Yonsei Med J.
2018 Oct;59(8):951-959. 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.8.951.
Prospective Single Arm Study on the Effect of Ilaprazole in Patients with Heartburn but No Reflux Esophagitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. SKLEE@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2419729
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.8.951
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease without esophagitis show varying responses to proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). The aim of this study was to objectively evaluate the effect of a new PPI, ilaprazole, on patients with heartburn but without reflux esophagitis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
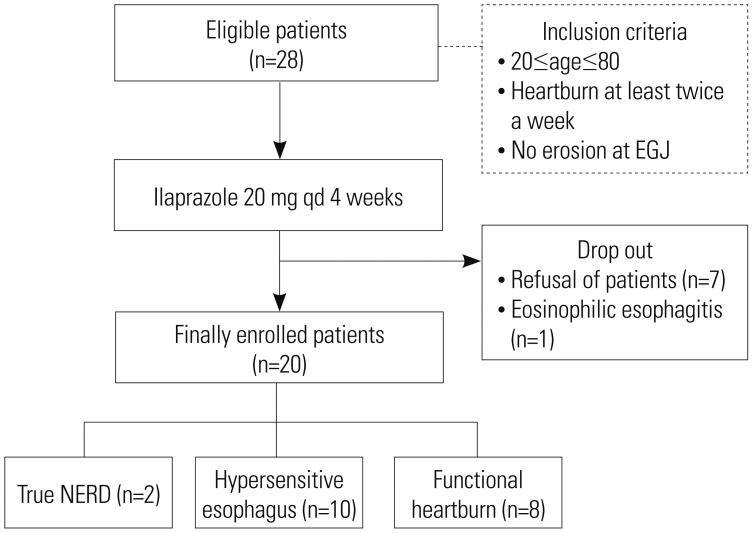
This prospective study was performed on 20 patients with heartburn but without reflux esophagitis. All patients underwent upper endoscopy and 24-hr combined multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH esophageal monitoring (MII-pH). They were then treated with ilaprazole (20 mg) once daily for 4 weeks. The GerdQ questionnaire, histologic findings, and inflammatory biomarkers were used for assessment before and after ilaprazole.
RESULTS
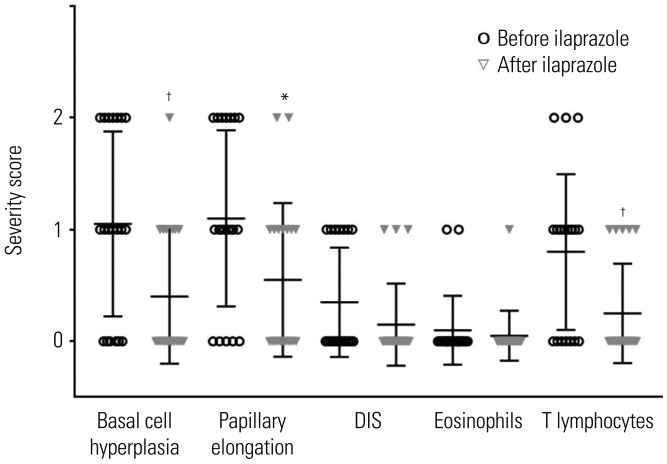
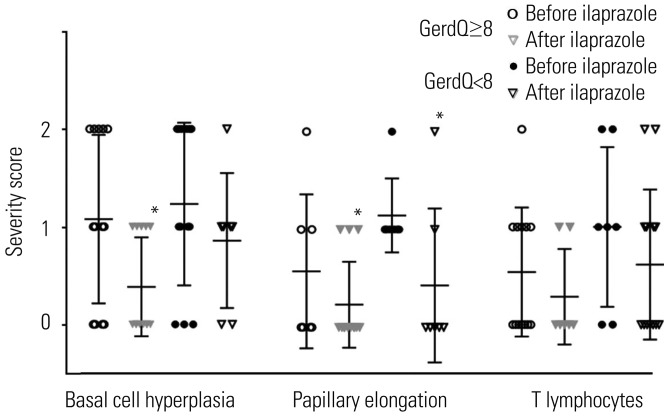
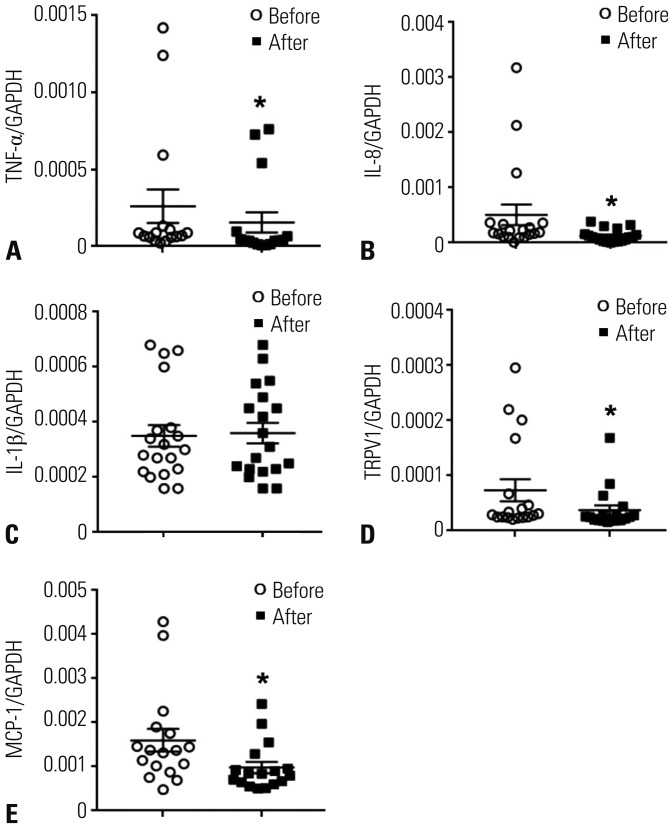
Among the 20 patients, 13 (65%) showed GerdQ score ≥8. Based on MII-pH results, patients were classified as true nonerosive reflux disease (n=2), hypersensitive esophagus (n=10), and functional heartburn (n=8). After treatment, patients showed a statistically significant improvement in GerdQ score (p < 0.001). Among histopathologic findings, basal cell hyperplasia, papillary elongation, and infiltration of intraepithelial T lymphocytes improved significantly (p=0.008, p=0.021, and p=0.008; respectively). Expression of TNF-α, IL-8, TRPV1, and MCP-1 decreased marginally after treatment (p=0.049, p=0.046, p=0.045, and p=0.042; respectively).
CONCLUSION
Daily ilaprazole (20 mg) is efficacious in improving symptom scores, histopathologic findings, and inflammatory biomarkers in patients with heartburn but no reflux esophagitis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dent J, El-Serag HB, Wallander MA, Johansson S. Epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut. 2005; 54:710–717. PMID: 15831922.
Article2. Dent J. Microscopic esophageal mucosal injury in nonerosive reflux disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 5:4–16. PMID: 17157563.
Article3. Savarino E, Zentilin P, Savarino V. NERD: an umbrella term including heterogeneous subpopulations. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 10:371–380. PMID: 23528345.
Article4. Savarino E, Zentilin P, Tutuian R, Pohl D, Casa DD, Frazzoni M, et al. The role of nonacid reflux in NERD: lessons learned from impedance-pH monitoring in 150 patients off therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008; 103:2685–2693. PMID: 18775017.
Article5. Dean BB, Gano AD Jr, Knight K, Ofman JJ, Fass R. Effectiveness of proton pump inhibitors in nonerosive reflux disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 2:656–664. PMID: 15290657.
Article6. Ji XQ, Du JF, Chen G, Chen G, Yu B. Efficacy of ilaprazole in the treatment of duodenal ulcers: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:5119–5123. PMID: 24803828.
Article7. Periclou AP, Goldwater R, Lee SM, Park DW, Kim DY, Cho KD, et al. A comparative pharmacodynamic study of IY-81149 versus omeprazole in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2000; 68:304–311. PMID: 11014412.
Article8. de Bortoli N, Martinucci I, Giacchino M, Blandizzi C, Marchi S, Savarino V, et al. The pharmacokinetics of ilaprazole for gastroesophageal reflux treatment. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2013; 9:1361–1369. PMID: 23802731.
Article9. Du YQ, Guo WY, Zou DW, Zhan XB, Li Z, Hu JH, et al. Acid inhibition effect of ilaprazole on Helicobacter pylori-negative healthy volunteers: an open randomized cross-over study. J Dig Dis. 2012; 13:113–119. PMID: 22257480.
Article10. Fiocca R, Mastracci L, Riddell R, Takubo K, Vieth M, Yerian L, et al. Development of consensus guidelines for the histologic recognition of microscopic esophagitis in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: the Esohisto project. Hum Pathol. 2010; 41:223–231. PMID: 19800099.
Article11. Yerian L, Fiocca R, Mastracci L, Riddell R, Vieth M, Sharma P, et al. Refinement and reproducibility of histologic criteria for the assessment of microscopic lesions in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: the Esohisto Project. Dig Dis Sci. 2011; 56:2656–2665. PMID: 21365241.
Article12. Weusten BL, Roelofs JM, Akkermans LM, Van Berge-Henegouwen GP, Smout AJ. The symptom-association probability: an improved method for symptom analysis of 24-hour esophageal pH data. Gastroenterology. 1994; 107:1741–1745. PMID: 7958686.
Article13. Ward BW, Wu WC, Richter JE, Lui KW, Castell DO. Ambulatory 24-hour esophageal pH monitoring. Technology searching for a clinical application. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1986; 8(Suppl 1):59–67. PMID: 3734378.14. Tielemans MM, van Oijen MG. Online follow-up of individuals with gastroesophageal reflux disease using a patient-reported outcomes instrument: results of an observational study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013; 13:144. PMID: 24083342.
Article15. Tielemans MM, Jansen JB, van Oijen MG. Open access capture of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease using an online patient-reported outcomes instrument. Interact J Med Res. 2012; 1:e7. PMID: 23611985.
Article16. Suzuki H, Matsuzaki J, Okada S, Hirata K, Fukuhara S, Hibi T. Validation of the GerdQ questionnaire for the management of gastrooesophageal reflux disease in Japan. United European Gastroenterol J. 2013; 1:175–183.
Article17. Quigley EM. Non-erosive reflux disease, functional heartburn and gastroesophageal reflux disease; insights into pathophysiology and clinical presentation. Chin J Dig Dis. 2006; 7:186–190. PMID: 17054579.
Article18. Savarino E, Zentilin P, Tutuian R, Pohl D, Gemignani L, Malesci A, et al. Impedance-pH reflux patterns can differentiate non-erosive reflux disease from functional heartburn patients. J Gastroenterol. 2012; 47:159–168. PMID: 22038553.
Article19. Long JD, Orlando RC. Nonerosive reflux disease: a pathophysiologic perspective. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2008; 10:200–207. PMID: 18625127.
Article20. Stolte M, Vieth M, Schmitz JM, Alexandridis T, Seifert E. Effects of long-term treatment with proton pump inhibitors in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease on the histological findings in the lower oesophagus. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2000; 35:1125–1130. PMID: 11145281.21. Vieth M, Peitz U, Labenz J, Kulig M, Nauclér E, Jaspersen D, et al. What parameters are relevant for the histological diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease without Barrett's mucosa? Dig Dis. 2004; 22:196–201. PMID: 15383761.
Article22. Kandulski A, Jechorek D, Caro C, Weigt J, Wex T, Mönkemüller K, et al. Histomorphological differentiation of non-erosive reflux disease and functional heartburn in patients with PPI-refractory heartburn. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013; 38:643–651. PMID: 23895770.
Article23. Funch-Jensen P, Kock K, Christensen LA, Fallingborg J, Kjaergaard JJ, Andersen SP, et al. Microscopic appearance of the esophageal mucosa in a consecutive series of patients submitted to upper endoscopy. Correlation with gastroesophageal reflux symptoms and macroscopic findings. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1986; 21:65–69. PMID: 3952454.
Article24. Kiesslich R, Kanzler S, Vieth M, Moehler M, Neidig J, Thanka Nadar BJ, et al. Minimal change esophagitis: prospective comparison of endoscopic and histological markers between patients with non-erosive reflux disease and normal controls using magnifying endoscopy. Dig Dis. 2004; 22:221–227. PMID: 15383765.
Article25. Farré R, Fornari F, Blondeau K, Vieth M, De Vos R, Bisschops R, et al. Acid and weakly acidic solutions impair mucosal integrity of distal exposed and proximal non-exposed human oesophagus. Gut. 2010; 59:164–169. PMID: 19880965.
Article26. Caviglia R, Ribolsi M, Maggiano N, Gabbrielli AM, Emerenziani S, Guarino MP, et al. Dilated intercellular spaces of esophageal epithelium in nonerosive reflux disease patients with physiological esophageal acid exposure. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:543–548. PMID: 15743349.
Article27. Isomoto H, Nishi Y, Kanazawa Y, Shikuwa S, Mizuta Y, Inoue K, et al. Immune and inflammatory responses in GERD and lansoprazole. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2007; 41:84–91. PMID: 18193101.
Article28. Isomoto H, Saenko VA, Kanazawa Y, Nishi Y, Ohtsuru A, Inoue K, et al. Enhanced expression of interleukin-8 and activation of nuclear factor kappa-B in endoscopy-negative gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004; 99:589–597. PMID: 15089887.
Article29. Mönkemüller K, Wex T, Kuester D, Fry LC, Peitz U, Beyer M, et al. Interleukin-1beta and interleukin-8 expression correlate with the histomorphological changes in esophageal mucosa of patients with erosive and non-erosive reflux disease. Digestion. 2009; 79:186–195. PMID: 19342859.
Article30. Shieh KR, Yi CH, Liu TT, Tseng HL, Ho HC, Hsieh HT, et al. Evidence for neurotrophic factors associating with TRPV1 gene expression in the inflamed human esophagus. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010; 22:971–977. e252. PMID: 20518854.
Article31. Isomoto H, Wang A, Mizuta Y, Akazawa Y, Ohba K, Omagari K, et al. Elevated levels of chemokines in esophageal mucosa of patients with reflux esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003; 98:551–556. PMID: 12650786.
Article32. Isomoto H, Nishi Y, Wang A, Takeshima F, Omagari K, Mizuta Y, et al. Mucosal concentrations of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines at gastric cardia: implication of Helicobacter pylori infection and gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004; 99:1063–1068. PMID: 15180726.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Camostat Mesilate in the Treatment of Reflux Esophagitis after Gastrectomy
- Incidence of Esophagitis in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- A Case of Barrett Esophagus Associated with Erosive Reflux Esophagitis in a Patient with Hiatal Hernia
- Unmet Needs in the Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- Radiologic studies on gastroesophageal reflux