Tuberc Respir Dis.
2018 Jul;81(3):167-174. 10.4046/trd.2017.0089.
Efficacy and Safety of Gabapentin in the Treatment of Chronic Cough: A Systematic Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Respiratory Medicine, Nantong Pulmonary Hospital (The Sixth People's Hospital of Nantong), Nantong, China. zhaohuan0525@126.com
- 2Medical School of Nantong University, Nantong, China.
- KMID: 2414559
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2017.0089
Abstract
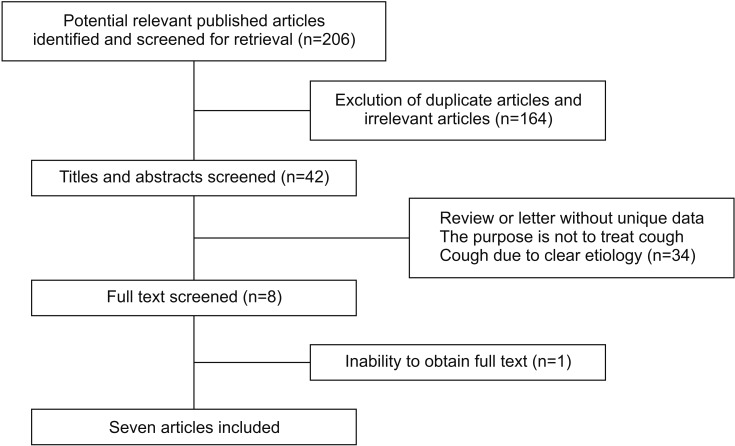
- Despite recent clinical guidelines, the optimal therapeutic strategy for the management of refractory chronic cough is still a challenge. The present systematic review was designed to assess the evidence for efficacy and safety of gabapentin in the treatment of chronic cough. A systematic search of PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library databases, and publications cited in bibliographies was performed. Articles were searched by two reviewers with a priori criteria for study selection. Seven relevant articles were identified, including two randomized controlled trials, one prospective case-series designed with consecutive patients, one retrospective case series of consecutive patients, one retrospective case series with unknown consecutive status, and two case reports comprising six and two patients, respectively. Improvements were detected in cough-specific quality of life (Leicester Cough Questionnaire score) and cough severity (visual analogue scale score) following gabapentin treatment in randomized controlled trials. The results of prospective case-series showed that the rate of overall improvement of cough and sensory neuropathy with gabapentin was 68%. Gabapentin treatment of patients with chronic cough showed superior efficacy and a good safety record compared with placebo or standard medications. Additional randomized and controlled trials are needed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gibson PG, Ryan NM. Cough pharmacotherapy: current and future status. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011; 12:1745–1755. PMID: 21524236.
Article2. Birring SS, Prudon B, Carr AJ, Singh SJ, Morgan MD, Pavord ID. Development of a symptom specific health status measure for patients with chronic cough: Leicester Cough Questionnaire (LCQ). Thorax. 2003; 58:339–343. PMID: 12668799.
Article3. Chung KF, Pavord ID. Prevalence, pathogenesis, and causes of chronic cough. Lancet. 2008; 371:1364–1374. PMID: 18424325.
Article4. Birring SS. Controversies in the evaluation and management of chronic cough. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011; 183:708–715. PMID: 21148722.
Article5. Pratter MR. Unexplained (idiopathic) cough: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2006; 129(1 Suppl):220S–221S. PMID: 16428714.6. Ryan NM, Gibson PG, Birring SS. Arnold's nerve cough reflex: evidence for chronic cough as a sensory vagal neuropathy. J Thorac Dis. 2014; 6(Suppl 7):S748–S752. PMID: 25383210.7. Canning BJ, Chang AB, Bolser DC, Smith JA, Mazzone SB, McGarvey L, et al. Anatomy and neurophysiology of cough: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel report. Chest. 2014; 146:1633–1648. PMID: 25188530.8. Haque RA, Usmani OS, Barnes PJ. Chronic idiopathic cough: a discrete clinical entity? Chest. 2005; 127:1710–1713. PMID: 15888850.9. Chung KF. Chronic ‘cough hypersensitivity syndrome’: a more precise label for chronic cough. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 24:267–271. PMID: 21292019.
Article10. Bastian RW, Vaidya AM, Delsupehe KG. Sensory neuropathic cough: a common and treatable cause of chronic cough. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006; 135:17–21. PMID: 16815176.
Article11. Chung KF, McGarvey L, Mazzone SB. Chronic cough as a neuropathic disorder. Lancet Respir Med. 2013; 1:414–422. PMID: 24429206.
Article12. Cohen SM, Misono S. Use of specific neuromodulators in the treatment of chronic, idiopathic cough: a systematic review. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013; 148:374–382. PMID: 23300226.13. Cukier-Blaj S, Bewley A, Aviv JE, Murry T. Paradoxical vocal fold motion: a sensory-motor laryngeal disorder. Laryngoscope. 2008; 118:367–370. PMID: 18000464.
Article14. Lee B, Woo P. Chronic cough as a sign of laryngeal sensory neuropathy: diagnosis and treatment. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2005; 114:253–257. PMID: 15895778.
Article15. Mintz S, Lee JK. Gabapentin in the treatment of intractable idiopathic chronic cough: case reports. Am J Med. 2006; 119:e13–e15.
Article16. Murry T, Branski RC, Yu K, Cukier-Blaj S, Duflo S, Aviv JE. Laryngeal sensory deficits in patients with chronic cough and paradoxical vocal fold movement disorder. Laryngoscope. 2010; 120:1576–1581. PMID: 20564660.
Article17. Ryan NM, Birring SS, Gibson PG. Gabapentin for refractory chronic cough: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2012; 380:1583–1589. PMID: 22951084.
Article18. Vertigan AE, Gibson PG. Chronic refractory cough as a sensory neuropathy: evidence from a reinterpretation of cough triggers. J Voice. 2011; 25:596–601. PMID: 21051202.
Article19. Fan H, Yu W, Zhang Q, Cao H, Li J, Wang J, et al. Efficacy and safety of gabapentin 1800 mg treatment for post-herpetic neuralgia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2014; 39:334–342. PMID: 24806220.20. Kimos P, Biggs C, Mah J, Heo G, Rashiq S, Thie NM, et al. Analgesic action of gabapentin on chronic pain in the masticatory muscles: a randomized controlled trial. Pain. 2007; 127:151–160. PMID: 17030096.
Article21. Madanick R, Sigmon L, Ferrell K, Shaheen N, Dellon E. Gabapentin for the treatment of chronic cough: a novel approach to treating a challenging clinical problem. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107(Suppl 1):S27–S28.
Article22. Ting L, Na C. The efficiency and safety of gabapentin in the treatment of pertinacious chronic cough. Int Med Health Guid News. 2016; 22:665–668.23. Van de Kerkhove C, Goeminne PC, Van Bleyenbergh P, Dupont LJ. A cohort description and analysis of the effect of gabapentin on idiopathic cough. Cough. 2012; 8:9. PMID: 23114102.
Article24. Bastian ZJ, Bastian RW. The use of neuralgia medications to treat sensory neuropathic cough: our experience in a retrospective cohort of thirty-two patients. PeerJ. 2015; 3:e816. PMID: 25780768.
Article