J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2017 Dec;52(6):552-555. 10.4055/jkoa.2017.52.6.552.
Pneumocephalus after Interlaminar Lumbar Epidural Block
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. bonjourksk@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2421349
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2017.52.6.552
Abstract
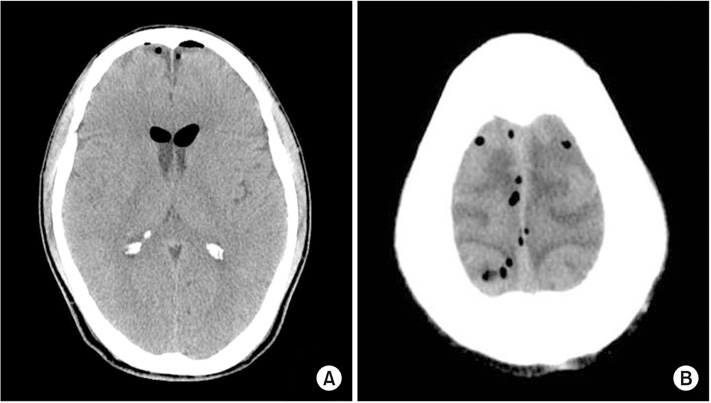
- Lumbar epidural block using a "loss of resistance" technique (LORT) with air can potentially cause pneumocephalus. Herein, we present a pneumocephalus that occurred after an epidural block. A 58-year-old male patient underwent an interlaminar lumbar epidural block using a LORT with air for L4-5 disc herniation. After the block, the patient complained of headache, vomiting, and truncal myoclonus. For further evaluation, a brain computed tomography was performed, and pneumocephalus was finally diagnosed. The patient underwent conservative treatment and recovered without any complications. He was discharged on the 11th day after the block.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, McManus CD, Pampati V, Smith HS. Preliminary results of a randomized, equivalence trial of fluoroscopic caudal epidural injections in managing chronic low back pain: part 1--discogenic pain without disc herniation or radiculitis. Pain Physician. 2008; 11:785–800.2. Boswell MV, Trescot AM, Datta S, et al. Interventional techniques: evidence-based practice guidelines in the management of chronic spinal pain. Pain Physician. 2007; 10:7–111.3. Kim YD, Lee JH, Cheong YK. Pneumocephalus in a patient with no cerebrospinal fluid leakage after lumbar epidural block: a case report. Korean J Pain. 2012; 25:262–266.4. Goodman BS, Posecion LW, Mallempati S, Bayazitoglu M. Complications and pitfalls of lumbar interlaminar and transforaminal epidural injections. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2008; 1:212–222.
Article5. Ozturk E, Kantarci M, Karaman K, Basekim CC, Kizilkaya E. Diffuse pneumocephalus associated with infratentorial and supratentorial hemorrhages as a complication of spinal surgery. Acta Radiol. 2006; 47:497–500.
Article6. Nafiu OO, Urquhart JC. Pneumocephalus with headache complicating labour epidural analgesia: should we still be using air? Int J Obstet Anesth. 2006; 15:237–239.
Article7. Verdun AV, Cohen SP, Williams BS, Hurley RW. Pneumocephalus after lumbar epidural steroid injection: a case report and review of the literature. A A Case Rep. 2014; 3:9–13.8. Dexter F, Reasoner DK. Theoretical assessment of normobaric oxygen therapy to treat pneumocephalus. Anesthesiology. 1996; 84:442–447.
Article9. Segal S, Arendt KW. A retrospective effectiveness study of loss of resistance to air or saline for identification of the epidural space. Anesth Analg. 2010; 110:558–563.
Article10. Shenouda PE, Cunningham BJ. Assessing the superiority of saline versus air for use in the epidural loss of resistance technique: a literature review. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2003; 28:48–53.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pneumocephalus in a Patient with No Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage after Lumbar Epidural Block: A Case Report
- Pneumocephalus following fluoroscopy-guided lumbar epidural injection in elderly patients: two cases report and a review of Korean literatures - Two cases report -
- Headache and Pneumocephalus after Lumbar Epidural Block: A case report
- Comparison of the Effects between Interlaminar Epidural Block and Transforaminal Epidural Block under C-arm Guide in Lumbar Disc Herniated Radiculopathy
- Pneumocephalus and Chemical Meningitis after Inadvertent Dural Puncture during Lumbar Epidural Injection