Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2018 Sep;23(3):158-161. 10.6065/apem.2018.23.3.158.
Compound heterozygosity for a whole gene deletion and p.R124C mutation in CYP21A2 causing nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Cleveland Clinic Children's Hospital, Cleveland, OH, USA.
- 2Dow Medical College, Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Pakistan.
- 3Aga khan University, Faculty of Medicine, Karachi, Pakistan.
- 4Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA.
- 5Division of Women and Child Health, Paediatrics and Child Health, Aga Khan University, Karachi, Pakistan. salman.kirmani@aku.edu
- KMID: 2422481
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2018.23.3.158
Abstract
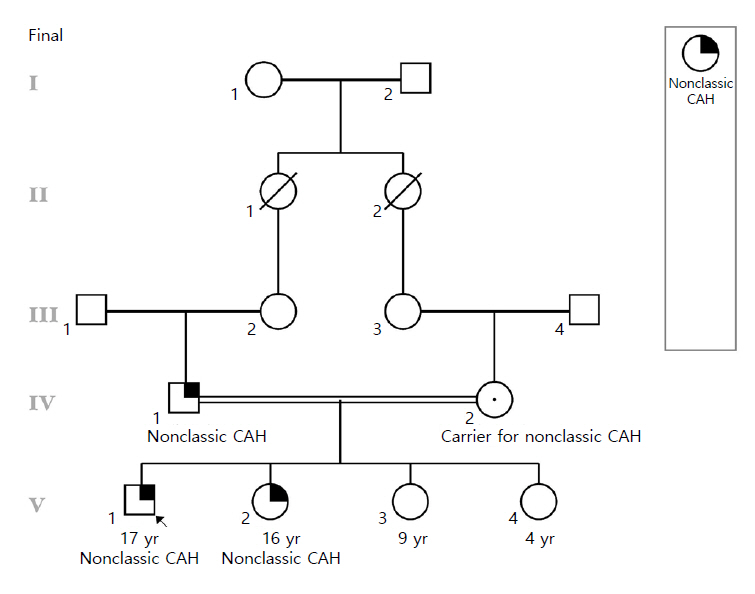
- We present a family with 2 members who received long-term steroid treatment for presumed classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency, until molecular testing revealed nonclassic CAH, not necessarily requiring treatment. A 17-year-old male presented to our clinic on glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid treatment for classic CAH. He was diagnosed at 4 years of age based on mild-moderate elevations of 17-hydroxyprogesterone (17-OHP) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), but without evidence of precocious adrenarche/puberty. Due to his diagnosis, his clinically asymptomatic 3-year-old sister was tested and also found to have elevated ACTH and 17-OHP levels and was started on glucocorticoids for classic CAH. Family history revealed a healthy sibling who had no biochemical evidence of CAH and consanguineous healthy parents. We questioned the diagnosis of classic CAH and performed an ACTH1-24 stimulation test, which showed a level of 17-OHP in the borderline range between classic and nonclassic CAH. Molecular testing, using sequencing and multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification analysis of CYP21A2, revealed that both affected siblings were compound heterozygotes for a whole-gene deletion and a, likely pathogenic (nonclassical), sequence variant, p.R124C. The asymptomatic father had the same genotype, while the mother showed one deleted copy and 2 active copies, making her an asymptomatic carrier. Our report demonstrates the importance of molecular testing in atypical cases of CAH, as well as the importance of both sequencing and deletion analysis. The results of molecular testing should be interpreted in clinical context, and treatment should be prescribed according to guidelines when available.
MeSH Terms
-
17-alpha-Hydroxyprogesterone
Adolescent
Adrenal Hyperplasia, Congenital*
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
Child, Preschool
Diagnosis
Fathers
Gene Deletion*
Genetic Testing
Genotype
Glucocorticoids
Heterozygote
Humans
Male
Mothers
Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction
Parents
Siblings
Steroid 21-Hydroxylase
17-alpha-Hydroxyprogesterone
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
Glucocorticoids
Steroid 21-Hydroxylase
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Mendes C, Vaz Matos I, Ribeiro L, Oliveira MJ, Cardoso H, Borges T. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency: genotype-phenotype correlation. Acta Med Port. 2015; 28:56–62.2. Speiser PW, Azziz R, Baskin LS, Ghizzoni L, Hensle TW, Merke DP, et al. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95:4133–60.
Article3. Falhammar H, Wedell A, Nordenström A. Biochemical and genetic diagnosis of 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Endocrine. 2015; 50:306–14.
Article4. Nimkarn S, Gangishetti PK, Yau M, New MI. 21-Hydroxylase-deficient congenital adrenal hyperplasia [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington;2016. [cited 2017 Aug 22]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1171/.5. Krone N, Rose IT, Willis DS, Hodson J, Wild SH, Doherty EJ, et al. Genotype-phenotype correlation in 153 adult patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency: analysis of the United Kingdom Congenital adrenal Hyperplasia Adult Study Executive (CaHASE) cohort. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:E346–54.
Article6. Usui T, Nishisho K, Kaji M, Ikuno N, Yorifuji T, Yasuda T, et al. Three novel mutations in Japanese patients with 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Horm Res. 2004; 61:126–32.
Article7. Haider S, Islam B, D'Atri V, Sgobba M, Poojari C, Sun L, et al. Structure-phenotype correlations of human CYP21A2 mutations in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013; 110:2605–10.
Article8. Trapp CM, Oberfield SE. Recommendations for treatment of nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia (NCCAH): an update. Steroids. 2012; 77:342–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Molecular Genetic Studies on the Human CYP21A2 Gene (1)
- Nonclassic congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia diagnosed at 17 months in a Korean boy with normal male genitalia: emphasis on pigmentation as a diagnostic clue
- Genotype-phenotype correlation in 27 pediatric patients in congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency in a single center
- Two Cases of Simple Virilizing Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia with Compound Heterozygous Mutations of CYP21 Gene
- CYP21A2 Mutation Analysis in Korean Patients With Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Using Complementary Methods: Sequencing After Long-Range PCR and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Analysis With Multiple Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification Assay