Infect Chemother.
2018 Sep;50(3):268-273. 10.3947/ic.2018.50.3.268.
Rapidly Fatal Emphysematous Osteomyelitis with Multiple Septic Emboli and Liver Abscess Caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. smkimkor@yahoo.com
- KMID: 2420912
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2018.50.3.268
Abstract
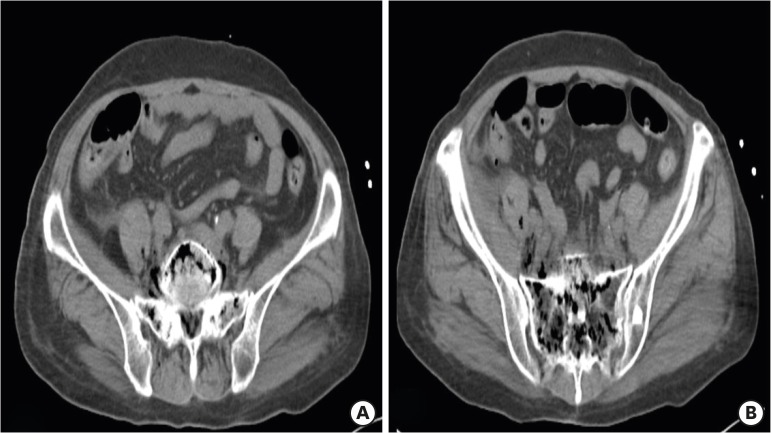
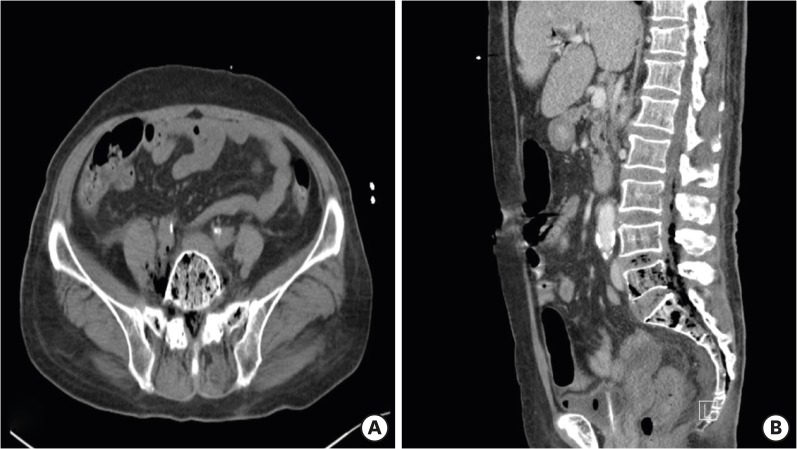
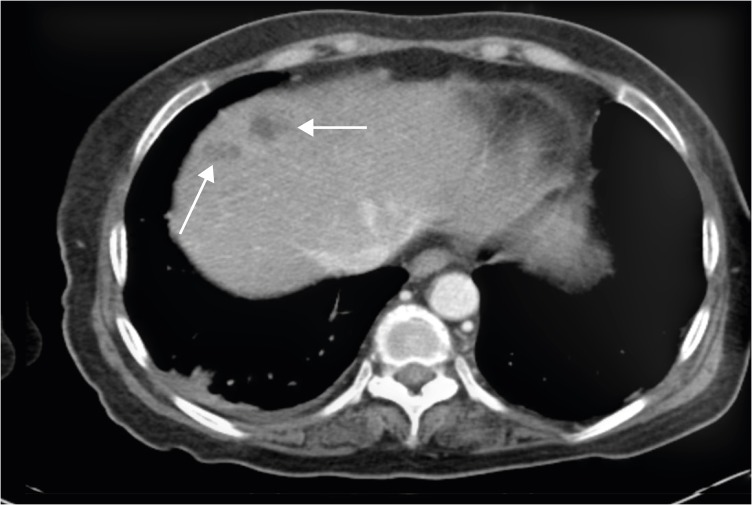
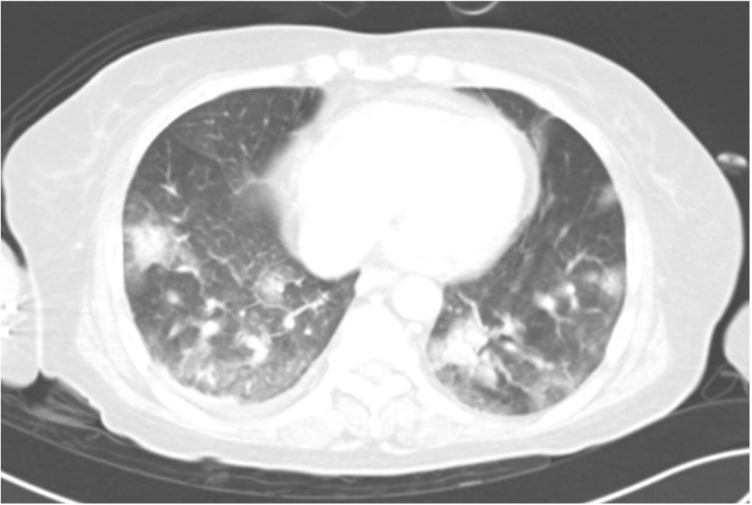
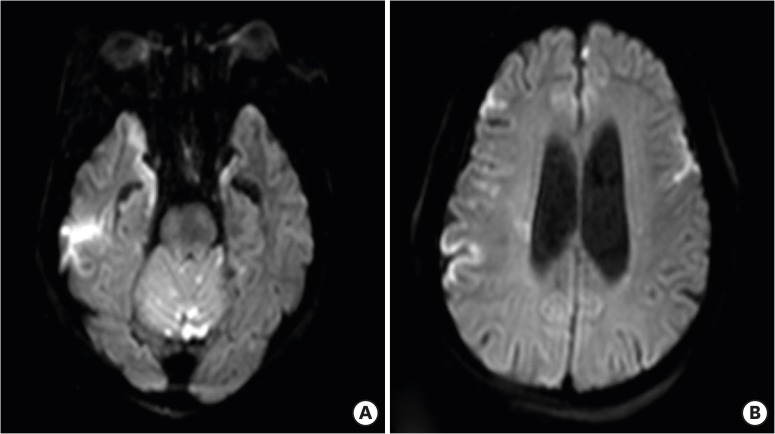
- Emphysematous osteomyelitis, characterized by intraosseous gas, is a rare but potentially fatal condition that requires prompt diagnosis and aggressive therapy. Causative organisms are members of the bacterial family Enterobacteriaceae or anaerobes in most cases and significant comorbidities such as diabetes mellitus and malignancy, may predispose an individual to the development of emphysematous osteomyelitis. We report a case of extensive emphysematous osteomyelitis via hematogenous spread from Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess, complicated by gas-containing abscesses in adjacent soft tissues and epidural space, and multiple systemic septic emboli in a diabetic patient.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ram PC, Martinez S, Korobkin M, Breiman RS, Gallis HR, Harrelson JM. CT detection of intraosseous gas: a new sign of osteomyelitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981; 137:721–723. PMID: 6974967.
Article2. Luey C, Tooley D, Briggs S. Emphysematous osteomyelitis: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Infect Dis. 2012; 16:e216–e220. PMID: 22230028.
Article3. McDonnell O, Khaleel Z. Emphysematous osteomyelitis. JAMA Neurol. 2014; 71:512. PMID: 24514429.
Article4. Larsen J, Mühlbauer J, Wigger T, Bardosi A. Emphysematous osteomyelitis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015; 15:486. PMID: 25809901.
Article5. Chen CW, Yang CJ, Huang JJ, Chuang YC, Young C. Gas-forming vertebral osteomyelitis in diabetic patients. Scand J Infect Dis. 1991; 23:263–265. PMID: 1853175.
Article6. Aghaei Lasboo A, Walker MT, Hijaz TA. An unusual appearance of discitis due to gas-forming Escherichia coli with associated pneumocephalus. Spine. 2010; 35:E257–E259. PMID: 20228705.7. Mautone M, Gray J, Naidoo P. A case of emphysematous osteomyelitis of the midfoot: imaging findings and review of the literature. Case Rep Radiol. 2014; 2014:616184. PMID: 25013735.
Article8. Bang JH, Cho KT. Rapidly progressive gas-containing lumbar spinal epidural abscess. Korean J Spine. 2015; 12:139–142. PMID: 26512268.
Article9. Liao PY, Chiang WC, Chen SY, Su CP, Wang JT, Hsueh PR. Rapidly fatal gas-forming pyogenic psoas abscess caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae . Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 44:1253–1255. PMID: 17407050.10. Siu LK, Yeh KM, Lin JC, Fung CP, Chang FY. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess: a new invasive syndrome. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012; 12:881–887. PMID: 23099082.11. Lee HL, Lee HC, Guo HR, Ko WC, Chen KW. Clinical significance and mechanism of gas formation of pyogenic liver abscess due to Klebsiella pneumoniae . J Clin Microbiol. 2004; 42:2783–2785. PMID: 15184470.12. Yoon JH, Kim YJ, Jun YH, Kim SI, Kang JY, Suk KT, Kim DJ. Liver abscess due to Klebsiella pneumoniae: risk factors for metastatic infection. Scand J Infect Dis. 2014; 46:21–26. PMID: 24228822.13. Lin YT, Wang FD, Wu PF, Fung CP. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess in diabetic patients: association of glycemic control with the clinical characteristics. BMC Infect Dis. 2013; 13:56. PMID: 23363608.
Article14. Wang HH, Tsai SH, Yu CY, Hsu HH, Liu CH, Lin JC, Huang GS, Cheng WT, Tung HJ, Chen CY, Chang WC. The association of haemoglobin A1C levels with the clinical and CT characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscesses in patients with diabetes mellitus. Eur Radiol. 2014; 24:980–989. PMID: 24563159.15. Jung J, Park KH, Park SY, Song EH, Lee EJ, Choi SH, Choo EJ, Kwak YG, Sung H, Kim SH, Lee SO, Kim MN, Kim YS, Woo JH, Choi SH. Comparison of the clinical characteristics and outcomes of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015; 82:87–91. PMID: 25752203.16. Fang CT, Lai SY, Yi WC, Hsueh PR, Liu KL, Chang SC. Klebsiella pneumoniae genotype K1: an emerging pathogen that causes septic ocular or central nervous system complications from pyogenic liver abscess. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 45:284–293. PMID: 17599305.17. Kawai T. Hypermucoviscosity: an extremely sticky phenotype of Klebsiella pneumoniae associated with emerging destructive tissue abscess syndrome. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 42:1359–1361. PMID: 16619145.18. Yu WL, Ko WC, Cheng KC, Lee HC, Ke DS, Lee CC, Fung CP, Chuang YC. Association between rmpA and magA genes and clinical syndromes caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae in Taiwan. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 42:1351–1358. PMID: 16619144.19. Chung DR, Lee SS, Lee HR, Kim HB, Choi HJ, Eom JS, Kim JS, Choi YH, Lee JS, Chung MH, Kim YS, Lee H, Lee MS, Park CK. Korean Study Group for Liver Abscess. Emerging invasive liver abscess caused by K1 serotype Klebsiella pneumoniae in Korea. J Infect. 2007; 54:578–583. PMID: 17175028.20. Kim JK, Chung DR, Wie SH, Yoo JH, Park SW. Korean Study Group for Liver Abscess. Risk factor analysis of invasive liver abscess caused by the K1 serotype Klebsiella pneumoniae . Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009; 28:109–111. PMID: 18663497.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Splenic Abscess with Multiple Fistulas Caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Klebsiella pneumoniae Brain Abscess and Endophthalmitis after Acute Epiglottitis
- Klebsiella pneumoniae Liver Abscess
- A Case of Endogenous endophthalmitis Caused by Klebsiella Pneumoniae from Emphysematous Pyelonephritis
- Endocarditis Caused by Community-Acquired Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection - A Case Report -