Transl Clin Pharmacol.
2018 Sep;26(3):118-127. 10.12793/tcp.2018.26.3.118.
Safety and efficacy of fimasartan with essential hypertension patients in real world clinical practice: data from a post marketing surveillance in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Seoul Research Institute, Boryung Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Seoul 03127, Republic of Korea. scchoejr@gmail.com
- KMID: 2420294
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12793/tcp.2018.26.3.118
Abstract
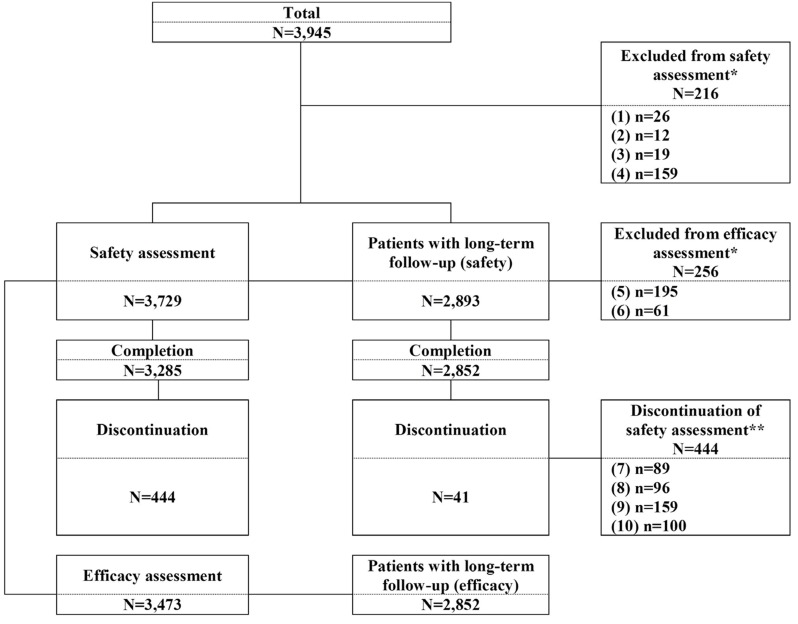
- The safety and efficacy of fimasartan have been evaluated through post-marketing surveillance in real world clinical practice. The multi-center, prospective, open-label and non-interventional study. A total of 3,945 patients (3,729 patients for safety assessment and 3,473 patients for efficacy assessment) were screened in patients with essential hypertension in 89 study centers from 9 September 2010 through 8 September 2016. Among the total patients, 2,893 patients (77.6%) were administered fimasartan for 24 weeks or longer and were classified as "˜patients with long-term follow-up', and the additional safety and efficacy analysis were performed. The improvement was defined as systolic blood pressure (SBP) controlled to ≤ 140 mmHg or decreased SBP differences ≥ 20 mmHg after treatment or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) controlled to ≤ 90 mmHg or decreased DBP differences ≥ 10 mmHg after treatment. Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) were reported in 3.8% patients; dizziness, and hypotension were the most frequently reported ADRs in total patients. The results of patients with long-term follow-up were comparable with total patients. The overall improvement rate in all efficacy assessment at the last visit was 87.1% (3,025/3,473 patients). The overall improvement rate of the patients with long-term follow-up was 88.9%. Fimasartan was well tolerated, with no new safety concerns identified and an effective treatment in the real world clinical practice for Korean patients with hypertension.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lawes CM, Vander Hoorn S, Rodgers A. International Society of Hypertension. Global burden of blood-pressure-related disease, 2001. Lancet. 2008; 371:1513–1518. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60655-8. PMID: 18456100.
Article2. Han MK, Huh Y, Lee SB, Park JH, Lee JJ, Choi EA, et al. Prevalence of stroke and transient ischemic attack in Korean elders: findings from the Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging (KLoSHA). Stroke. 2009; 40:966–969. DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.524983. PMID: 19150874.3. Choi CU, Park CG. Estimating the probability of stroke in Korean hypertensive patients visiting tertiary hospitals using a risk profile from the Framingham study. BMC Neurol. 2009; 9:16. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2377-9-16. PMID: 19386109.
Article4. Shin CY, Yun KE, Park HS. Blood pressure has a greater impact on cardiovascular mortality than other components of metabolic syndrome in Koreans. Atherosclerosis. 2009; 205:614–619. DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2009.01.014. PMID: 19232617.
Article5. Murray CJL, Lopez AD. The global burden of disease: a comprehensive assessment of mortality and disability from diseases, injuries, and risk factors in 1990 and projected to 2020. Boston, MA: Harvard University Press;1996. ISBN: 0-9655466-0-8.6. Antonaccio MJ, Wright JJ. Enzyme inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system. Prog Drug Res. 1987; 31:161–191. PMID: 3326029.
Article7. Wood SM, Mann RD, Rawlins MD. Angio-oedema and urticaria associated with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1987; 294:91–92.
Article8. Gravras H, Gravras I. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. Properties and side effects. Hypertension. 1998; 11:II37–II41.
Article9. Lee HY, Oh BH. Fimasartan: A new angiotensin receptor blocker. Drugs. 2016; 76:1015–1022. DOI: 10.1007/s40265-016-0592-1. PMID: 27272555.
Article10. Lee H, Yang HM, Lee HY, Kim JJ, Choi DJ, Seung KB, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of once-daily oral fimasartan 20 to 240 mg/d in Korean Patients with hypertension: findings from Two Phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies. Clin Ther. 2012; 34:1273–1289. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2012.04.021. PMID: 22608107.
Article11. Lee H, Kim KS, Chae SC, Jeong MH, Kim DS, Oh BH. Ambulatory blood pressure response to once-daily fimasartan: an 8-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, active-comparator, parallel-group study in Korean patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension. Clin Ther. 2013; 35:1337–1349. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2013.06.021. PMID: 23932463.
Article12. Lee SE, Kim YJ, Lee HY, Yang HM, Park CG, Kim JJ, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of fimasartan, a new angiotensin receptor blocker, compared with losartan (50/100 mg): a 12-week, phase III, multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, dose escalation clinical trial with an optional 12-week extension phase in adult Korean patients with mild-to-moderate hypertension. Clin Ther. 2012; 34:552–568. 568.e1–568.e9. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2012.01.024. PMID: 22381711.
Article13. Lee JH, Yang DH, Hwang JY, Hur SH, Cha TJ, Kim KS, et al. A randomized, Double-blind, Candesartan-controlled, Parallel group comparison clinical trial to evaluate the antihypertensive efficacy and safety of fimasartan in patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension. Clin Ther. 2016; 38:1485–1497. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2016.04.005. PMID: 27161546.
Article14. Naritomi H, Fujita T, Ito S, Ogihara T, Shimada K, Shimamoto K, et al. Efficacy and safety of long-term losartan therapy demonstrated by a prospective observational study in Japanese patients with hypertension: The Japan Hypertension Evaluation with Angiotensin II Antagonist Losartan Therapy (J-HEALTH) study. Hypertens Res. 2008; 31:295–304. DOI: 10.1291/hypres.31.295. PMID: 18360050.
Article15. Park JB, Sung KC, Kang SM, Cho EJ. Safety and efficacy of fimasartan in patients with arterial hypertension (Safe-KanArb study): an open-label observational study. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2013; 13:47–56. DOI: 10.1007/s40256-013-0004-9. PMID: 23344912.16. Youn JC, Ihm SH, Bae JH, Park SM, Jeon DW, Jung BC, et al. Efficacy and safety of 30-mg fimasartan for the treatment of patients with mild to moderate hypertension: an 8-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, phase III clinical study. Clin Ther. 2014; 36:1412–1421. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.07.004. PMID: 25092393.
Article17. Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr, Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. 2018; 71:1269–1324. DOI: 10.1161/HYP.0000000000000066. PMID: 29133354.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Problems within the post-marketing surveillance system in Korea: Time for a change
- Short-term Efficacy and Safety of Ranibizumab for Neovascular Age-related Macular Degeneration in the Real World: A Post-marketing Surveillance Study
- Case Analysis in Drug Approval by FDA/EMA Using Real-World Data/Real-World Evidence
- Improvement of Re-examination System of New Drugs: A Safety Monitoring Study using Real-World Data on Re-examined Drugs
- Current Status of Post-marketing Safety Management in United States, Europe and Japan: Risk Management Plan