Korean J Gastroenterol.
2018 Jul;72(1):1-5. 10.4166/kjg.2018.72.1.1.
Esophageal Foreign Body: Treatment and Complications
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. kimhup@jejunu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2416928
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2018.72.1.1
Abstract
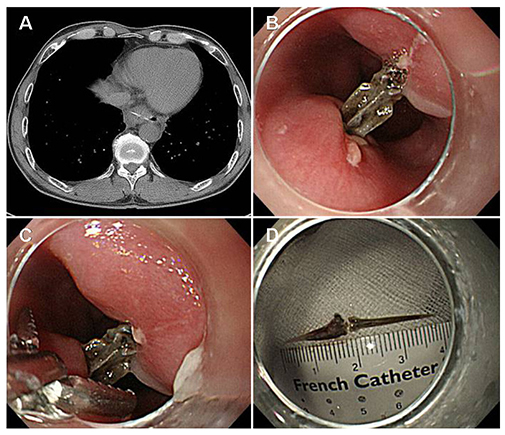
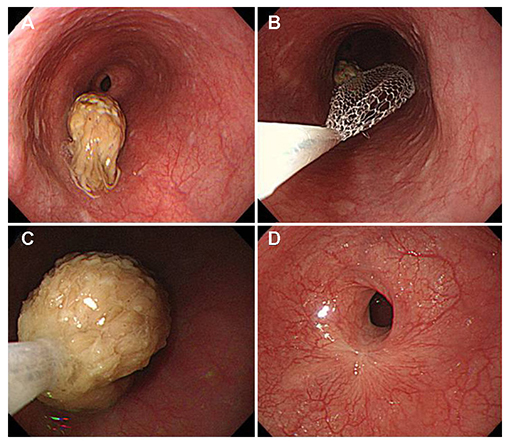
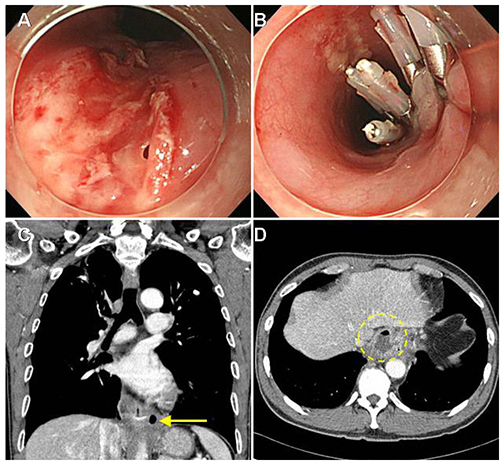
- The most common cause of esophageal foreign bodies in adults is meat in Western countries and fish bones in Asian countries, including Korea. Although most ingested foreign bodies pass spontaneously through the esophagus without any clinical sequelae, some sharp foreign bodies, such as fish bones embedded in the esophagus, require treatment. Endoscopic management is the first choice in the treatment of esophageal foreign bodies because it is quite safe and effective. Major complications occur as a result of esophageal perforation; in particular, sharp foreign bodies, such as fish bones, are more likely to cause perforation. Complications include mediastinitis, paraesophageal abscess, pneumomediastinum, subcutaneous emphysema, pneumothorax, tracheoesophagal fistula, aortoesophageal fistula, aspiration, and asphyxia. Unnecessary delays should be avoided in endoscopic intervention for esophageal foreign bodies to prevent complications.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Eisen GM, Baron TH, Dominitz JA, et al. Guideline for the management of ingested foreign bodies. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:802–806.
Article2. Athanassiadi K, Gerazounis M, Metaxas E, Kalantzi N. Management of esophageal foreign bodies: a retrospective review of 400 cases. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2002; 21:653–656.3. Sugawa C, Ono H, Taleb M, Lucas CE. Endoscopic management of foreign bodies in the upper gastrointestinal tract: a review. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 6:475–481.
Article4. Li ZS, Sun ZX, Zou DW, Xu GM, Wu RP, Liao Z. Endoscopic management of foreign bodies in the upper-GI tract: experience with 1088 cases in China. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 64:485–492.
Article5. Desai TK, Stecevic V, Chang CH, Goldstein NS, Badizadegan K, Furuta GT. Association of eosinophilic inflammation with esophageal food impaction in adults. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 61:795–801.
Article6. Blaho KE, Merigian KS, Winbery SL, Park LJ, Cockrell M. Foreign body ingestions in the emergency department: case reports and review of treatment. J Emerg Med. 1998; 16:21–26.
Article7. Park JH, Park CH, Park JH, et al. Review of 209 cases of foreign bodies in the upper gastrointestinal tract and clinical factors for successful endoscopic removal. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2004; 43:226–233.8. Kim HU. Oroesophageal fish bone foreign body. Clin Endosc. 2016; 49:318–326.
Article9. Kim JE, Ryoo SM, Kim YJ, et al. Incidence and clinical features of esophageal perforation caused by ingested foreign body. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2015; 66:255–260.
Article10. Bekkerman M, Sachdev AH, Andrade J, Twersky Y, Iqbal S. Endoscopic management of foreign bodies in the gastrointestinal tract: a review of the literature. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2016; 2016:8520767.
Article11. Dong A, Zhang L, Wang Y, Zuo C. Chronic esophageal perforation with periesophageal abscess mimicking malignancy on FDG PET/CT. Clin Nucl Med. 2016; 41:494–496.
Article12. Ginsberg GG. Management of ingested foreign objects and food bolus impactions. Gastrointest Endosc. 1995; 41:33–38.
Article13. ASGE Standards of Practice Committee. Ikenberry SO, Jue TL, et al. Management of ingested foreign bodies and food impactions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73:1085–1091.14. Lin AY, Tillman BN, Thatcher AL, Graves CR, Prince ME. Comparison of outcomes in medical therapy vs surgical intervention of esophageal foreign bodies. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018; 06. 05. [Epub ahead of print].
Article15. Faigel DO, Stotland BR, Kochman ML, et al. Device choice and experience level in endoscopic foreign object retrieval: an in vivo study. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997; 45:490–492.
Article16. Nelson DB, Bosco JJ, Curtis WD, et al. ASGE technology status evaluation report. Endoscopic retrieval devices. February 1999. American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999; 50:932–934.17. Vicari JJ, Johanson JF, Frakes JT. Outcomes of acute esophageal food impaction: success of the push technique. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 53:178–181.
Article18. Longstreth GF, Longstreth KJ, Yao JF. Esophageal food impaction: epidemiology and therapy. A retrospective, observational study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 53:193–198.
Article19. Ko HH, Enns R. Review of food bolus management. Can J Gastroenterol. 2008; 22:805–808.
Article20. Gordon AC, Gough MH. Oesophageal perforation after button battery ingestion. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1993; 75:362–364.21. Loh KS, Tan LK, Smith JD, Yeoh KH, Dong F. Complications of foreign bodies in the esophagus. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000; 123:613–616.
Article22. Singh B, Kantu M, Har-El G, Lucente FE. Complications associated with 327 foreign bodies of the pharynx, larynx, and esophagus. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1997; 106:301–304.
Article23. van Heel NC, Haringsma J, Spaander MC, Bruno MJ, Kuipers EJ. Short-term esophageal stenting in the management of benign perforations. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010; 105:1515–1520.
Article24. Mantzoukis K, Papadimitriou K, Kouvelis I, et al. Endoscopic closure of an iatrogenic rupture of upper esophagus (Lannier's triangle) with the use of endoclips - case report and review of the literature. Ann Gastroenterol. 2011; 24:55–58.25. Qadeer MA, Dumot JA, Vargo JJ, Lopez AR, Rice TW. Endoscopic clips for closing esophageal perforations: case report and pooled analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:605–611.
Article26. Li N, Manetta F, Iqbal S. Endoscopic management for delayed diagnosis of a foreign body penetrating the esophagus into the lung. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:221–222.
Article27. Vanbiervliet G, Filippi J, Karimdjee BS, et al. The role of clips in preventing migration of fully covered metallic esophageal stents: a pilot comparative study. Surg Endosc. 2012; 26:53–59.
Article28. Vallböhmer D, Holscher AH, Hölscher M, et al. Options in the management of esophageal perforation: analysis over a 12-year period. Dis Esophagus. 2010; 23:185–190.
Article29. Shimizu T, Marusawa H, Yamashita Y. Pneumothorax following esophageal perforation due to ingested fish bone. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 8:A24.
Article30. Sia KJ, Ashok GD, Ahmad FM, Kong CK. Aorto-oesophageal fistula and aortic pseudoaneurysm caused by a swallowed fish bone. Hong Kong Med J. 2013; 19:542–544.
Article31. Mukhopadhyay B, Tripathy BB, Saha S, Shukla RM, Saha SR. Acquired tracheo-oesophageal fistula: a case report. J Indian Med Assoc. 2008; 106:806. 808.32. Macchi V, Porzionato A, Bardini R, Parenti A, De Caro R. Rupture of ascending aorta secondary to esophageal perforation by fish bone. J Forensic Sci. 2008; 53:1181–1184.
Article33. Kelly SL, Peters P, Ogg MJ, Li A, Smithers BM. Successful management of an aortoesophageal fistula caused by a fish bone--case report and review of literature. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009; 4:21.
Article34. Nazir Z, Khan MAM, Qamar J. Recurrent and acquired tracheoesophageal fistulae (TEF)-minimally invasive management. J Pediatr Surg. 2017; 52:1688–1690.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Removal of an Impacted Fishhook That Was in the Esophagus for Two Months
- Risk factors predicting development of complications in 72 dogs with esophageal foreign bodies
- Esophageal Perforation with Delayed Detection of a Foreign Body: A Case Report
- Endoscopic Removal of Esophageal Foreign Body Complicated with Esophageal Ulcer: Case report
- Choking by Esophageal Foreign Body Impaction