J Korean Soc Radiol.
2018 Aug;79(2):106-109. 10.3348/jksr.2018.79.2.106.
An Unusual Cause of Knee Pain: Periosteal Glomus Tumor of the Distal Femur
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. glassesik@gmail.com
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2416397
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2018.79.2.106
Abstract
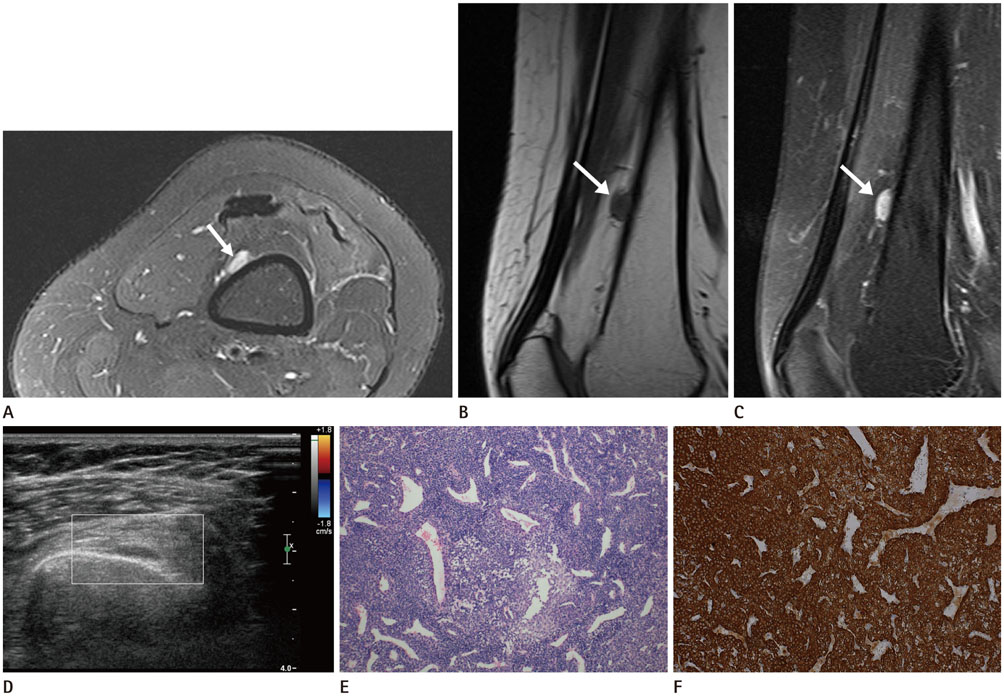
- Glomus tumors are rare neoplasms that characteristically occur in subungual regions, but may also be found in other regions of the body. The clinical diagnosis of this tumor may be difficult if the tumor is located in an extradigital site. Most extradigital glomus tumors form in superficial locations. Herein, we present the case of a 34-year-old woman who experienced chronic knee pain with pinpoint tenderness resulting from a deep-seated periosteal glomus tumor of the distal femur. Extradigital glomus tumors should be considered in the differential diagnosis when characteristic clinical features and imaging findings indicative of glomus tumors are present, even if the tumor is located within deep tissues.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gombos Z, Zhang PJ. Glomus tumor. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008; 132:1448–1452.
Article2. Soule EH, Ghormley RK, Bulbulian AH. Scientific exhibits: primary tumors of the soft tissues of the extremities exclusive of epithelial tumors; an analysis of five hundred consecutive cases. AMA Arch Surg. 1955; 70:462–474.3. Mravic M, LaChaud G, Nguyen A, Scott MA, Dry SM, James AW. Clinical and histopathological diagnosis of glomus tumor: an institutional experience of 138 cases. Int J Surg Pathol. 2015; 23:181–188.4. Schiefer TK, Parker WL, Anakwenze OA, Amadio PC, Inwards CY, Spinner RJ. Extradigital glomus tumors: a 20-year experience. Mayo Clin Proc. 2006; 81:1337–1344.
Article5. Proietti A, Alì G, Quilici F, Bertoglio P, Mussi A, Fontanini G. Glomus tumor of the shoulder: a case report and review of the literature. Oncol Lett. 2013; 6:1021–1024.
Article6. Lee TS, Wu HT, Chan RC, Wang JC. Sonographic diagnosis of a glomus tumor of the thigh. J Clin Ultrasound. 2017; 45:50–52.
Article7. González-Llanos F, López-Barea F, Isla A, Fernández-Prieto A, Zubillaga A, Alvarez F. Periosteal glomus tumor of the femur: a case report. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000; (380):199–203.8. Perks FJ, Beggs I, Lawson GM, Davie R. Juxtacortical glomus tumor of the distal femur adjacent to the popliteal fossa. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 181:1590–1592.
Article9. Hermann G, Klein MJ, Springfield D, Abdelwahab IF, Hoch BL. Glomus tumor of the thigh: confluent with the periosteum of the femur. Skeletal Radiol. 2005; 34:116–120.
Article10. Glazebrook KN, Laundre BJ, Schiefer TK, Inwards CY. Imaging features of glomus tumors. Skeletal Radiol. 2011; 40:855–862.
Article