J Vet Sci.
2018 Jul;19(4):483-491. 10.4142/jvs.2018.19.4.483.
Comparison of electrophysiological properties of two types of pre-sympathetic neurons intermingled in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Pharmacology, College of Veterinary Medicine and Research Institute of Veterinary Science, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea. pdryu@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Oral Physiology, School of Dentistry and Institute of Oral Bioscience, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju 54896, Korea.
- KMID: 2417562
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2018.19.4.483
Abstract
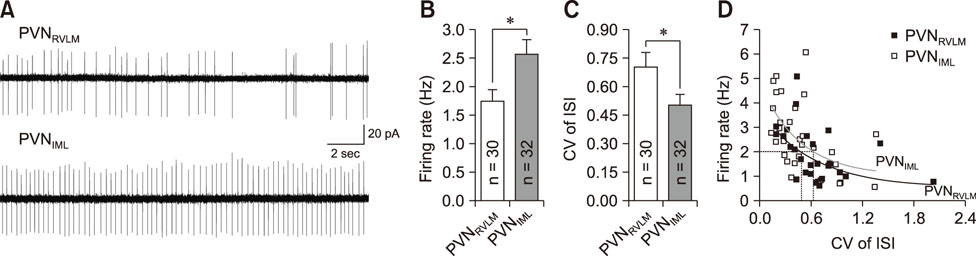
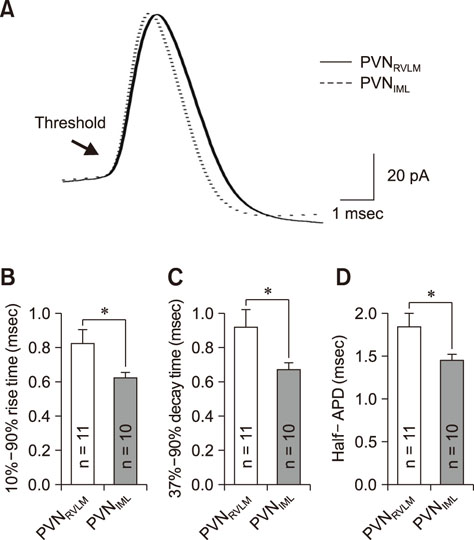
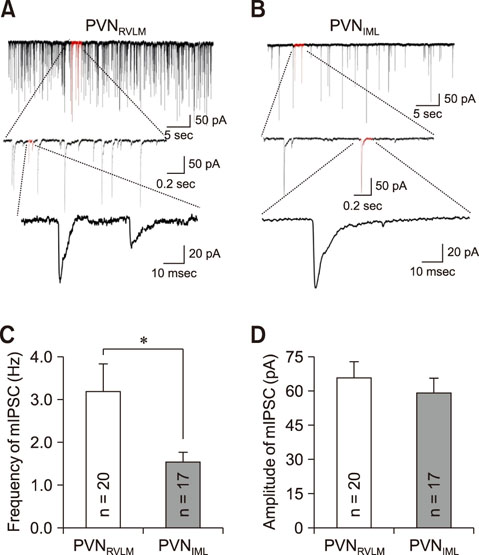
- The hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) contains two types of neurons projecting to either the rostral ventrolateral medulla (PVN(RVLM)) or the intermediolateral horn (IML) of the spinal cord (PVN(IML)). These two neuron groups are intermingled in the same subdivisions of the PVN and differentially regulate sympathetic outflow. However, electrophysiological evidence supporting such functional differences is largely lacking. Herein, we compared the electrophysiological properties of these neurons by using patch-clamp and retrograde-tracing techniques. Most neurons (>70%) in both groups spontaneously fired in the cell-attached mode. When compared to the PVN(IML) neurons, the PVN(RVLM) neurons had a lower firing rate and a more irregular firing pattern (p < 0.05). The PVN(RVLM) neurons showed smaller resting membrane potential, slower rise and decay times, and greater duration of spontaneous action potentials (p < 0.05). The PVN(RVLM) neurons received greater inhibitory synaptic inputs (frequency, p < 0.05) with a shorter rise time (p < 0.05). Taken together, the results indicate that the two pre-sympathetic neurons differ in their intrinsic and extrinsic electrophysiological properties, which may explain the lower firing activity of the PVN(RVLM) neurons. The greater inhibitory synaptic inputs to the PVN(RVLM) neurons also imply that these neurons have more integrative roles in regulation of sympathetic activity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Abbott LF, Fusi S, Miller KD. Theoretical approaches to neuroscience: examples from single neurons to networks. In : Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S, editors. Principles of Neural Science. 5th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional Publishing;2012. p. 1601–1617.2. Badoer E. Hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus and cardiovascular regulation. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2001; 28:95–99.
Article3. Berkefeld H, Fakler B. Repolarizing responses of BKCa-Cav complexes are distinctly shaped by their Cav subunits. J Neurosci. 2008; 28:8238–8245.
Article4. Brown CH, Bains JS, Ludwig M, Stern JE. Physiological regulation of magnocellular neurosecretory cell activity: integration of intrinsic, local and afferent mechanisms. J Neuroendocrinol. 2013; 25:678–710.
Article5. Carrive P, Gorissen M. Premotor sympathetic neurons of conditioned fear in the rat. Eur J Neurosci. 2008; 28:428–446.
Article6. Cechetto DF, Saper CB. Neurochemical organization of the hypothalamic projection to the spinal cord in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1988; 272:579–604.
Article7. Cham JL, Badoer E. Exposure to a hot environment can activate rostral ventrolateral medulla-projecting neurones in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in conscious rats. Exp Physiol. 2008; 93:64–74.
Article8. Cham JL, Klein R, Owens NC, Mathai M, McKinley M, Badoer E. Activation of spinally projecting and nitrergic neurons in the PVN following heat exposure. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006; 291:R91–R101.
Article9. Chen QH, Toney GM. Identification and characterization of two functionally distinct groups of spinal cord-projecting paraventricular nucleus neurons with sympathetic-related activity. Neuroscience. 2003; 118:797–807.
Article10. Coote JH. A role for the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in the autonomic control of heart and kidney. Exp Physiol. 2005; 90:169–173.
Article11. Cullinan WE, Ziegler DR, Herman JP. Functional role of local GABAergic influences on the HPA axis. Brain Struct Funct. 2008; 213:63–72.
Article12. Engelmann M, Landgraf R, Wotjak CT. The hypothalamic-neurohypophysial system regulates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis under stress: an old concept revisited. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2004; 25:132–149.
Article13. Erisir A, Lau D, Rudy B, Leonard CS. Function of specific K+ channels in sustained high-frequency firing of fast-spiking neocortical interneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1999; 82:2476–2489.
Article14. Farrant M, Nusser Z. Variations on an inhibitory theme: phasic and tonic activation of GABAA receptors. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005; 6:215–229.
Article15. Hallbeck M, Larhammar D, Blomqvist A. Neuropeptide expression in rat paraventricular hypothalamic neurons that project to the spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 2001; 433:222–238.
Article16. Hammond C. The voltage-gated channels of Na+ action potentials: generalization. In : Hammond C, editor. Cellular and Molecular Neurophysiology. 3rd ed. San Diego: Academic Press;2008. p. 45–82.17. Han SK, Chong W, Li LH, Lee IS, Murase K, Ryu PD. Noradrenaline excites and inhibits GABAergic transmission in parvocellular neurons of rat hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. J Neurophysiol. 2002; 87:2287–2296.
Article18. Han TH, Lee K, Park JB, Ahn D, Park JH, Kim DY, Stern JE, Lee SY, Ryu PD. Reduction in synaptic GABA release contributes to target-selective elevation of PVN neuronal activity in rats with myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010; 299:R129–R139.
Article19. Hodgkin AL, Huxley AF. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952; 117:500–544.
Article20. Jansen AS, Wessendorf MW, Loewy AD. Transneuronal labeling of CNS neuropeptide and monoamine neurons after pseudorabies virus injections into the stellate ganglion. Brain Res. 1995; 683:1–24.
Article21. Kole MH, Ilschner SU, Kampa BM, Williams SR, Ruben PC, Stuart GJ. Action potential generation requires a high sodium channel density in the axon initial segment. Nat Neurosci. 2008; 11:178–186.
Article22. Luther JA, Tasker JG. Voltage-gated currents distinguish parvocellular from magnocellular neurones in the rat hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. J Physiol. 2000; 523:193–209.
Article23. Palkovits M. Interconnections between the neuroendocrine hypothalamus and the central autonomic system: Geoffrey Harris Memorial Lecture, Kitakyushu, Japan, October 1998. Front Neuroendocrinol. 1999; 20:270–295.
Article24. Pandit S, Jo JY, Lee SU, Lee YJ, Lee SY, Ryu PD, Lee JU, Kim HW, Jeon BH, Park JB. Enhanced astroglial GABA uptake attenuates tonic GABAA inhibition of the presympathetic hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus neurons in heart failure. J Neurophysiol. 2015; 114:914–926.
Article25. Paxinos G, Watson C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. 2nd ed. San Diego: Academic Press;1986.26. Pyner S, Coote JH. Identification of branching paraventricular neurons of the hypothalamus that project to the rostroventrolateral medulla and spinal cord. Neuroscience. 2000; 100:549–556.
Article27. Rehak R, Bartoletti TM, Engbers JD, Berecki G, Turner RW, Zamponi GW. Low voltage activation of KCa1.1 current by Cav3-KCa1.1 complexes. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e61844.
Article28. Renaud LP, Bourque CW. Neurophysiology and neuropharmacology of hypothalamic magnocellular neurons secreting vasopressin and oxytocin. Prog Neurobiol. 1991; 36:131–169.
Article29. Salin PA, Prince DA. Spontaneous GABAA receptor-mediated inhibitory currents in adult rat somatosensory cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1996; 75:1573–1588.
Article30. Saper CB. Central autonomic system. In : Paxinos G, editor. The Rat Nervous System. 3rd ed. San Diego: Elsevier;2004. p. 761–796.31. Sawchenko PE, Brown ER, Chan RK, Ericsson A, Li HY, Roland BL, Kovács KJ. The paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and the functional neuroanatomy of visceromotor responses to stress. Prog Brain Res. 1996; 107:201–222.32. Sawchenko PE, Li HY, Ericsson A. Circuits and mechanisms governing hypothalamic responses to stress: a tale of two paradigms. Prog Brain Res. 2000; 122:61–78.
Article33. Schofield PR, Darlison MG, Fujita N, Burt DR, Stephenson FA, Rodriguez H, Rhee LM, Ramachandran J, Reale V, Glencorse TA, Seeburg PH, Barnard EA. Sequence and functional expression of the GABAA receptor shows a ligand-gated receptor super-family. Nature. 1987; 328:221–227.
Article34. Stern JE. Electrophysiological and morphological properties of pre-autonomic neurones in the rat hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. J Physiol. 2001; 537:161–177.
Article35. Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE. Hypothalamic integration: organization of the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1983; 6:269–324.
Article36. Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE. Paraventricular nucleus: a site for the integration of neuroendocrine and autonomic mechanisms. Neuroendocrinology. 1980; 31:410–417.
Article37. Wu X, Wu Z, Ning G, Guo Y, Ali R, Macdonald RL, De Blas AL, Luscher B, Chen G. γ-Aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor α subunits play a direct role in synaptic versus extrasynaptic targeting. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287:27417–27430.
Article38. Xu B, Zheng H, Patel KP. Enhanced activation of RVLM-projecting PVN neurons in rats with chronic heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012; 302:H1700–H1711.
Article39. Zhou FW, Roper SN. Altered firing rates and patterns in interneurons in experimental cortical dysplasia. Cereb Cortex. 2011; 21:1645–1658.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dopaminergic Neurons in the Diencephalon of Striped Field Mouse[Apodemus agrarius coreae]
- Effect of Chronic Alcohol Intake on Vasopressin and Oxytocin-containing Neurons in the Paraventricular and Supraoptic Nucleus of the Rat Hypothalamus
- Organotypic slice culture of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of rat
- Coexistence of Tyrosine Hydroxylase and Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate-Diaphorase in Hypothalamic Neurons of the Rat
- Immunohistochemical Localization of Brain Natriuretic Peptide in the Hypothalamus of the Rat