J Surg Ultrasound.
2022 Nov;9(2):30-35. 10.46268/jsu.2022.9.2.30.
The Usefulness of Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration in Breast Lesions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Breast, Department of Surgery, Dong-A University Hospital, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2538388
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.46268/jsu.2022.9.2.30
Abstract
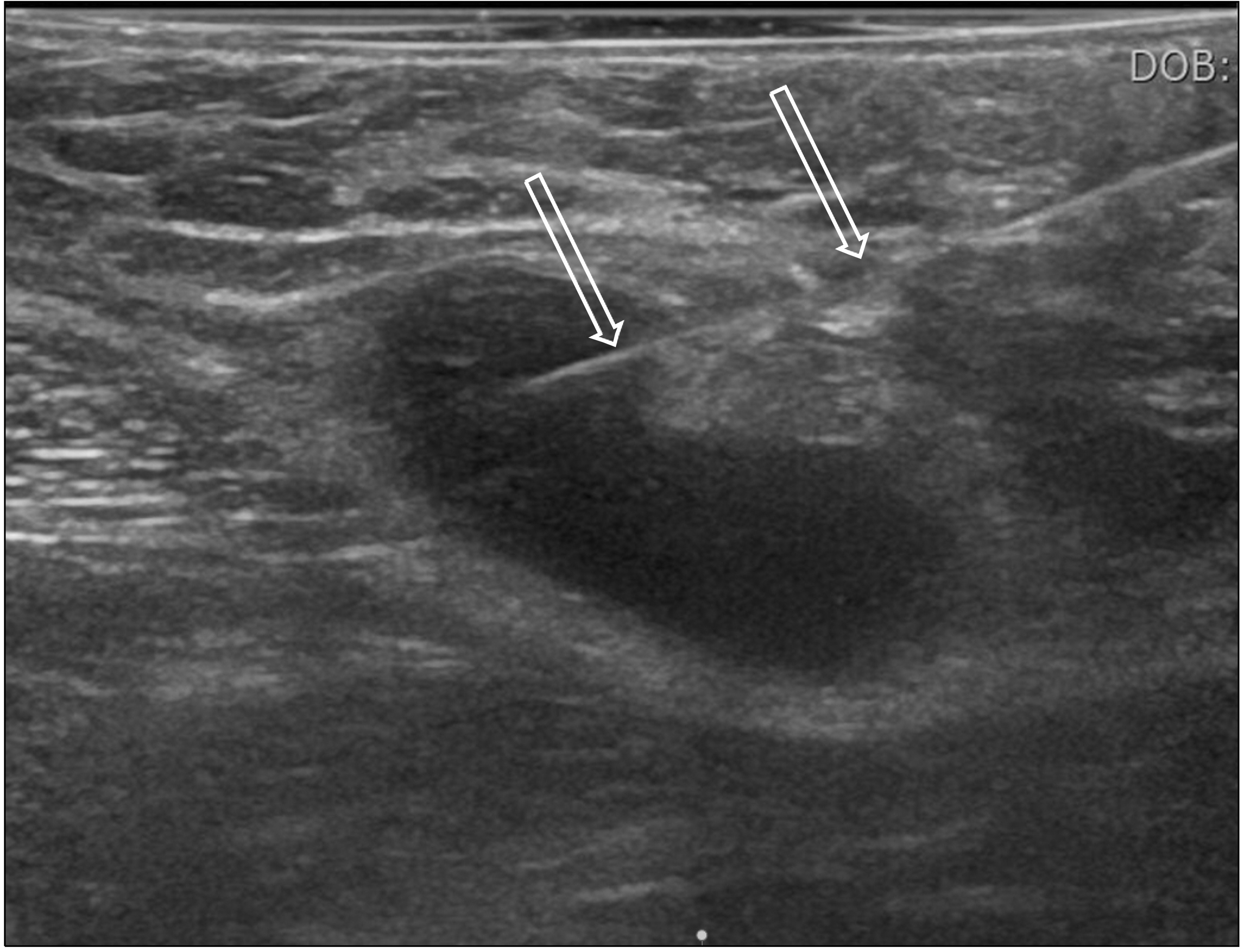
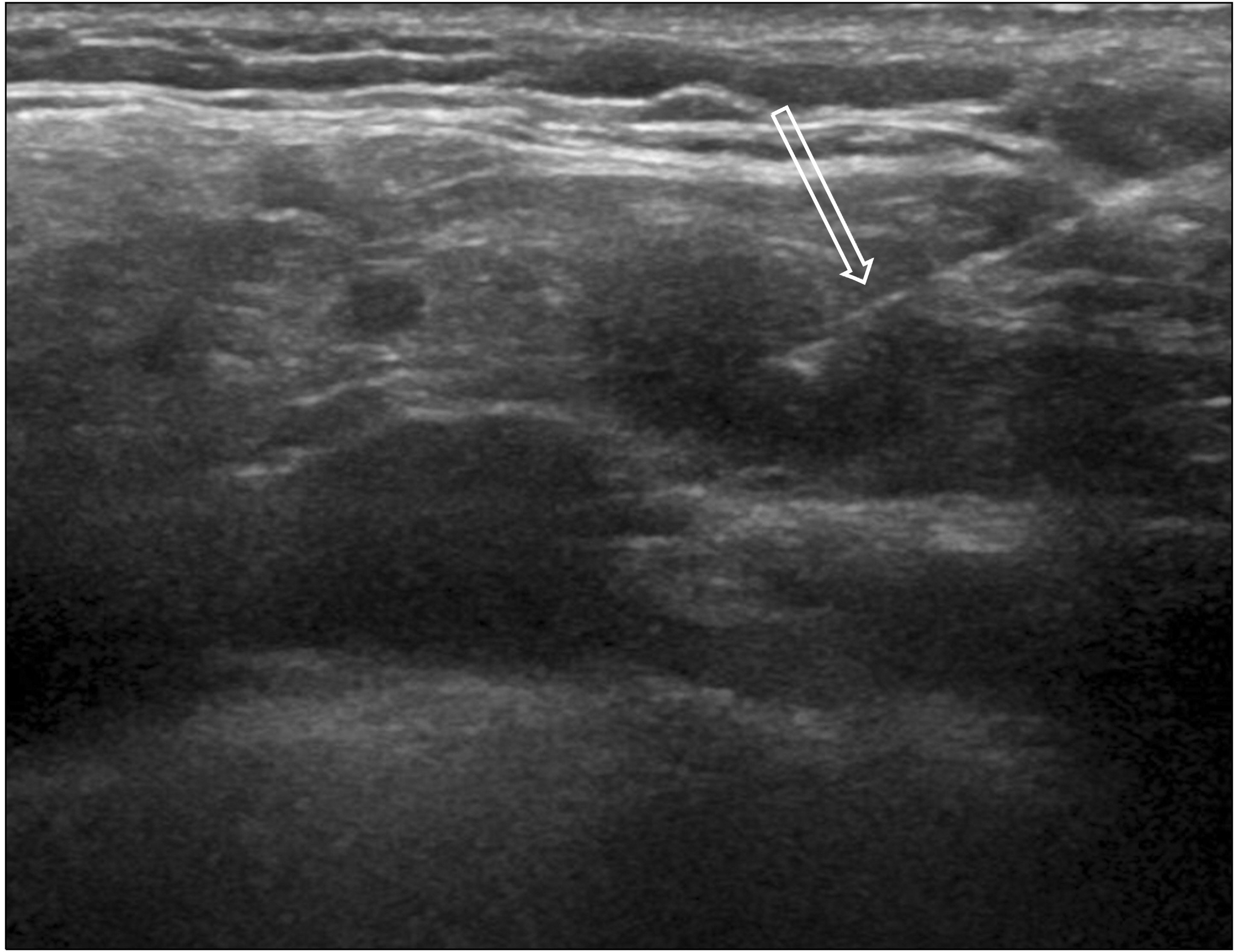
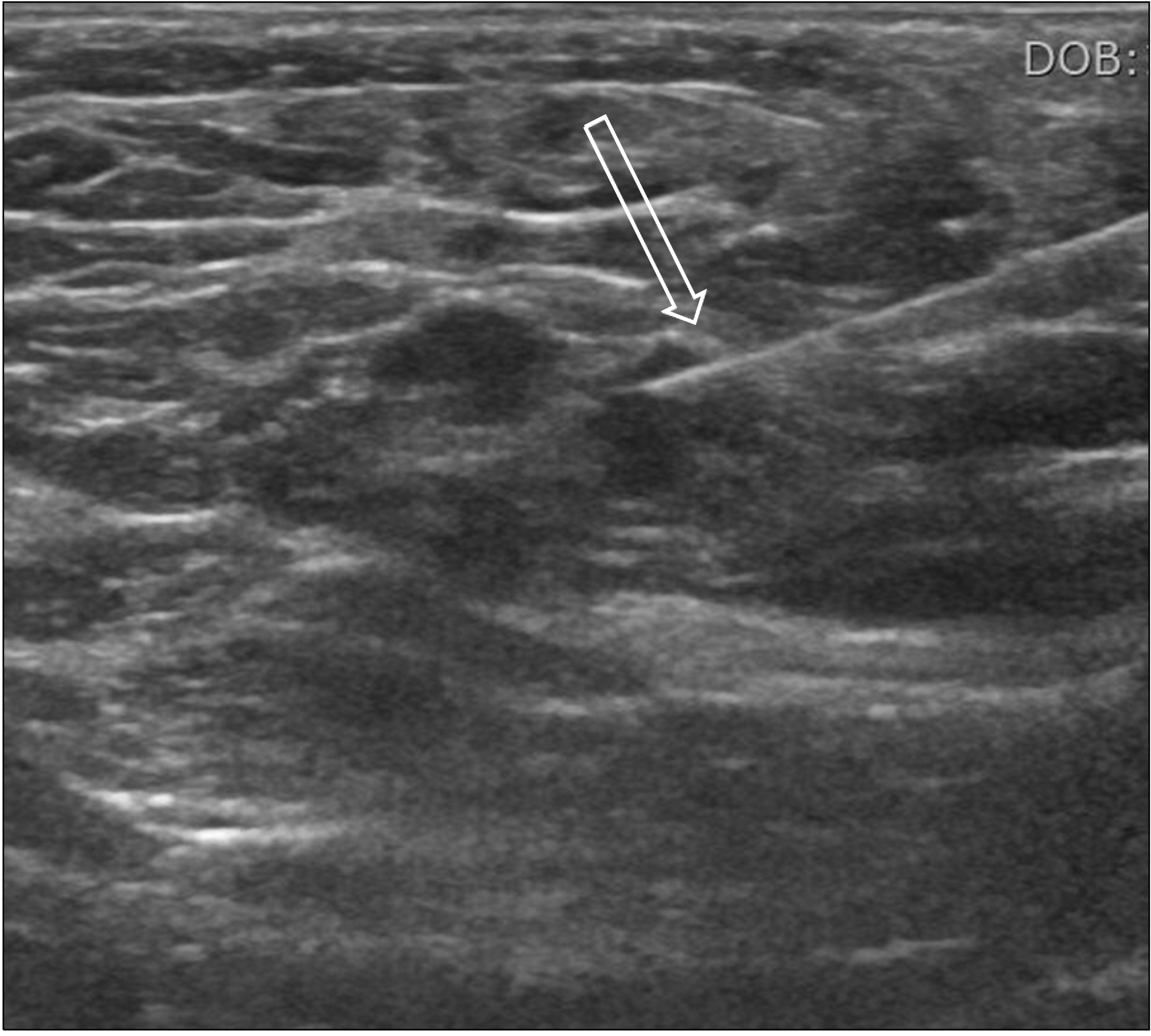
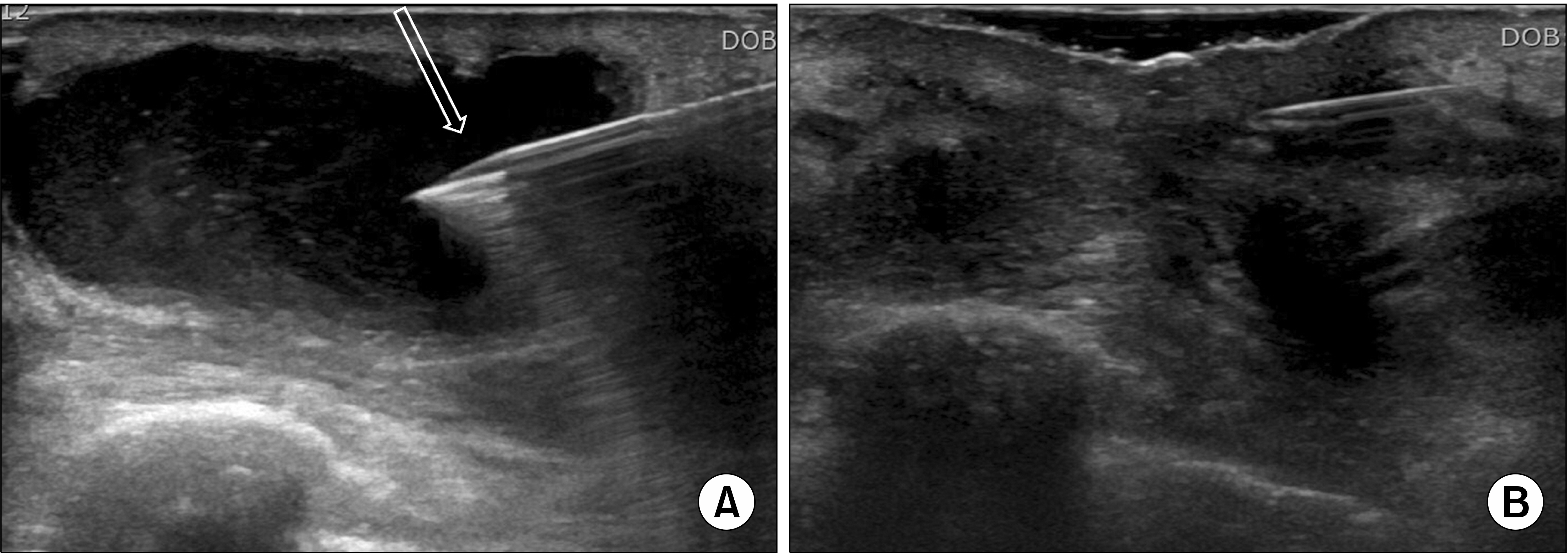
- Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) has been used extensively for the diagnosis of breast lesions over the past decade and has now been largely replaced by core needle biopsy. However, ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology (US-guided FNAC) is still widely used because of its advantages of simple procedure, low cost, fewer side effects, and excellent tolerance by patients. Indeed, US-FNAC of indeterminate/suspicious lymph nodes in breast cancer patients can provide a more definitive diagnosis than ultrasonography alone. This review article summarizes the method of use and utility of US-guided FNAC in breast lesions.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. National Health Insuarance Service. 2021. 2016 cancer registry statistics in Korea [Internet]. Statistics Korea;Daejeon: cited 2021 Dec 30.2. Kim EK, Oh KK, Kim MH, You JK, Kwak JY, Park BW, et al. 2002; Changes in diagnostic methods of non-palpable breast lesions: analysis for 5 years. J Korean Radiol Soc. 47:93–8. DOI: 10.3348/jkrs.2002.47.1.93.
Article3. Silverman JF, Lannin DR, O'Brien K, Norris HT. 1987; The triage role of fine needle aspiration biopsy of palpable breast masses. Diagnosticaccuracy and cost-effectiveness. Acta Cytol. 31:731–6. PMID: 3425133.4. Fornage BD, Faroux MJ, Simatos A. 1987; Breast masses: US-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy. Radiology. 162:409–14. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.162.2.3541029. PMID: 3541029.
Article5. Gordon PB, Goldenberg SL, Chan NH. 1993; Solid breast lesions: diagnosis with US-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy. Radiology. 189:573–80. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.189.2.8210392. PMID: 8210392.
Article6. Hann L, Ducatman BS, Wang HH, Fein V, McIntire JM. 1989; Nonpalpable breast lesions: evaluation by means of fine-needle aspiration cytology. Radiology. 171:373–6. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.171.2.2539608. PMID: 2539608.
Article7. Fornage BD. 1990; Guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy of nonpalpable breast lesions: calculation of accuracy values. Radiology. 884–5. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.177.3.2244007. PMID: 2244007.
Article8. Dixon JM, Clarke PJ, Crucioli V, Dehn TC, Lee EC, Greenall MJ. 1987; Reduction of the surgical excision rate in benign breast disease using fine needle aspiration cytology with immediate reporting. Br J Surg. 74:1014–6. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.1800741119. PMID: 3690225.
Article9. Pisano ED, Fajardo LL, Caudry DJ, Sneige N, Frable WJ, Berg WA, et al. 2001; Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of nonpalpable breast lesions in a multicenter clinical trial: results from the radiologic diagnostic oncology group V. Radiology. 219:785–92. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.219.3.r01jn28785. PMID: 11376270.
Article10. Jackson VP. 1992; The status of mammographically guided fine needle aspiration biopsy of nonpalpable breast lesions. Radiol Clin North Am. 30:155–66. DOI: 10.1016/S0033-8389(22)02492-7. PMID: 1732924.
Article11. Meunier M, Clough K. 2002; Fine needle aspiration cytology versus percutaneous biopsy of nonpalpable breast lesions. Eur J Radiol. 42:10–6. DOI: 10.1016/S0720-048X(01)00480-6. PMID: 12039016.
Article12. Simsir A, Rapkiewicz A, Cangiarella J. 2009; Current utilization of breast FNA in a cytology practice. Diagn Cytopathol. 37:140–2. DOI: 10.1002/dc.20987. PMID: 19021200.
Article13. MacNeill M, Arnott I, Thomas J. 2011; Fine needle aspiration cytology is a valuable adjunct to axillary ultrasound in the preoperative staging of breast cancer. J Clin Pathol. 64:42–6. DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2010.083063. PMID: 21097541.
Article14. Bruneton JN, Caramella E, Héry M, Aubanel D, Manzino JJ, Picard JL. 1986; Axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer: preoperative detection with US. Radiology. 158:325–6. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.158.2.3510440. PMID: 3510440.
Article15. de Freitas R Jr, Costa MV, Schneider SV, Nicolau MA, Marussi E. 1991; Accuracy of ultrasound and clinical examination in the diagnosis of axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 17:240–4. PMID: 2044777.16. van Rijk MC, Deurloo EE, Nieweg OE, Gilhuijs KG, Peterse JL, Rutgers EJ, et al. 2006; Ultrasonography and fine-needle aspiration cytology can spare breast cancer patients unnecessary sentinel lymph node biopsy. Ann Surg Oncol. 13:31–5. DOI: 10.1245/ASO.2005.01.024. PMID: 16372147.
Article17. Davis JT, Brill YM, Simmons S, Sachleben BC, Cibull ML, McGrath P, et al. 2006; Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of clinically negative lymph nodes versus sentinel node mapping in patients at high risk for axillary metastasis. Ann Surg Oncol. 13:1545–52. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-006-9095-8. PMID: 17009156.
Article18. Houssami N, Ciatto S, Turner RM, Cody HS 3rd, Macaskill P. 2011; Preoperative ultrasound-guided needle biopsy of axillary nodes in invasive breast cancer: meta-analysis of its accuracy and utility in staging the axilla. Ann Surg. 254:243–51. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31821f1564. PMID: 21597359.19. Rao R, Lilley L, Andrews V, Radford L, Ulissey M. 2009; Axillary staging by percutaneous biopsy: sensitivity of fine-needle aspiration versus core needle biopsy. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:1170–5. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-009-0421-9. PMID: 19263171.
Article20. de Kanter AY, van Eijck CH, van Geel AN, Kruijt RH, Henzen SC, Paul MA, et al. 1999; Multicentre study of ultrasonographically guided axillary node biopsy in patients with breast cancer. Br J Surg. 86:1459–62. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2168.1999.01243.x. PMID: 10583296.
Article21. Kim JY. 2007; General cytological characters of malignant breast lesions. Korean J Cytopathol. 18:100–11.22. Mendoza P, Lacambra M, Tan PH, Tse GM. 2011; Fine needle aspiration cytology of the breast: the nonmalignant categories. Patholog Res Int. 2011:547580. DOI: 10.4061/2011/547580. PMID: 21660275. PMCID: PMC3108472.23. Lieu D. 2009; Value of cytopathologist-performed ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration as a screening test for ultrasound-guided core-needle biopsy in nonpalpable breast masses. Diagn Cytopathol. 37:262–9. DOI: 10.1002/dc.20984. PMID: 19217029.
Article24. He Q, Fan X, Yuan T, Kong L, Du X, Zhuang D, et al. 2007; Eleven years of experience reveals that fine-needle aspiration cytology is still a useful method for preoperative diagnosis of breast carcinoma. Breast. 16:303–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.breast.2006.12.006. PMID: 17287118.
Article25. Berner A, Davidson B, Sigstad E, Risberg B. 2003; Fine-needle aspiration cytology vs. core biopsy in the diagnosis of breast lesions. Diagn Cytopathol. 29:344–8. DOI: 10.1002/dc.10372. PMID: 14648793.
Article26. Pisano ED, Fajardo LL, Tsimikas J, Sneige N, Frable WJ, Gatsonis CA, et al. 1998; Rate of insufficient samples for fine-needle aspiration for nonpalpable breast lesions in a multicenter clinical trial: the radiologic diagnostic oncology group 5 study. The RDOG5 investigators. Cancer. 82:679–88. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19980215)82:4<679::AID-CNCR10>3.0.CO;2-V. PMID: 9477100.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Fine Needle Aspiration versus Core Biopsy for the Diagnosis of Subepithelial Tumors
- How Can We Get the Best Results with Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration?
- Fine-Needle Biopsy: Should This Be the First Choice in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition?
- How to optimize the diagnostic yield of endoscopic ultrasoundguided fine-needle sampling in solid pancreatic lesions from a technical perspective
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration in Cystic Pancreatic Lesions