Yonsei Med J.
2017 Jul;58(4):878-883. 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.4.878.
A Combined Closing Wedge Distal Femoral Osteotomy and Medial Reefing Procedure for Recurrent Patellar Dislocation with Genu Valgum
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul National University, Boramae Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Breach Candy Hospital, Mumbai, India.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea. kwnhamj@hotmail.com
- 4Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Barunsesang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2419098
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2017.58.4.878
Abstract
- PURPOSE
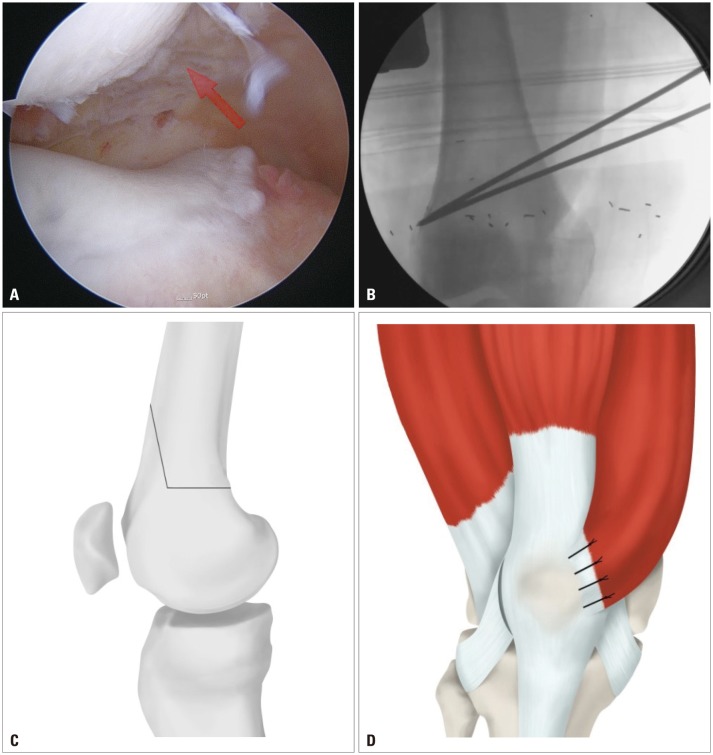
Recurrent patellar dislocation is often associated with genu valgum. The purpose of this study was to analyze the short-term results of single-incision, closing-wedge distal femoral osteotomy (CWDFO) combined with medial reefing and lateral release for recurrent patellar instability with genu valgum.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
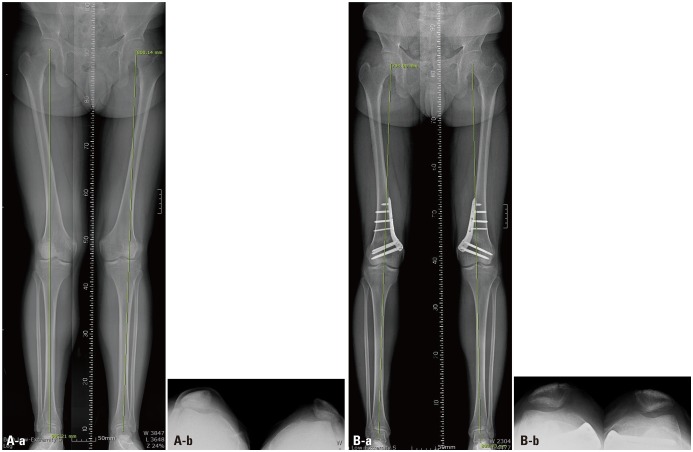
Combined CWDFO/medial reefing/lateral release was performed on 10 knees. Clinical evaluation was based on pre- and postoperative Knee Society Score (KSS) and Kujala patellofemoral score. Radiographic evaluation was performed with reference to the weight-bearing line (WBL), the femorotibial angle (FTA), and the mechanical lateral distal femoral angles in the knee-standing view.
RESULTS
At a mean follow-up of 20±11.7 months (range, 12-42 months), KSS scores improved significantly, from 46.7±5.2 preoperatively to 87±4.4 postoperatively (p<0.001), as did the Kujala score, from 44±8 preoperatively to 86.6±6.8 postoperatively (p<0.001). The WBL decreased significantly, from 76±7% preoperatively to 41±11% postoperatively (p<0.001). The FTA was improved significantly, from 12.7±1.7° preoperatively to 4±4° postoperatively (p<0.001), as was the mLDFA, from 83±4° preoperatively to 91±1.3° postoperatively (p<0.001).
CONCLUSION
Use of single-incision CWDFO combined with medial reefing and lateral release prevents patellar dislocation, corrects deformity, and improves clinical outcomes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ries Z, Bollier M. Patellofemoral instability in active adolescents. J Knee Surg. 2015; 28:265–277. PMID: 25892009.
Article2. Waterman BR, Belmont PJ Jr, Owens BD. Patellar dislocation in the United States: role of sex, age, race, and athletic participation. J Knee Surg. 2012; 25:51–57. PMID: 22624248.
Article3. Smith TO, Song F, Donell ST, Hing CB. Operative versus non-operative management of patellar dislocation. A meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011; 19:988–998. PMID: 21234544.
Article4. Lee JJ, Lee SJ, Won YG, Choi CH. Lateral release and medial plication for recurrent patella dislocation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012; 20:2438–2444. PMID: 22426853.
Article5. Ricchetti ET, Mehta S, Sennett BJ, Huffman GR. Comparison of lateral release versus lateral release with medial soft-tissue realignment for the treatment of recurrent patellar instability: a systematic review. Arthroscopy. 2007; 23:463–468. PMID: 17478275.
Article6. Drexler M, Dwyer T, Dolkart O, Goldstein Y, Steinberg EL, Chakravertty R, et al. Tibial rotational osteotomy and distal tuberosity transfer for patella subluxation secondary to excessive external tibial torsion: surgical technique and clinical outcome. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014; 22:2682–2689. PMID: 23740327.
Article7. Hall MJ, Mandalia VI. Tibial tubercle osteotomy for patello-femoral joint disorders. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016; 24:855–861. PMID: 25326765.
Article8. Shen HC, Chao KH, Huang GS, Pan RY, Lee CH. Combined proximal and distal realignment procedures to treat the habitual dislocation of the patella in adults. Am J Sports Med. 2007; 35:2101–2108. PMID: 17724090.
Article9. Brinkman JM, Freiling D, Lobenhoffer P, Staubli AE, van Heerwaarden RJ. Supracondylar femur osteotomies around the knee: patient selection, planning, operative techniques, stability of fixation, and bone healing. Orthopade. 2014; 43(Suppl 1):S1–S10. PMID: 25331499.10. Hinterwimmer S, Minzlaff P, Saier T, Niemeyer P, Imhoff AB, Feucht MJ. Biplanar supracondylar femoral derotation osteotomy for patellofemoral malalignment: the anterior closed-wedge technique. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014; 22:2518–2521. PMID: 24748287.
Article11. Kwak JH, Sim JA, Kim NK, Lee BK. Surgical treatment of habitual patella dislocation with genu valgum. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2011; 23:177–179. PMID: 22570831.
Article12. Kwon JH, Kim JI, Seo DH, Kang KW, Nam JH, Nha KW. Patellar dislocation with genu valgum treated by DFO. Orthopedics. 2013; 36:840–843. PMID: 23746026.
Article13. Purushothaman B, Agarwal A, Dawson M. Posttraumatic chronic patellar dislocation treated by distal femoral osteotomy and medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction. Orthopedics. 2012; 35:e1668–e1672. PMID: 23127463.
Article14. Brinkman JM, Hurschler C, Staubli AE, van Heerwaarden RJ. Axial and torsional stability of an improved single-plane and a new biplane osteotomy technique for supracondylar femur osteotomies. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011; 19:1090–1098. PMID: 21161172.
Article15. van Heerwaarden R, Najfeld M, Brinkman M, Seil R, Madry H, Pape D. Wedge volume and osteotomy surface depend on surgical technique for distal femoral osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013; 21:206–212. PMID: 22766687.
Article16. Iliadis AD, Jaiswal PK, Khan W, Johnstone D. The operative management of patella malalignment. Open Orthop J. 2012; 6:327–339. PMID: 22927893.
Article17. Forkel P, Achtnich A, Metzlaff S, Zantop T, Petersen W. Midterm results following medial closed wedge distal femoral osteotomy stabilized with a locking internal fixation device. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015; 23:2061–2067. PMID: 24676790.
Article18. Haviv B, Bronak S, Thein R, Thein R. The results of corrective osteotomy for valgus arthritic knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013; 21:49–56. PMID: 22940779.
Article19. Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN. Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; (248):13–14. PMID: 2805470.
Article20. Kujala UM, Jaakkola LH, Koskinen SK, Taimela S, Hurme M, Neli-markka O. Scoring of patellofemoral disorders. Arthroscopy. 1993; 9:159–163. PMID: 8461073.
Article21. Eilert RE. Congenital dislocation of the patella. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; (389):22–29.
Article22. Sherman SL, Erickson BJ, Cvetanovich GL, Chalmers PN, Farr J 2nd, Bach BR Jr, et al. Tibial tuberosity osteotomy: indications, techniques, and outcomes. Am J Sports Med. 2014; 42:2006–2017. PMID: 24197613.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Surgical Treatment of Habitual Patella Dislocation with Genu Valgum
- Surgical Technique for Distal Femur Varization Osteotomy
- Severe Genu Recurvatum after a Closing-wedge High Tibial Osteotomy: A Case Report
- Distal Femoral Medial Opening Wedge Osteotomy for Post-Traumatic, Distal Femoral Varus Deformity
- Recurrent dislocation of the Patella: Experience with Ten Knees