J Breast Cancer.
2016 Sep;19(3):330-333. 10.4048/jbc.2016.19.3.330.
Radiologic Findings of Primary Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma of the Breast: A Report of Two Cases and a Literature Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. claudel@skku.edu
- 2Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2413959
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2016.19.3.330
Abstract
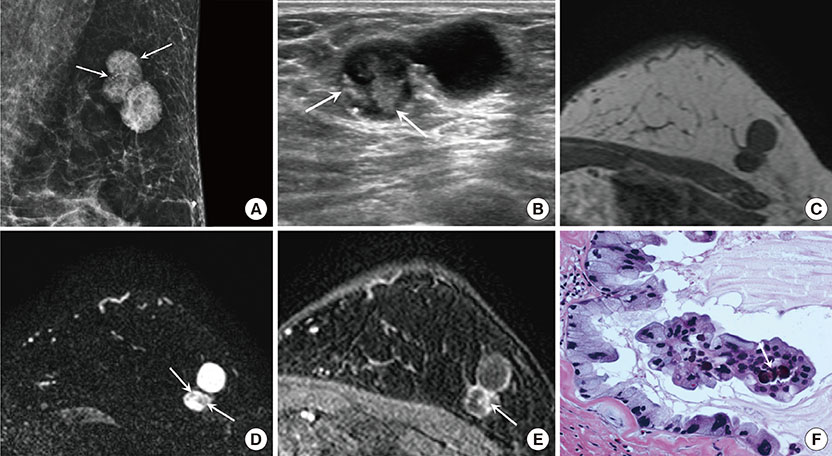
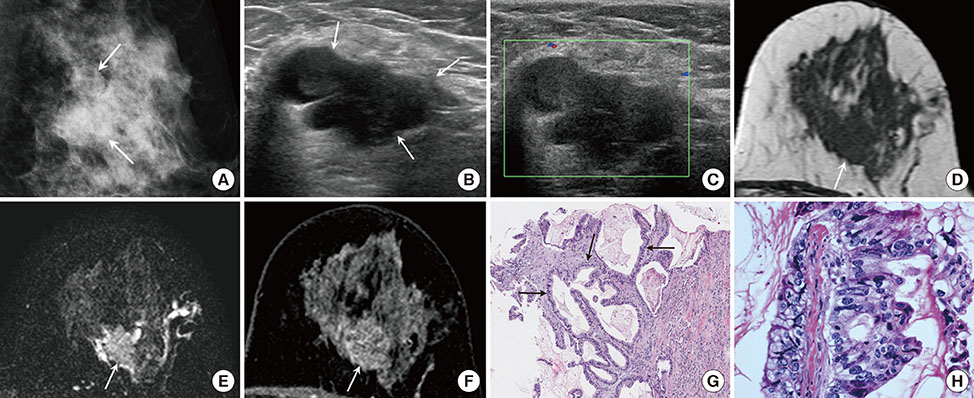
- Primary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma (MCA) of the breast is a rare but pathologically distinct breast tumor. There have been some case reports on primary MCA of the breast; however, they have all focused on pathologic findings. Here, we report the radiologic findings of two cases of MCA along with a review of the literature. Breast MCA shows a circumscribed mass with some calcifications on mammography, an intracystic solid mass without increased vascularity or a vascular stalk on ultrasound, and a heterogeneously enhancing mass within a rim-enhancing cyst with intermediate signal intensity on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. These radiologic findings and the presence of mucin in the percutaneous biopsy specimen should suggest the possibility of MCA in the differential diagnosis of a breast tumor.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Honma N, Sakamoto G, Ikenaga M, Kuroiwa K, Younes M, Takubo K. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast: a case report and review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003; 127:1031–1033.
Article2. Chen WY, Chen CS, Chen HC, Hung YJ, Chu JS. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast coexisting with infiltrating ductal carcinoma. Pathol Int. 2004; 54:781–786.
Article3. Rakıcı S, Gönüllü G, Gürsel SB, Yıldız L, Bayrak IK, Yücel I. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast with estrogen receptor expression: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Oncol. 2009; 2:210–216.
Article4. Deng Y, Xue D, Wang X, Xu S, Ao Q, Hu Z, et al. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast with a basal-like immunophenotype. Pathol Int. 2012; 62:429–432.
Article5. Kim SE, Park JH, Hong S, Koo JS, Jeong J, Jung WH. Primary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast: cytologic finding and expression of MUC5 are different from mucinous carcinoma. Korean J Pathol. 2012; 46:611–616.
Article6. Li X, Peng J, Zhang Z, Zhang Y. Mammary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma. Breast J. 2012; 18:282–283.
Article7. Sentani K, Tashiro T, Uraoka N, Aosaki Y, Yano S, Takaeko F, et al. Primary mammary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma: cytological and histological findings. Diagn Cytopathol. 2012; 40:624–628.
Article8. Lin DL, Hu JL, Shao SH, Sun DM, Wang JG. Primary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast with endocervical-like mucinous epithelium. Breast Care (Basel). 2013; 8:445–447.
Article9. Lee SH, Chaung CR. Mucinous metaplasia of breast carcinoma with macrocystic transformation resembling ovarian mucinous cystadenocarcinoma in a case of synchronous bilateral infiltrating ductal carcinoma. Pathol Int. 2008; 58:601–605.
Article10. Witherspoon LE, Oxenhandler RW. A rare tumor: mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast. Am Surg. 2015; 81:E106–E108.
Article11. Ellis IO, Cornelisse CJ, Schnitt SJ, Sasco AJ, Sastre-Garau X, Kaaks R, et al. Mucin producing carcinomas. In : Tavassoli FA, Devilee P, editors. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Breast and Female Genital Organs. Lyon: IARC;2003. p. 30–32.12. Rodríguez MC, Secades AL, Angulo JM. Best cases from the AFIP: intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast. Radiographics. 2010; 30:2021–2027.13. Lam WW, Chu WC, Tse GM, Ma TK. Sonographic appearance of mucinous carcinoma of the breast. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 182:1069–1074.
Article14. Monzawa S, Yokokawa M, Sakuma T, Takao S, Hirokaga K, Hanioka K, et al. Mucinous carcinoma of the breast: MRI features of pure and mixed forms with histopathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 192:W125–W131.
Article15. Kim SM, Kim HH, Kang DK, Shin HJ, Cho N, Park JM, et al. Mucocele-like tumors of the breast as cystic lesions: sonographic-pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 196:1424–1430.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Primary Retroperitoneal Mucinous Cystadenocarcioma Involving the Splenic Hilum
- Primary Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma of the Breast: Cytologic Finding and Expression of MUC5 Are Different from Mucinous Carcinoma
- Primary Retroperitoneal Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of ovary with metastasis in 14-year-old girl
- MR Imaging of Primary Retroperitoneal Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma in Pregnant Woman