Yonsei Med J.
2018 Oct;59(8):968-974. 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.8.968.
Proper Cut-off Levels of Serum Specific IgE to Cefaclor for Patients with Cefaclor Allergy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. ye9007@ajou.ac.kr
- 3Pharmacovigilance Center, Ajou University Hospital, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2419731
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.8.968
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Cefaclor, a second-generation oral cephalosporin, is known to cause IgE-mediated hypersensitivity. Assays of serum-specific IgE (sIgE) to cefaclor are commercially available via the ImmunoCAP system (Thermo Fisher Scientific). While serum levels of sIgE >0.35 kU/L are considered indicative of an allergy, some patients with cefaclor allergy show low serum IgE levels. This study aimed to evaluate the proper cut-off levels of sIgE in the diagnosis of immediate hypersensitivity to cefaclor.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
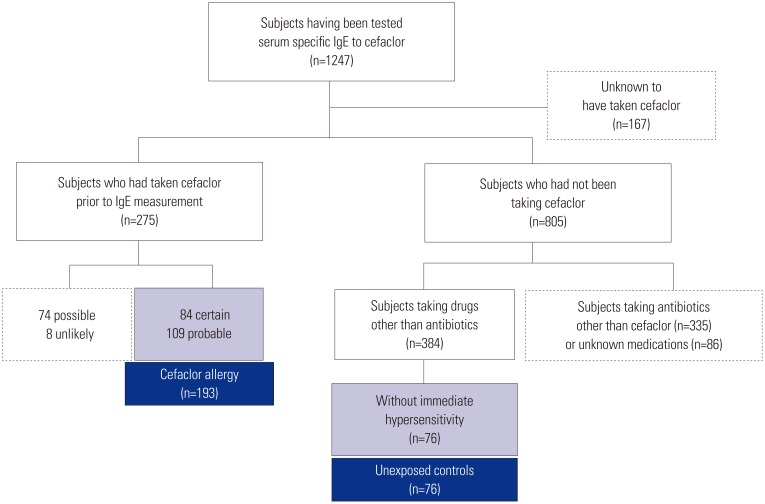
A total of 269 patients with drug allergy history, who underwent assays of sIgE to cefaclor at Ajou University hospital and Dong-A University Hospital, were reviewed retrospectively. Among them, 193 patients exhibited cefaclor-induced immediate hypersensitivity with certain or probable causality of an adverse drug reaction according to the WHO-UMC (the World Health Organization-the Uppsala Monitoring Centre) algorithm, and 76 controls showed delayed hypersensitivity reactions to non-antibiotics.
RESULTS
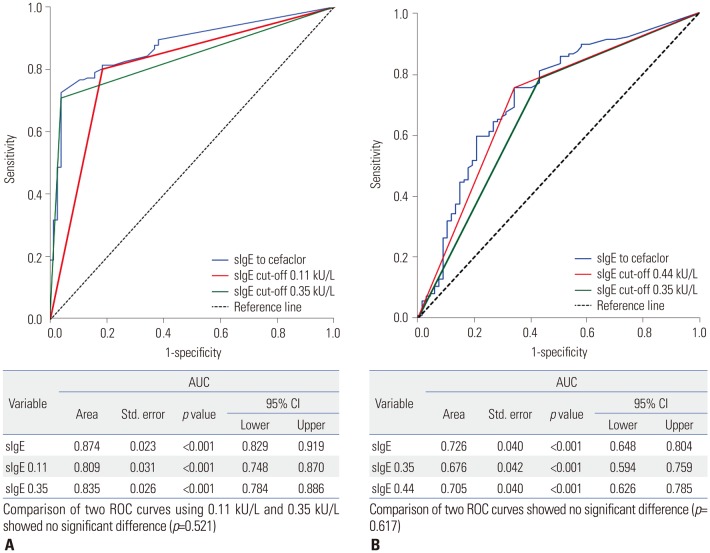
In total, 126 of the 193 patients (65.3%) experienced anaphylaxis; they had higher serum sIgE levels than patients with immediate hypersensitivity who did not experience anaphylaxis (6.36±12.39 kU/L vs. 4.28±13.61 kU/L, p < 0.001). The best cut-off value for cefaclor-induced immediate hypersensitivity was 0.11 kU/L, with sensitivity of 80.2% and specificity of 81.6%. A cut-off value of 0.44 kU/L showed the best sensitivity (75.4%) and specificity (65.7%) for differentiating anaphylaxis from immediate hypersensitivity reactions.
CONCLUSION
Patients with cefaclor anaphylaxis exhibit high serum IgE levels. A cut-off value of 0.11 kU/L of sIgE to cefaclor is proper for identifying patients with cefaclor allergy, and 0.44 kU/L may be useful to detect anaphylaxis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Beghetti M, Wilson GJ, Bohn D, Benson L. Hypersensitivity myocarditis caused by an allergic reaction to cefaclor. J Pediatr. 1998; 132:172–173. PMID: 9470025.
Article2. Kearns GL, Wheeler JG, Rieder MJ, Reid J. Serum sickness-like reaction to cefaclor: lack of in vitro cross-reactivity with loracarbef. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1998; 63:686–693. PMID: 9663184.
Article3. King BA, Geelhoed GC. Adverse skin and joint reactions associated with oral antibiotics in children: the role of cefaclor in serum sickness-like reactions. J Paediatr Child Health. 2003; 39:677–681. PMID: 14629499.
Article4. Novembre E, Mori F, Pucci N, Bernardini R, Romano A. Cefaclor anaphylaxis in children. Allergy. 2009; 64:1233–1235. PMID: 19385950.
Article5. Nam YH, Kim JE, Hwang EK, Jin HJ, Shin YS, Ye YM, et al. Clinical and immunologic evaluations of immediate hypersensitivity to cefaclor. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 31:192–198.6. Atanasković-Marković M, Velicković TC, Gavrović-Jankulović M, Vucković O, Nestorović B. Immediate allergic reactions to cephalosporins and penicillins and their cross-reactivity in children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2005; 16:341–347. PMID: 15943598.
Article7. Yoo HS, Kim SH, Kwon HS, Kim TB, Nam YH, Ye YM, et al. Immunologic evaluation of immediate hypersensitivity to cefaclor. Yonsei Med J. 2014; 55:1473–1483. PMID: 25323882.
Article8. Doña I, Torres MJ, Montañez MI, Fernández TD. In vitro diagnostic testing for antibiotic allergy. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017; 9:288–298. PMID: 28497915.
Article9. Gomes ER, Demoly P. Epidemiology of hypersensitivity drug reactions. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 5:309–316. PMID: 15985812.
Article10. Har D, Solensky R. Penicillin and beta-lactam hypersensitivity. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2017; 37:643–662. PMID: 28965632.
Article11. Antunez C, Blanca-Lopez N, Torres MJ, Mayorga C, Perez-Inestrosa E, Montañez MI, et al. Immediate allergic reactions to cephalosporins: evaluation of cross-reactivity with a panel of penicillins and cephalosporins. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 117:404–410. PMID: 16461141.
Article12. Romano A, Guéant-Rodriguez RM, Viola M, Amoghly F, Gaeta F, Nicolas JP, et al. Diagnosing immediate reactions to cephalosporins. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005; 35:1234–1242. PMID: 16164453.
Article13. Pumphrey RS, Davis S. Under-reporting of antibiotic anaphylaxis may put patients at risk. Lancet. 1999; 353:1157–1158.
Article14. Pham NH, Baldo BA. beta-Lactam drug allergens: fine structural recognition patterns of cephalosporin-reactive IgE antibodies. J Mol Recognit. 1996; 9:287–296. PMID: 9131470.15. Baldo BA. Penicillins and cephalosporins as allergens--structural aspects of recognition and cross-reactions. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999; 29:744–749. PMID: 10336588.16. Romano A, Gaeta F, Valluzzi RL, Maggioletti M, Zaffiro A, Caruso C, et al. IgE-mediated hypersensitivity to cephalosporins: cross-reactivity and tolerability of alternative cephalosporins. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015; 136:685–691.e3. PMID: 25930196.
Article17. Venemalm L. Pyrazinone conjugates as potential cephalosporin allergens. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2001; 11:1869–1870. PMID: 11459649.
Article18. Pichichero ME, Zagursky R. Penicillin and cephalosporin allergy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014; 112:404–412. PMID: 24767695.
Article19. Ariza A, Mayorga C, Fernandez TD, Barbero N, Martín-Serrano A, Pérez-Sala D, et al. Hypersensitivity reactions to β-lactams: relevance of hapten-protein conjugates. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2015; 25:12–25.20. Blanca M, Torres MJ, García JJ, Romano A, Mayorga C, de Ramon E, et al. Natural evolution of skin test sensitivity in patients allergic to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 103(5 Pt 1):918–924. PMID: 10329829.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Anaphylaxis after Exposure to Oral Cefaclor
- A case of immediate hypersensitivity to cefaclor: serum specific IgE detection
- Clinical and Immunologic Evaluations of Immediate Hypersensitivity to Cefaclor
- A Case of Anaphylaxis Induced by Oral Cefaclor in Aspirin Idiosyncratic Patient
- Immunologic Evaluation of Immediate Hypersensitivity to Cefaclor