Blood Res.
2017 Jun;52(2):148-150. 10.5045/br.2017.52.2.148.
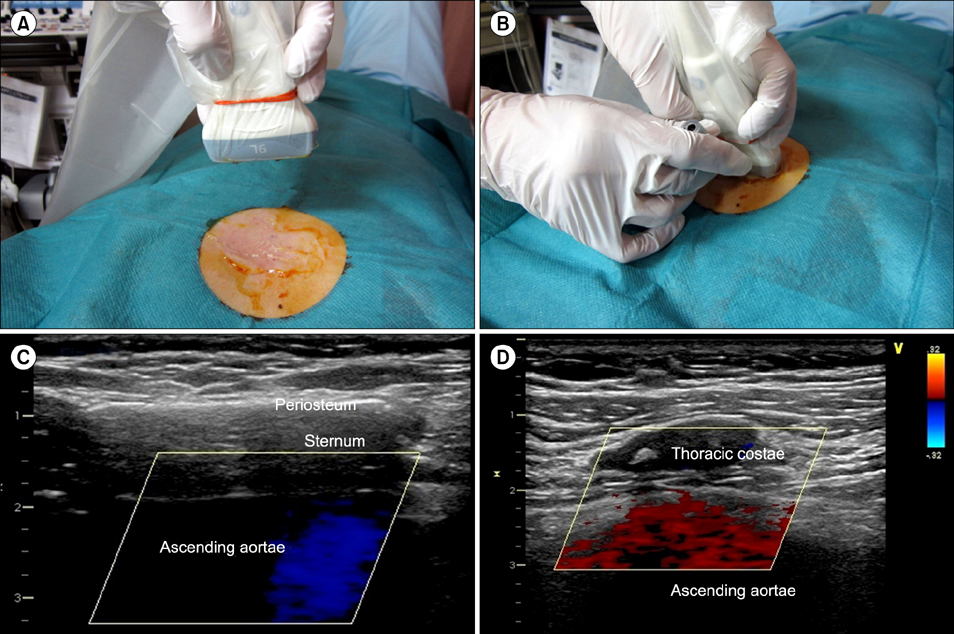
Ultrasound-guided sternal bone marrow aspiration
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, Nagoya Kyoritsu Hospital, Nagoya, Japan. yasakura@kaikou.or.jp
- 2Department of Anesthesiology, Tokyo Womens' Medical University, Tokyo, Japan.
- KMID: 2413338
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2017.52.2.148
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Santavy P, Troubil M, Lonsky V. Pericardial tamponade: a rare complication of sternal bone marrow biopsy. Hematol Rep. 2013; 5:e13.
Article2. Song IK, Choi JY, Lee JH, et al. Short-axis/out-of-plane or long-axis/in-plane ultrasound-guided arterial cannulation in children: A randomised controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2016; 33:522–527.
Article3. Asakura Y, Kandatsu N, Kato N, Sato Y, Fujiwara Y, Komatsu T. Ultra-sound guided sciatic nerve block combined with lumbar plexus block for infra-inguinal artery bypass graft surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2008; 52:721–722.
Article4. Asakura Y, Mizuno T, Kato N, Kandatsu N, Fujiwara Y, Komatsu T. Respiratory status that facilitates subclavian venous catheterization. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2008; 52:867–869.
Article5. Asakura Y, Kandatsu N, Hashimoto A, Kamiya M, Akashi M, Komatsu T. Ultrasound-guided neuroaxial anesthesia: accurate diagnosis of spina bifida occulta by ultrasonography. J Anesth. 2009; 23:312–313.
Article6. Asakura Y, Nakamichi Y, Mori K, Ibuki K, Kasuga H, Hori H. Ultrasound-guided central venous catheterization: efficacy of simultaneous perioperative ultrasonographic scanning for the presence of carotid plaques in the prevention of the perioperative development of ischemic stroke. J Anesth. 2012; 26:621–622.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Usefulness of Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration in Breast Lesions
- Fine-Needle Biopsy: Should This Be the First Choice in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition?
- Role of Repeated Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration for Inconclusive Initial Cytology Result
- How Can We Get the Best Results with Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration?
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis Arising from the Mandible as Diagnosed by US-guided Core Biopsy