Lab Med Online.
2018 Jul;8(3):87-93. 10.3343/lmo.2018.8.3.87.
Comparison of Auto RPR Plus and Auto TPIM Plus with Mediace RPR and Abbott Syphilis TP for Serologic Diagnosis of Syphilis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Korea Association of Health Promotion, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Health Promotion Research Institute, Korea Association of Health Promotion, Seoul, Korea. cellonah@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2414129
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2018.8.3.87
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Serologic testing is considered a standard method for syphilis diagnosis. We compared Auto RPR Plus and Auto TPIM Plus with previously developed assays.
METHODS
The precision around the cut-off, linearity, and recovery rate of Auto RPR Plus and Auto TPIM Plus was evaluated using their positive/negative control materials. The results of these two tests were compared with those of Mediace RPR and Abbott Syphilis TP using 431 remnant serum samples collected from people who underwent medical examinations.
RESULTS
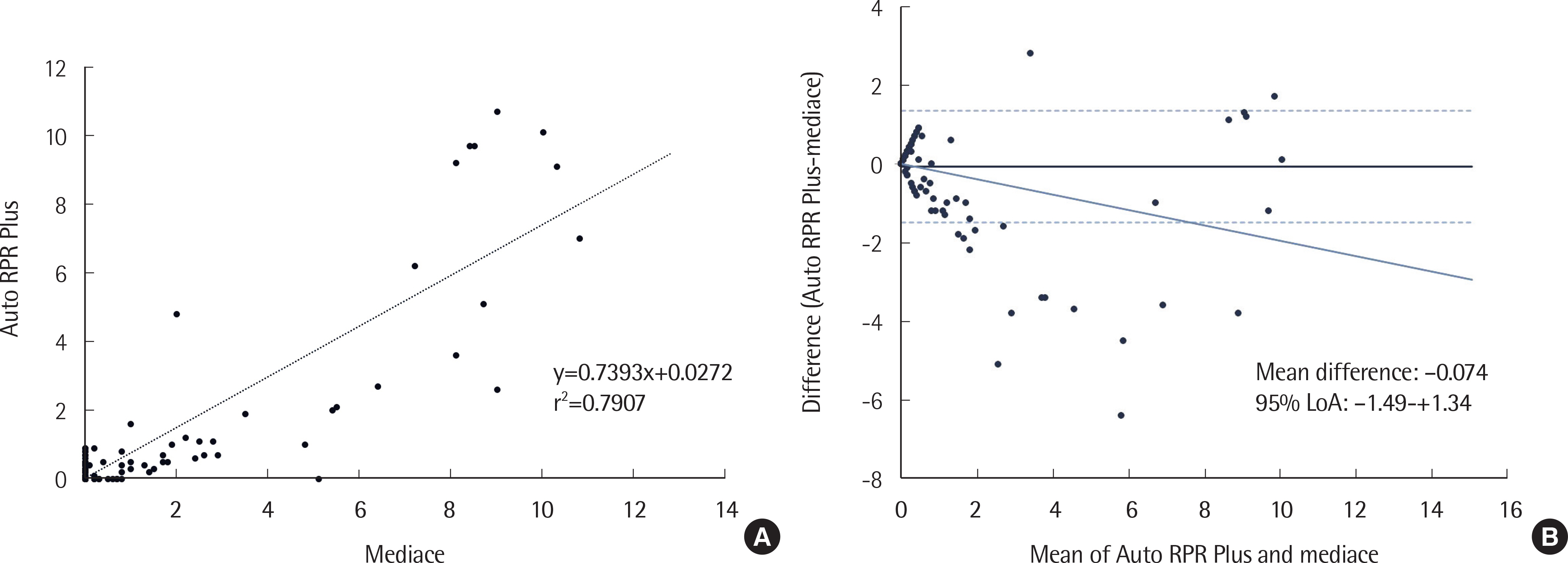
The within-run precisions (coefficient of variation, CV values) of negative/positive control materials of Auto RPR Plus, Mediace RPR, Auto TPIM Plus and Abbott Syphilis TP were 15.7/2.3%, 20.4/2.3%, -/2.7%, and 8.5/2.3%, respectively; between-run precisions were 67.7/3.3%, 39.1/3.4%, -/4.0%, and 7.0/1.5%, respectively. Auto RPR Plus showed better precision around the cutoff level (1.0 U) compared to Mediace RPR (7.2-7.3% vs. 12.2-14.3%). The CVs of Auto TPIM Plus around the cutoff (10.0 U) were 13.5% at 10.5 U and 6.6% at 12.5 U. Agreement rates between Auto RPR Plus and Mediace RPR and between Auto TPIM Plus and Abbott Syphilis TP were 97.2% and 98.4%, respectively. However, twelve samples showed discrepant results for Auto RPR Plus (−)/Mediace RPR (+) and false-positive Mediace RPR results could not be excluded around the cutoff of 1.0 U.
CONCLUSIONS
Auto RPR Plus showing good precision near the cutoff can be used for syphilis screening in health checkups. However, Auto TPIM Plus needs improvement in precision and adjusting the cutoff to be used for syphilis screening.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1.The Korean Society for Laboratory Medicine. Laboratory Medicine. 5th ed.Seoul: Beommun Education;2014. p. 845–6.2.Park MJ., Park PW., Seo YH., Ahn JY., Kim KH., Seo JY, et al. Evaluation of AutoLab rapid plasma reagin and AutoLab Treponema pallidum latex agglutination for syphilis infection testing. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2015. 37:29–36.
Article3.Tong ML., Lin LR., Liu LL., Zhang HL., Huang SJ., Chen YY, et al. Analysis of 3 algorithms for syphilis serodiagnosis and implications for clinical management. Clin Infect Dis. 2014. 58:1116–24.
Article4.Marangoni A., Moroni A., Accardo S., Cevenini R. Laboratory diagnosis of syphilis with automated immunoassay. J Clin Lab Anal. 2009. 23:1–6.5.Young H., Pryde J., Duncan L., Dave J. The Architect Syphilis assay for antibodies to Treponema pallidum: an automated screening assay with high sensitivity in primary syphilis. Sex Transm Infect. 2009. 85:19–23.
Article6.Kim HS., Lee YK., Kang HJ. Serologic test for syphilis by Mediace RPR test for chemistry autoanalyzer. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2007. 29:195–9.7.National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. User verifca-tion of precision and estimation of bias; approved guideline EP15-A3. Wayne, PA: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. 2014.8.National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Evaluation of the llinearity of quantitative measurement procedures: a statistical approach; approved guideline EP6-A. Wayne, PA: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. 2008.9.Park HJ. Clinical observation and statistical consideration of syphilis (2000–2007). Korean J Dermatol. 2008. 46:1344–52.10.Larsen SA., Steiner BM., Rudolph AH. Laboratory diagnosis and interpretation of tests for syphilis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1995. 8:1–21.
Article11.Song EY., Yang JS., Chae SL., Kim S., Choi YS., Cha YJ. Current status of external quality assessment of syphilis test in Korea. Korean J Lab Med. 2008. 28:207–13.
Article12.WiseMeditech. Reagent information of Auto RPR Plus. Mar. 2014.13.WiseMeditech. Reagent information of Auto TPIM Plus. Jan. 2014.14.Noh J., Ko HH., Yun Y., Choi YS., Lee SG., Shin S, et al. Evaluation of performance and false positivity of Mediace RPR test that uses a chemistry autoanalyzer. Korean J Lab Med. 2008. 28:312–8.
Article15.Morshed M., Singh AE. Recent trends in the serologic diagnosis of syphilis. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015. 22:137–47.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Serologic Test for Syphilis by Mediace RPR Test for Chemistry Autoanalyzer
- Comparison of Quantitative Results among Two Automated Rapid Plasma Reagin (RPR) Assays and a Manual RPR Test
- Comparison of the Results among Automated Treponema pallidum Latex Agglutination, Rapid Plasma Regain and Treponema pallidum Particle Agglutination, Rapid Plasma Regain Card Test in Blood Donors
- Practical Application of Quantitative HiSens Auto Rapid Plasma Reagin Latex Turbidimetric Immunoagglutination for Diagnosing Syphilis; Comparison Analysis between Rapid Plasma Reagin Latex Turbidimetric Immunoagglutination Test and Rapid Plasma Reagin Card Test
- Evaluation of AutoLab Rapid Plasma Reagin and AutoLab Treponema pallidum Latex Agglutination for Syphilis Infection Testing