Infect Chemother.
2018 Sep;50(3):219-227. 10.3947/ic.2018.50.3.219.
Journal Metrics of Infection & Chemotherapy and Current Scholarly Journal Publication Issues
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Parasitology and Institute of Medical Education, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea. shuh@hallym.ac.kr
- KMID: 2420906
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2018.50.3.219
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
In 2013, Infection & Chemotherapy changed the main language of its articles to English so that they could be submitted to PubMed Central. This study presents the recent status of journal metrics for Infection & Chemotherapy and introduces scholarly journal publishing policies or guidelines that have recently appeared.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A variety of journal metrics were analyzed based on the Web of Science Core Collection, including the nationality of authors the proportion of funded articles to original articles , manually calculated impact factor, the titles of journals in which articles were cited", and the Hirsch index.
RESULTS
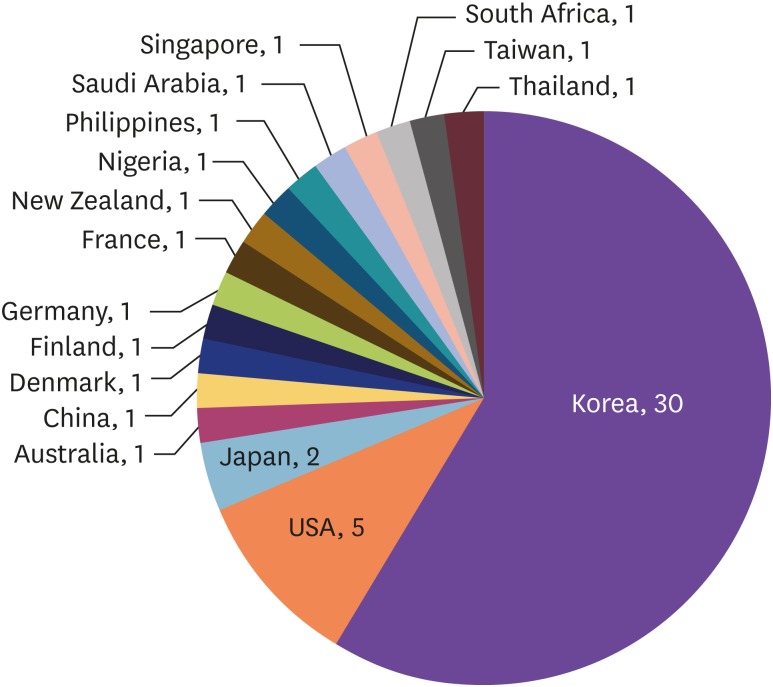
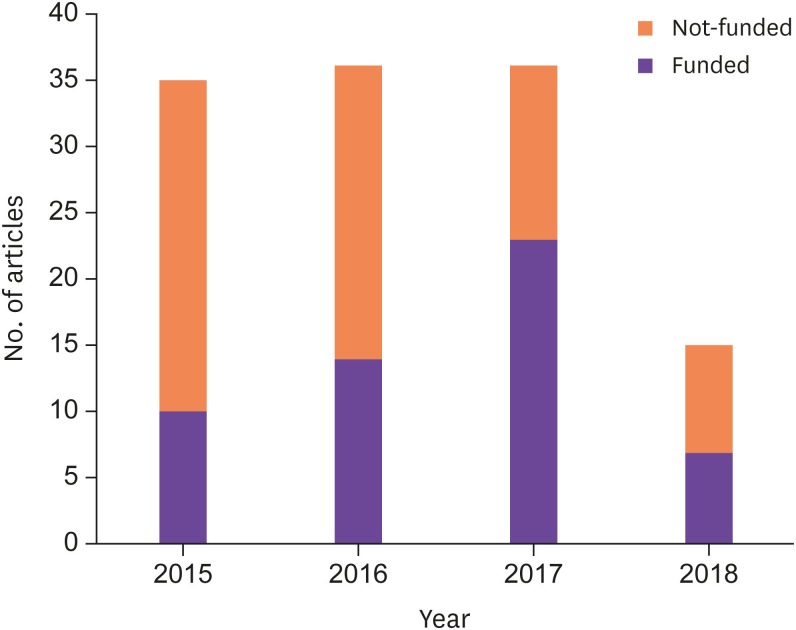
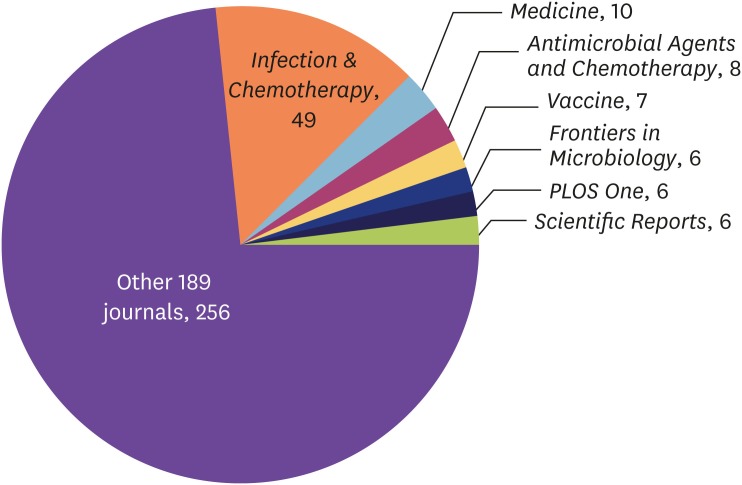
Out of 181 articles of Infection & Chemotherapy published between 2015 and 2018, the highest number of authors were from Korea (165, 91.2%). There were articles from 11 other countries. The proportion of funded articles to original articles has increased yearly and has reached 46.7% in 2018. The manually calculated impact factor of the year 2017 was 1.728, which corresponded to 21.5% of the 2017 Journal Citation Reports (JCR) category of "infectious diseases". There were 196 source journal titles that cited Infection & Chemotherapy in the 2015-2018 issues. The Hirsch index was 15.
CONCLUSION
The metrics results above demonstrate that over the years, Infection & Chemotherapy was developed into a top-level international-level journal so that it could be utilized by researchers across the world. The adoption of new policies including author taxonomy, an open data policy, a clinical data sharing policy, the principles of transparency and best practice in scholarly publishing 3rd edition will help increase the transparency of the authorship and the scientific integrity of the articles.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
Reference
-
1. Schwarzman AB. Journal article tag suite subset and Schematron: achieving the right balance. Sci Ed. 2018; 5:2–15.
Article2. Kim K, Chung Y. Overview of journal metrics. Sci Ed. 2018; 5:16–20.
Article3. Hirsch JE. An index to quantify an individual's scientific research output. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:16569–16572. PMID: 16275915.
Article4. Allen L, Scott J, Brand A, Hlava M, Altman M. Publishing: credit where credit is due. Nature. 2014; 508:312–313. PMID: 24745070.
Article5. Lim EY, Yim MK, Huh S. Smart device-based testing for medical students in Korea: satisfaction, convenience, and advantages. J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2017; 14:7. PMID: 28835015.
Article6. Zuiderwijk A, Janssen M. Open data policies, their implementation and impact: A framework for comparison. Gov Inf Q. 2014; 31:17–29.
Article7. Huh S. What can Asian editors contribute to European editors? Sci Ed. 2016; 3:122–124.
Article8. Huh S. Promotion to MEDLINE, indexing with Medical Subject Headings, and open data policy for the journal of educational evaluation for health professions. J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2016; 13:14. PMID: 27030394.9. Huh S. Establishment of an open data policy for Journal of Educational Evaluation for Health Professions, appreciation for invited reviewers, and acknowledgement of volunteers who made audio recordings. J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2017; 14:37. PMID: 29284767.10. Taichman DB, Sahni P, Pinborg A, Peiperl L, Laine C, James A, Hong ST, Haileamlak A, Gollogly L, Godlee F, Frizelle FA, Florenzano F, Drazen JM, Bauchner H, Baethge C, Backus J. Data sharing statements for clinical trials: a requirement of the international committee of medical journal editors. J Korean Med Sci. 2017; 32:1051–1053. PMID: 28581257.
Article11. Huh S. Adherence of the Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism to the Principles of Transparency and Best Practice in Scholarly Publishing . Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2018; 23:1–3. PMID: 29609442.12. Huh S. The 14th European Association of Science Editors Conference, Bucharest 2018. Sci Ed. 2018; 5:155–158.
Article13. Huh S. How to prepare Endocrinology and Metabolism for reapplication to MEDLINE. Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 32:58–61.14. Huh S. Journal metrics of Clinical and Molecular Hepatology based on the Web of Science Core Collection. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2018; 24:137–143. PMID: 29961305.
Article15. Huh S. Clinical and Experimental Vaccine Research's promotion to internationally competitive journal evidenced by journal metrics. Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2017; 6:67–71. PMID: 28775970.16. Huh S. The rapid internationalization of Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism as evidenced by journal metrics. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 22:77–81. PMID: 28690984.17. Jeong GH, Huh S. The great rise of Intestinal Research as an international journal 3 years after its language change to English as evidenced by journal metrics. Intest Res. 2017; 15:1–4. PMID: 28239311.18. Huh S. Promotion of Neurointervention to international journal based on journal metrics. Neurointervention. 2016; 11:5–9. PMID: 26958406.19. Huh S. Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery's evolution into an international journal based on journal metrics. Clin Orthop Surg. 2016; 8:127–132. PMID: 27247735.
Article20. Huh S. How much progress has Blood Research made since the change of the journal title in 2013. Blood Res. 2018; 53:95–100. PMID: 29963510.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ethical issues in clinical research and publication
- Recent Issues in Medical Journal Publishing and Editing Policies: Adoption of Artificial Intelligence, Preprints, Open Peer Review, Model Text Recycling Policies, Best Practice in Scholarly Publishing 4th Version, and Country Names in Titles
- Cartoons in Scholarly Publishing: Considerations for Authors, Reviewers, and Editors
- What is the position of Clinical and Experimental Reproductive Medicine in its scholarly journal network based on journal metrics?
- Retraction: A Case of Disseminated Scedosporium apiospermum Infection in a Liver Transplant Patient. Infection and Chemotherapy 2006;38(5):290-295