J Dent Anesth Pain Med.
2018 Aug;18(4):197-204. 10.17245/jdapm.2018.18.4.197.
Computerized intraligamental anesthesia in children: A review of clinical considerations
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric Dentistry, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. k.k.h.baghlaf@qmul.ac.uk, dr-loda@hotmail.com
- 2Institute of Dentistry, Queen Mary University, London, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
- 3Pedodontic Department, El Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt.
- KMID: 2419062
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2018.18.4.197
Abstract
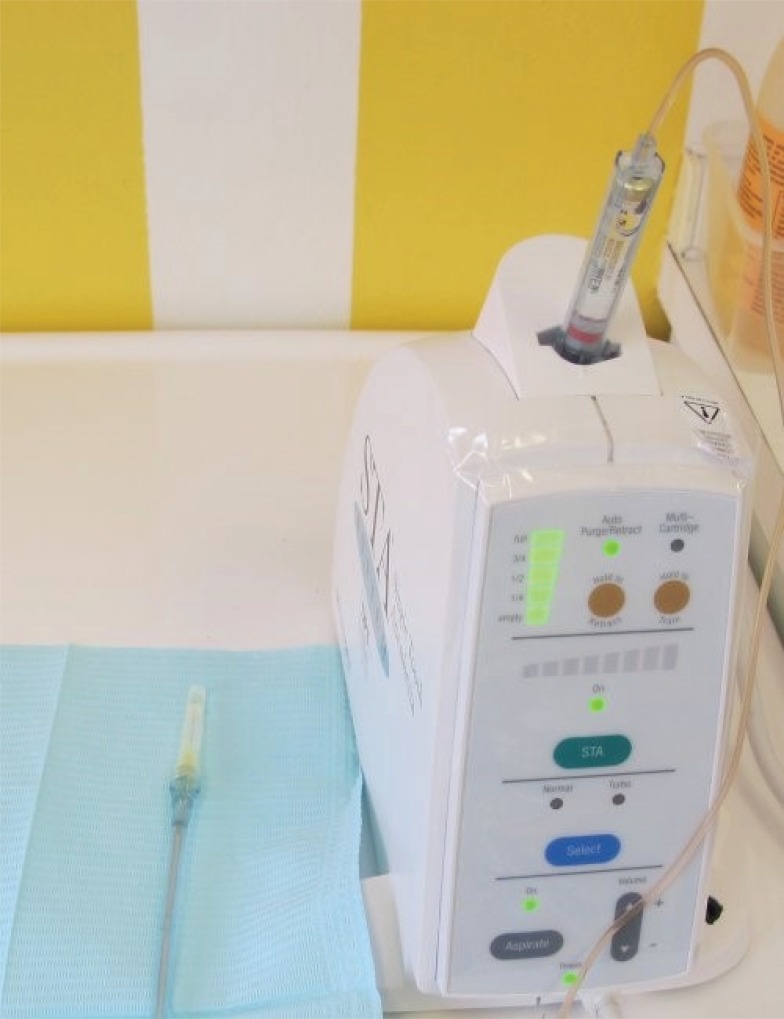
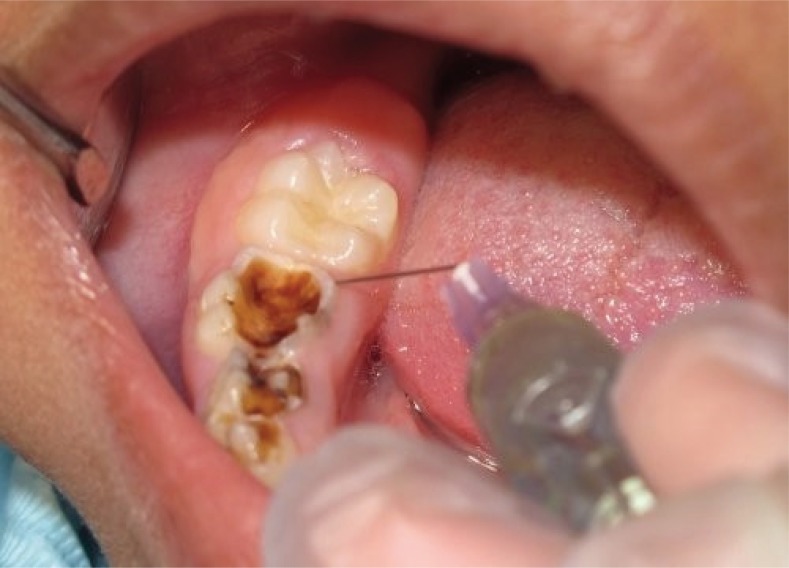
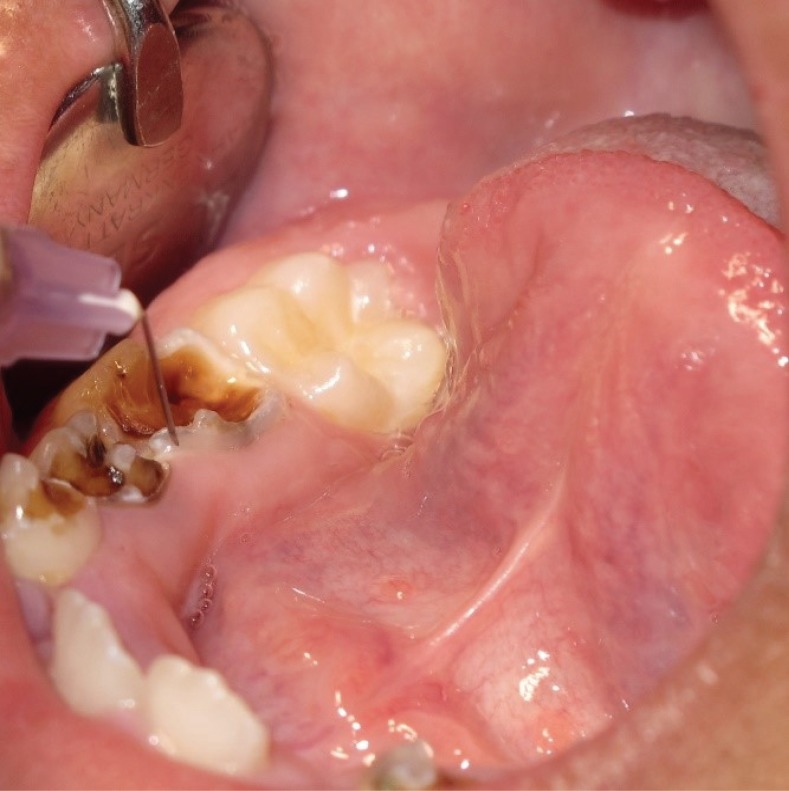
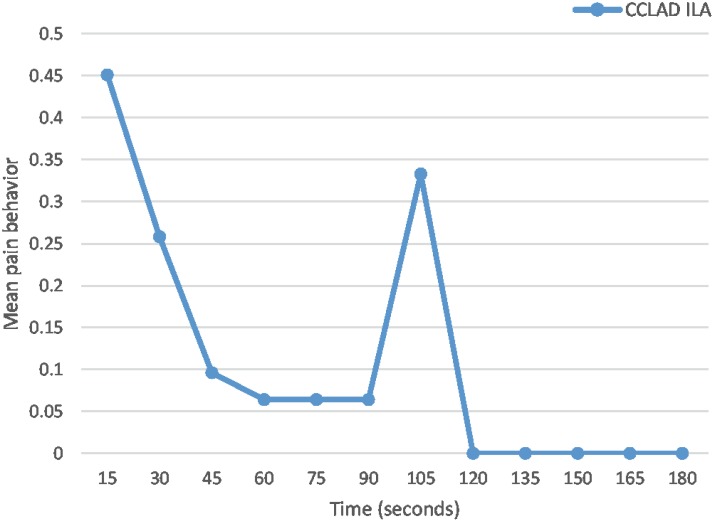
- Pain control by means of local anesthesia is an intrinsic part of clinical practice in dentistry. Several studies evaluated intraligamental anesthesia using a computer-controlled anesthetic device in children. There is a need to provide a clinical guide for the use of computerized intraligamental anesthesia in children. Intraligamental anesthesia using a computer-controlled anesthetic device was found to cause significantly lower pain perception scores and lower pain-related behavior than traditional techniques. This device proven to be effective in restorative and pulp treatment in children; however, its effectiveness in primary teeth extraction is controversial. It is important to withdraw recommendations necessity of future studies concerning the side effects of computerized intraligamental anesthesia in children. The present study aims to review different clinical aspects of computerized intraligamental anesthesia in children along with the side-effects, type of local anesthesia and postoperative pain of this technique. This study provides dentists with a clinical guide for the use of computerized intraligamental anesthesia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fischer G, Riethmueller RH. Local Anesthesia in Dentistry. Lea & Febiger;1912.2. Blanton PL, Jeske AH. Dental local anesthetics: alternative delivery methods. J Am Dent Assoc. 2003; 134:228–234. PMID: 12636129.3. Hochman MN. Single-tooth anesthesia: pressure-sensing technology provides innovative advancement in the field of dental local anesthesia. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2007; 28:186–188. 190192–193. PMID: 17487044.4. Amoudi NA, Feda M, Sharaf A, Hanno A, Farsi N. Assessment of the anesthetic effectiveness of anterior and middle superior alveolar injection using a computerized device versus traditional technique in children. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2008; 33:97–102. PMID: 19358373.
Article5. Feda M, Al Amoudi N, Sharaf A, Hanno A, Farsi N, Masoud I, et al. A comparative study of children's pain reactions and perceptions to AMSA injection using CCLAD versus traditional injections. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2010; 34:217–222. PMID: 20578658.
Article6. Mittal M, Kumar A, Srivastava D, Sharma P, Sharma S. Pain perception: computerized versus traditional local anesthesia in pediatric patients. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2015; 39:470–474. PMID: 26551372.
Article7. Versloot J, Veerkamp J, Hoogstraten J. Pain behaviour and distress in children during two sequential dental visits comparing a computerised anaesthesia delivery system and a traditional syringe. Br Dent J. 2008; 205:E2. PMID: 18493254.
Article8. Ram D, Peretz B. The assessment of pain sensation during local anesthesia using a computerized local anesthesia (Wand) and a conventional syringe. J Dent Child (Chic). 2003; 70:130–133. PMID: 14528773.9. Klein U, Hunzeker C, Hutfless S, Galloway A. Quality of anesthesia for the maxillary primary anterior segment in pediatric patients: Comparison of the P-ASA nerve block using compumed delivery system vs traditional supraperiosteal injections. J Dent Child. 2005; 72:119–125.10. Kandiah P, Tahmassebi JF. Comparing the onset of maxillary infiltration local anaesthesia and pain experience using the conventional technique vs. the Wand in children. Br Dent J. 2012; 213:E15. PMID: 23138830.
Article11. Baghlaf K, Alamoudi N, Elashiry E, Farsi N, El Derwi DA, Abdullah AM. The pain-related behavior and pain perception associated with computerized anesthesia in pulpotomies of mandibular primary molars: A randomized controlled trial. Quintessence Int. 2015; 46:799–806. PMID: 26287025.12. Alamoudi NM, Baghlaf KK, Elashiry EA, Farsi NM, El Derwi DA, Bayoumi AM. The effectiveness of computerized anesthesia in primary mandibular molar pulpotomy: A randomized controlled trial. Quintessence Int. 2016; 47:217–224. PMID: 26504907.13. Elbay ÜŞ, Elbay M, Kaya E, Cilasun Ü. Intraligamentary and supraperiosteal anesthesia efficacy using a computer controlled delivery system in mandibular molars. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2016; 40:193–199. PMID: 27472565.
Article14. Öztaş N, Ulusu T, Bodur H, Doğan C. The Wand in pulp therapy: an alternative to inferior alveolar nerve block. Quintessence Int. 2005; 36:559–564. PMID: 15997937.15. Ram D, Kassirer J. Assessment of a palatal approachanterior superior alveolar (P-ASA) nerve block with the Wand® in paediatric dental patients. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2006; 16:348–351. PMID: 16879332.16. Kim S. Ligamental injection: A physiological explantation of its efficacy. J Endod. 1986; 12:486–491. PMID: 3465854.
Article17. Kaufman E, Weinstein P, Milgrom P. Difficulties in achieving local anesthesia. J Am Dent Assoc. 1984; 108:205–208. PMID: 6584494.
Article18. Malamed SF. The periodontal ligament (PDL) injection: an alternative to inferior alveolar nerve block. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1982; 53:117–121. PMID: 6949113.
Article19. Davidson L, Craig S. The use of the periodontal ligament injection in children. J Dent. 1987; 15:204–208. PMID: 3479463.
Article20. Krochak M, Friedman N. Using a precision-metered injection system to minimize dental injection anxiety. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 1998; 19:137–140. 142–143. 146PMID: 9656861.21. Saxena P, Gupta SK, Newaskar V, Chandra A. Advances in dental local anesthesia techniques and devices: An update. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2013; 4:19–24. PMID: 24163548.
Article22. Thoppe-Dhamodhara YK, Asokan S, John BJ, Pollachi-Ramakrishnan G, Ramachandran P, Vilvanathan P. Cartridge syringe vs computer controlled local anesthetic delivery system: Pain related behaviour over two sequential visits–a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Exp Dent. 2015; 7:e513–e518. PMID: 26535099.23. Garret-Bernardin A, Cantile T, D'Antò V, Galanakis A, Fauxpoint G, Ferrazzano GF, et al. Pain Experience and Behavior Management in Pediatric Dentistry: A Comparison between Traditional Local Anesthesia and the Wand Computerized Delivery System. Pain Res Manag. 2017; 2017:7941238. PMID: 28293129.
Article24. Brännström M, Nordenvall K, Hedström K. Periodontal tissue changes after intraligamentary anesthesia. ASDC J Dent Child. 1982; 49:417. PMID: 6960028.25. Ashkenazi M, Blumer S, Eli I. Effect of computerized delivery intraligamental injection in primary molars on their corresponding permanent tooth buds. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2010; 20:270–275. PMID: 20536588.
Article26. Nusstein JM, Reader A, Drum M. Local anesthesia strategies for the patient with a “hot” tooth. Dent Clin. 2010; 54:237–247.
Article27. Shabazfar N, Daubländer M, Al-Nawas B, Kämmerer P. Periodontal intraligament injection as alternative to inferior alveolar nerve block—meta-analysis of the literature from 1979 to 2012. Clin Oral Investig. 2014; 18:351–358.
Article28. Allard G, Stokes T. Continuous observation: a detailed record of children's behavior during dental treatment. ASDC J Dent Child. 1980; 47:246. PMID: 6938534.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Low-flow anesthesia in children: theory and clinical practice
- What is your optimal target of oxygen during general anesthesia in pediatric patients?
- Who are at high risk of mortality and morbidity among children with congenital heart disease undergoing noncardiac surgery?
- Sugammadex for our little ones: a brief narrative review
- Home mechanical ventilation in children with chronic respiratory failure: a narrative review