J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2005 Sep;30(5):385-392.
The effect of canal filling with gutta-percha or resilon on Enterococcus faecalis in bovine dentinal tubules
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, Yonsei University, Korea. andyendo@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Oral Biology, College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Korea.
Abstract
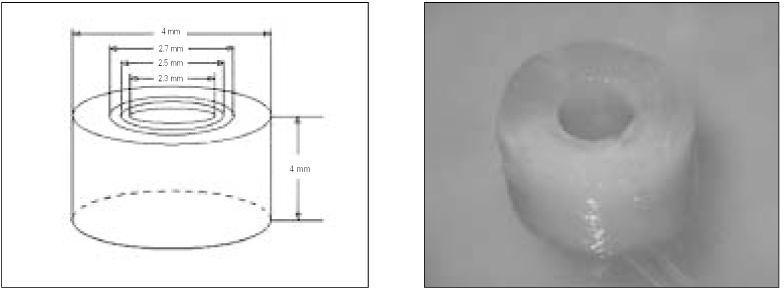
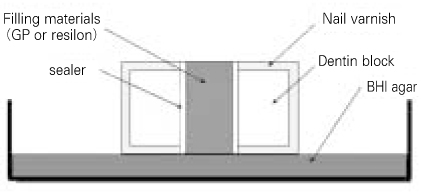
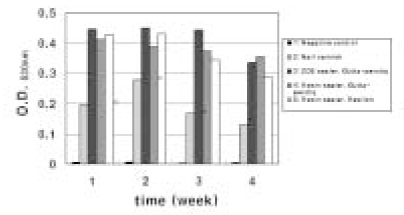
- The purpose of this study was to observe the effect of canal filling on the bacteria left in the dentinal tubules and to compare the sealing ability between Gutta-percha and Resilon. The bovine dentin block models were prepared. E. faecalis was inoculated to dentin blocks and incubated. The dentin blocks were divided into 5 groups. Group 1 was the negative control. Group 2 was the positive control. Group 3 was filled with ZOE based sealer and Gutta-percha, Group 4 with resin based sealer and Gutta-percha, and Group 5 with resin based sealer and Resilon. After 24 hour, the blocks were incubated at 37degrees C for 1, 2, 3 and 4 weeks on BHI agar plates. The internal dentin portion of the blocks was removed using ISO 027, 029, 031, 035 round burs and the dentin chips were incubated at 37degrees C for 24 hour. Following incubation, the optical density of the medium was measured. The data were statistically analysed using repeated measures ANOVA and one-way ANOVA. The results were as follows, 1. There was statistically significant reduction in the number of E. faecalis of the group where dentinal tubules were completely sealed with nail varnish in comparison with the groups obturated with gutta-percha or resilon (p < 0.05). 2. In group 5, the number of E. faecalis in the dentinal tubules decreased significantly with time (p < 0.05), whereas in Group 3 and 4, there was no reduction in its number (p > 0.05). 3. Under the conditions of this experiment, E. faecalis survived up to 4 weeks after obturation with gutta-percha or resilon (p > 0.05).
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kakehashi S, Stanley HR, Fitzgerald RJ. The effects of surgical exposures of dental pulps in germ-free and conventional laboratory rats. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1965. 20:340–349.
Article2. Möller AJ, Fabricius L, Dahlen G, Ohman AE, Heyden G. Influence on periapical tissues of indigenous oral bacteria and necrotic pulp tissue in monkeys. Scand J Dent Res. 1981. 89:475–484.
Article3. Sundqvist G. Bacteriological studies of nectrotic dental pulps. Umea Univ Odontol Diss. 1976. 7:1–94. Thesis. Ref Type: Generic.4. Byström A, Sundqvist G. Bacteriologic evaluation of the efficacy of mechanical root canal instrumentation in endodontic therapy. Scand J Dent Res. 1981. 89:321–328.
Article5. Abou-Rass M, Piccinino MV. The effectiveness of four clinical irrigation methods on the removal of root canal debris. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1982. 54:323–328.
Article6. Byström A, Claesson R, Sundqvist G. The antibacterial effect of camphorated paramonochlorophenol, camphorated phenol and calcium hydroxide in the treatment of infectedroot canals. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1985. 1:170–175.7. Sjögren U, Figdor D, Spangberg L, Sundqvist G. The antimicrobial effect of calcium hydroxide as a short-term intracanal dressing. Int Endod J. 1991. 24:119–125.
Article8. Chong BS, Pitt Ford TR. The role of intracanal medication in root canal treatment. Int Endod J. 1992. 25:97–106.
Article9. Walton RE, Torabinejad M. Principles and Practice of Endodontics. 2002. 3rd ed. W.B. Saunders company;232–234.10. Peters LB, van Winkelhoff AJ, Buijs JF, Wesselink PR. Effects of instrumentation, irrigation and dressing with calcium hydroxide on infection in pulpless teeth with periapical bone lesions. Int Endod J. 2002. 35:13–21.
Article11. Haapasalo HK, Siren EK, Waltimo TM, Orstavik D, Haapasalo MP. Inactivation of local root canal medicaments by dentine: an in vitro study. Int Endod J. 2000. 33:126–131.
Article12. Portenier I, Haapasalo H, Rye A, Waltimo T, Orstavik D, Haapasalo M. Inactivation of root canal medicaments by dentine, hydroxylapatite and bovine serum albumin. Int Endod J. 2001. 34:184–188.
Article13. Ørstavik D, Haapasalo M. Disinfection by endodontic irrigants and dressings of experimentally infected dentinal tubules. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1990. 6:142–149.
Article14. Estrela C, Pimenta FC, Ito IY, Bammann LL. Antimicrobial evaluation of calcium hydroxide in infected dentinal tubules. J Endod. 1999. 25:416–418.
Article15. Molander A, Reit C, Dahlen G, Kvist T. Microbiological status of root-filled teeth with apical periodontitis. Int Endod J. 1998. 31:1–7.
Article16. Sundqvist G, Figdor D. Microbiological analysis of teeth with failed endodontic treatment and the outcome of conservative retreatment. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998. 85:86–93.
Article17. Evans M, Davies JK, Sundqvist G, Figdor D. Mechanisms involved in the resistance of Enterococcus faecalis to calcium hydroxide. Int Endod J. 2002. 35:221–228.
Article18. Kim SK, Kim YO. Influence of calcium hydroxide intracanal medication on apical seal. Int Endod J. 2002. 35:623–628.
Article19. Soltanoff W. A comparative study of the single-visit and the multiple-visit edodontic procedure. J Endod. 1978. 4:278–281.
Article20. Oliet S. Single-visit endodontics: a clinical study. J Endod. 1983. 9:147–152.
Article21. Peters LB, Wesselink PR. Periapical healing of endodontically treated teeth in one and two visits obturated in the presence or absence of detectable microorganisms. Int Endod J. 2002. 35:660–667.
Article22. Moorer WR, Genet JM. Evidence for antibacterial activity of endodontic gutta-percha cones. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1982. 53:503–507.
Article23. Heling I, Chandler NP. The antimicrobial effect within dentinal tubules of four root canal sealers. J Endod. 1996. 22:257–259.
Article24. Kaplan AE, Picca M, Gonzalez MI, Macchi RL, Molgatini SL. Antimicrobial effect of six endodontic sealers: an in vitro evaluation. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1999. 15:42–45.25. Fuss Z, Charniaque O, Pilo R, Weiss E. Effect of various mixing ratios on antibacterial properties and hardness of endodontic sealers. J Endod. 2000. 26:519–522.
Article26. Siqueira JF Jr, Favieri A, Gahyva SM, Moraes SR, Lima KC, Lopes HP. Antimicrobial activity and flow rate of newer and established root canal sealers. J Endod. 2000. 26:274–277.
Article27. Saleh IM, Ruyter IE, Haapasalo M, Orstavik D. Survival of Enterococcus faecalis in infected dentinal tubules after root canal filling with different root canal sealers in vitro. Int Endod J. 2004. 37:193–198.
Article28. Peters LB, Wesselink PR, Moorer WR. The fate and the role of bacteria left in root dentinal tubules. Int Endod J. 1995. 28:95–99.
Article29. Weiger R, Rosendahl R, Lost C. Influence of calcium hydroxide intracanal dressings on the prognosis of teeth with endodontically induced periapical lesions. Int Endod J. 2000. 33:219–226.
Article30. Swanson K, Madison S. An evaluation of coronal microleakage in endodontically treated teeth. Part I. Time periods. J Endod. 1987. 13:56–59.
Article31. Torabinejad M, Ung B, Kettering JD. In vitro bacterial penetration of coronally unsealed endodontically treated teeth. J Endod. 1990. 16:566–569.
Article32. Khayat A, Lee SJ, Torabinejad M. Human saliva penetration of coronally unsealed obturated root canals. J Endod. 1993. 19:458–461.
Article33. Magura ME, Kafrawy AH, Brown CE Jr, Newton CW. Human saliva coronal microleakage in obturated root canals: an in vitro study. J Endod. 1991. 17:324–331.
Article34. Gish SP, Drake DR, Walton RE, Wilcox L. bacterial penetration through obturated canals following post preparation. J Am Dent Assoc. 1994. 125:1369–1372.
Article35. Ingle JI. Endodontics. 2002. 4th ed. Hamilton: BC Decker Inc;752–753.36. Tidmarsh BG. Acid-cleansed and resin-sealed root canals. J Endod. 1978. 4:117–121.
Article37. Leonard JE, Gutmann JL, Guo IY. Apical and coronal seal of roots obturated with a dentine bonding agent and resin. Int Endod J. 1996. 29:76–83.
Article38. Mannocci F, Ferrari M. Apical seal of roots obturated with laterally condensed gutta-percha, epoxy resin cement, and dentin bonding agent. J Endod. 1998. 24:41–44.
Article39. Mounce R, Glassman G. Bonded endodontic obturation: Another quantum leap forward for endodontics. Oral Health. 2004. 94(6):13–22.40. Shipper G, Orstavik D, Teixeira FB, Trope M. An evaluation of microbial leakage in roots filled with a thermoplastic synthetic polymer-based root canal filling material (Resilon). J Endod. 2004. 30:342–347.
Article41. Teixeira FB, Teixeira EC, Thompson JY, Trope M. Fracture resistance of roots endodontically treated with a new resin filling material. J Am Dent Assoc. 2004. 135:646–652.
Article42. Hata G, Kawazoe S, Toda T, Weine FS. Sealing ability of Thermafil with and without sealer. J Endod. 1992. 18:322–326.
Article43. Orstavik D. Weight loss of endodontic sealers, cements and pastes in water. Scand J Dent Res. 1983. 91:316–319.
Article44. Peters DD. Two-year in vitro solubility evaluation of four Gutta-percha sealer obturation techniques. J Endod. 1986. 12:139–145.
Article45. Tronstad L, Barnett F, Flax M. Solubility and biocompatibility of calcium hydroxide-containing root canal sealers. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1988. 4:152–159.
Article46. Kontakiotis EG, Wu MK, Wesselink PR. Effect of sealer thickness on long-term sealing ability: a 2-year follow-up study. Int Endod J. 1997. 30:307–312.
Article47. Wu MK, Ozok AR, Wesselink PR. Sealer distribution in root canals obturated by three techniques. Int Endod J. 2000. 33:340–345.
Article48. Nair PN, Sjogren U, Krey G, Kahnberg KE, Sundqvist G. Intraradicular bacteria and fungi in root-filled, asymptomatic human teeth with therapy-resistant periapical lesions: a long-term light and electron microscopic follow-up study. J Endod. 1990. 16:580–588.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Measurement of thermal expansion characteristic of root canal filling materials: Gutta-percha and Resilon
- Effect of irrigation methods on the adhesion of Resilon/Epiphany sealer and gutta-percha/AH 26 sealer to intracanal dentin
- Evaluation of retrievability using a new soft resin based root canal filling material
- Microorganism penetration in dentinal tubules of instrumented and retreated root canal walls. In vitro SEM study
- Rheological characterization of thermoplasticized injectable gutta percha and resilon