Ann Dermatol.
2018 Jun;30(3):364-367. 10.5021/ad.2018.30.3.364.
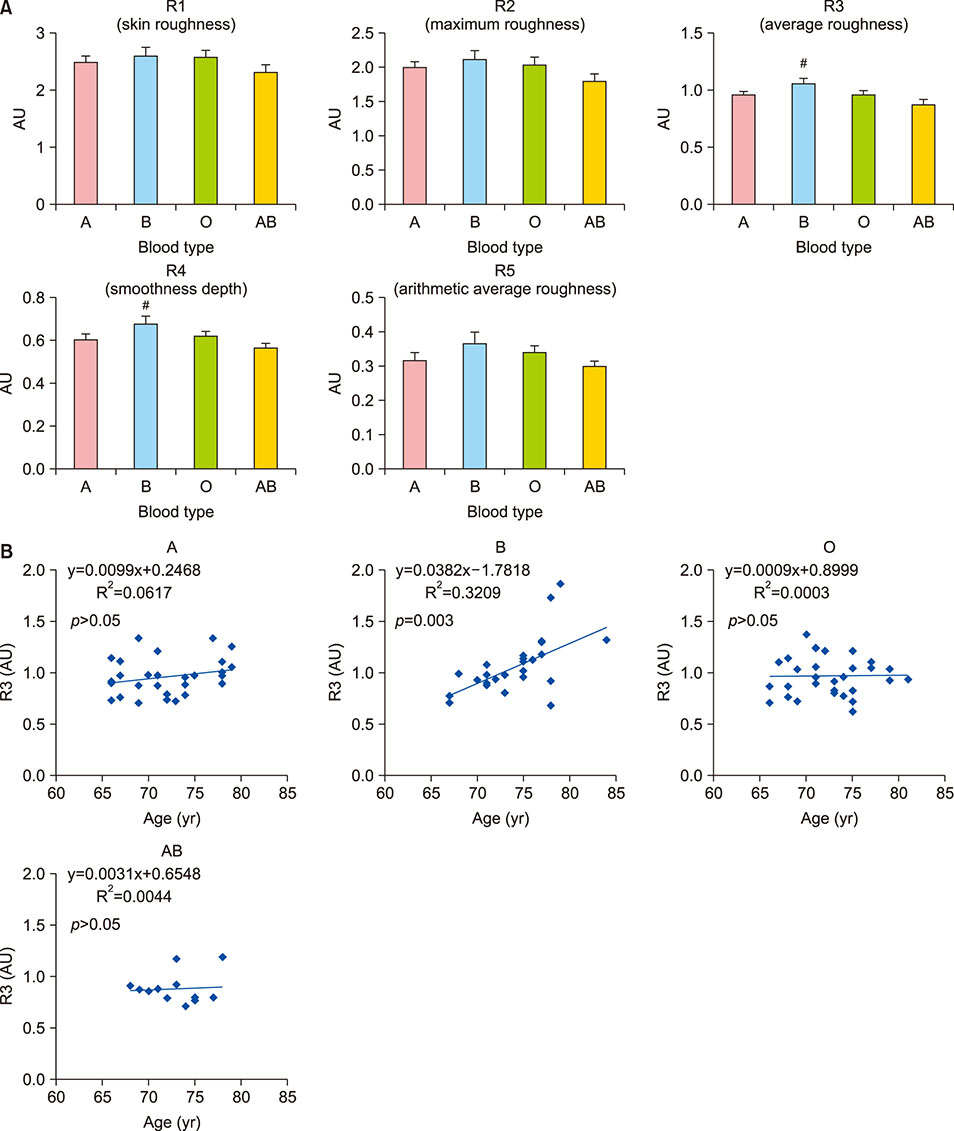
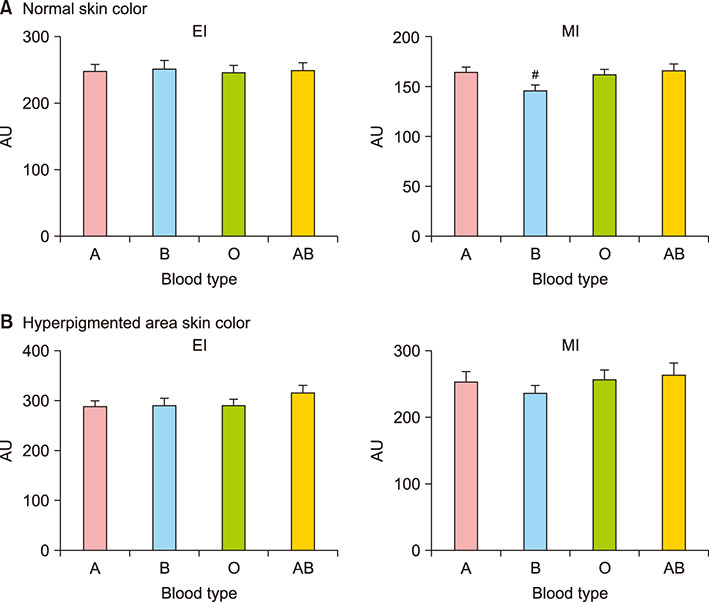
Deeper Wrinkle Formation and Less Melanin Production in Aged Korean Women with B Blood Type
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jhchung@snu.ac.kr
- 2Laboratory of Cutaneous Aging Research, Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Institute of Human-Environment Interface Biology, Medical Research Center, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Dermatology, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 5SNU Institute on Aging, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2419184
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2018.30.3.364
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Greenwell P. Blood group antigens: molecules seeking a function? Glycoconj J. 1997; 14:159–173.2. Ravn V, Dabelsteen E. Tissue distribution of histo-blood group antigens. APMIS. 2000; 108:1–28.3. Yamamoto F, Clausen H, White T, Marken J, Hakomori S. Molecular genetic basis of the histo-blood group ABO system. Nature. 1990; 345:229–233.
Article4. Lee DH, Jung JY, Oh JH, Lee S, Kim YK, Chung JH. Ultraviolet irradiation modulates ABO blood group antigens in human skin in vivo: possible implication in skin aging. J Dermatol Sci. 2012; 66:71–73.
Article5. Chung JH, Lee SH, Youn CS, Park BJ, Kim KH, Park KC, et al. Cutaneous photodamage in Koreans: influence of sex, sun exposure, smoking, and skin color. Arch Dermatol. 2001; 137:1043–1051.6. Franchini M, Favaloro EJ, Targher G, Lippi G. ABO blood group, hypercoagulability, and cardiovascular and cancer risk. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2012; 49:137–149.
Article7. Weiss FU, Schurmann C, Guenther A, Ernst F, Teumer A, Mayerle J, et al. Fucosyltransferase 2 (FUT2) non-secretor status and blood group B are associated with elevated serum lipase activity in asymptomatic subjects, and an increased risk for chronic pancreatitis: a genetic association study. Gut. 2015; 64:646–656.
Article8. Hobgood DK. Personality traits of aggression-submissiveness and perfectionism associate with ABO blood groups through catecholamine activities. Med Hypotheses. 2011; 77:294–300.
Article9. Grando SA, Pittelkow MR, Schallreuter KU. Adrenergic and cholinergic control in the biology of epidermis: physiological and clinical significance. J Invest Dermatol. 2006; 126:1948–1965.
Article10. Romana-Souza B, Santos Lima-Cezar G, Monte-Alto-Costa A. Psychological stress-induced catecholamines accelerates cutaneous aging in mice. Mech Ageing Dev. 2015; 152:63–73.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Periorbital Skin Rejuvenation of Asian Skin Using Microneedle Fractional Radiofrequency
- Piperine Regulates Melanogenesis through ERK Activation and Proteasomal Degradation of MITF
- Fungistatic Activity of Kojic Acid Against Human Pathogenic Fungi and Inhibition of Melanin-production in Cryptococcus neoformans
- Phenol peeling for treatment of deep wrinkle in leprosy patient
- The effects of prestaglandin Ea o the synthesis of type I collagenase mRNA of cultured fibroblasts from hypertrophic scar and keloid