarani M, Cervantes F, et al. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2003; 3. 13. 348(11):994–1004. PMID: 12637609.17. Olfa CW, Imen R, Leila K, Hichem K, Adnane A, Mourad C, et al. Diagnosis of chronic myeloid leukemia from acute intracerebral hemorrhage: a case report. J Acute Dis. 2015; 8. 4(3):252–254.
Article18. Vasudev Rao T, Deshpande D. Malignant subdural effusion. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1980; 3. 52(1-2):61–65. PMID: 7376947.19. Rollison DE, Howlader N, Smith MT, Strom SS, Merritt WD, Ries LA, et al. Epidemiology of myelodysplastic syndromes and chronic myeloproliferative disorders in the United States, 2001–2004, using data from the NAACCR and SEER programs. Blood. 2008; 7. 01. 112(1):45–52. PMID: 18443215.
Article20. Sato M, Saito T, Yamaguchi K, Sakuma H. A case of acute subdural hematoma due to dural metastasis from malignant pleural mesothelioma. No Shinkei Geka. 1994; 3. 22(3):247–251. PMID: 8133966.21. Song KW, Rifkind J, Al-Beirouti B, Yee K, McCrae J, Messner HA, et al. Subdural hematomas during CML therapy with imatinib mesylate. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004; 8. 45(8):1633–1636. PMID: 15370217.
Article22. Such E, Germing U, Malcovati L, Cervera J, Kuendgen A, Della Porta MG, et al. Development and validation of a prognostic scoring system for patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Blood. 2013; 4. 11. 121(15):3005–3015. PMID: 23372164.
Article23. Takahashi K, Muraoka K, Sugiura T, Maeda Y, Mandai S, Gohda Y, et al. Middle meningeal artery embolization for refractory chronic subdural hematoma: 3 case reports. No Shinkei Geka. 2002; 5. 30(5):535–539. PMID: 11993178.24. Tanaka T, Fujimoto S, Saitoh K, Satoh S, Nagamatsu K, Midorikawa H. Superselective angiographic findings of ipsilateral middle meningeal artery of chronic subdural hematoma in adults. No Shinkei Geka. 1998; 4. 26(4):339–347. PMID: 9592815.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endovascular surgery for chronic subdural hematoma
- Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization in Recurrent Chronic Subdural Hematoma Combined with Arachnoid Cyst
- Middle meningeal artery embolization for postoperative supratentorial chronic subdural hematoma occurring after posterior fossa neurosurgery
- Retrograde Middle Meningeal Artery Embolization through Mini Craniotomy for Subdural Hematoma Evacuation: A Technical Note
- Middle meningeal artery embolization for chronic subdural hematoma in elderly patients at high risk of surgical treatment