Implications of para-aortic lymph node metastasis in patients with endometrial cancer without pelvic lymph node metastasis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gynecologic Oncology, National Hospital Organization, Hokkaido Cancer Center, Sapporo, Japan. yukiharu@sap-cc.go.jp
- 2Division of Pathology, National Hospital Organization, Hokkaido Cancer Center, Sapporo, Japan.
- KMID: 2413220
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3802/jgo.2017.28.e59
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The aim of this study was to confirm the incidence and implications of a lymphatic spread pattern involving para-aortic lymph node (PAN) metastasis in the absence of pelvic lymph node (PLN) metastasis in patients with endometrial cancer.
METHODS
We carried out a retrospective chart review of 380 patients with endometrial cancer treated by surgery including PLN dissection and PAN dissection at Hokkaido Cancer Center between 2003 and 2016. We determined the probability of PAN metastasis in patients without PLN metastasis and investigated survival outcomes of PLN−PAN+ patients.
RESULTS
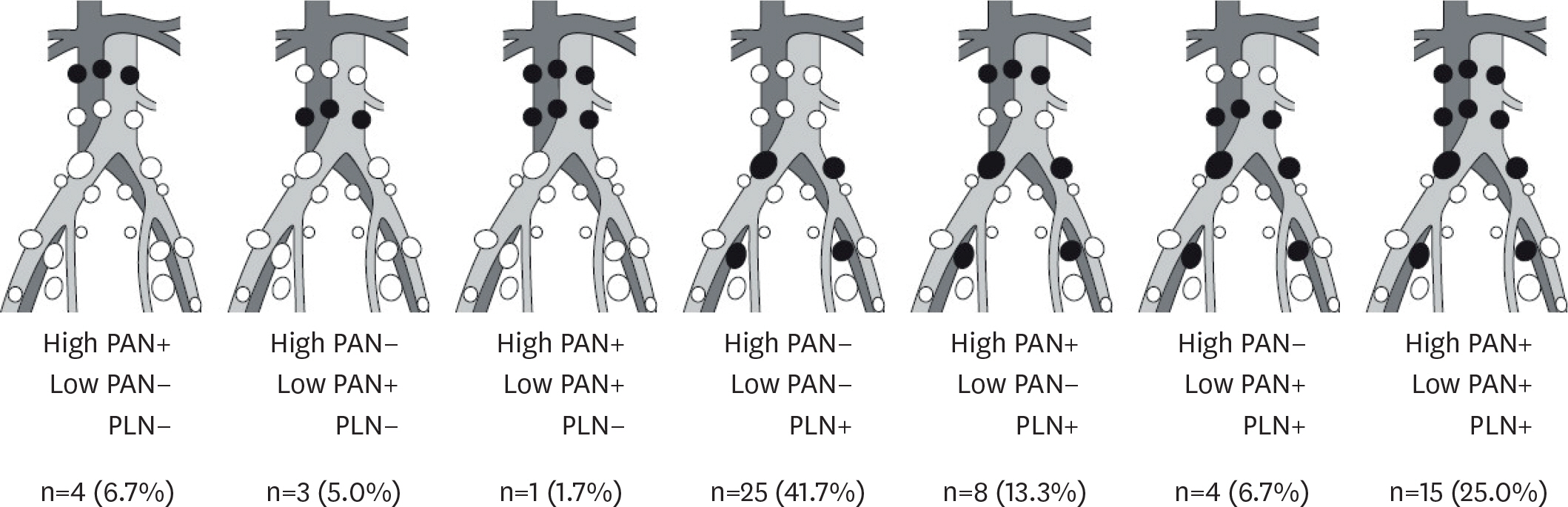
The median numbers of PLN and PAN removed at surgery were 41 (range: 11-107) and 16 (range: 1-65), respectively. Sixty-four patients (16.8%) had lymph node metastasis, including 39 (10.3%) with PAN metastasis. The most frequent lymphatic spread pattern was PLN+PAN+ (7.9%), followed by PLN+PAN− (6.6%), and PLN−PAN+ (2.4%). The probability of PAN metastasis in patients without PLN metastasis was 2.8% (9/325). The 5-year overall survival rates were 96.5% in PLN−PAN−, 77.6% in PLN+PAN−, 63.4% in PLN+PAN+, and 53.6% in PLN−PAN+ patients.
CONCLUSION
The likelihood of PAN metastasis in endometrial cancer patients without PLN metastasis is not negligible, and the prognosis of PLN−PAN+ is likely to be poor. The implications of a PLN−PAN+ lymphatic spread pattern should thus be taken into consideration when determining patient management strategies.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Prognostic value of metabolic tumor volume and total lesion glycolysis from 18F-FDG PET/CT in lymph node metastases and risk stratification of endometrial carcinoma
Dou-dou Liu, Jianfang Li, Xiaomao Li, Liangjun Xie, Luping Qin, Fangyu Peng, Mu-hua Cheng
J Gynecol Oncol. 2019;30(6):e89. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2019.30.e89.Prognostic value of metabolic tumor volume and total lesion glycolysis from 18 F-FDG PET/CT in lymph node metastases and risk stratification of endometrial carcinoma
Dou-dou Liu, Jianfang Li, Xiaomao Li, Liangjun Xie, Luping Qin, Fangyu Peng, Mu-hua Cheng
J Gynecol Oncol. 2019;30(6):. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2019.30.e89.Sentinel lymph node biopsy in high-risk endometrial cancer: performance, outcomes, and future avenues
Yoo-Na Kim, Young Tae Kim
Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2022;65(5):395-405. doi: 10.5468/ogs.22146.
Reference
-
References
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017; 67:7–30.
Article2. Parker SL, Tong T, Bolden S, Wingo PA. Cancer statistics, 1997. CA Cancer J Clin. 1997; 47:5–27.
Article3. Abu-Rustum NR. The increasing credibility of sentinel lymph node mapping in endometrial cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013; 20:353–4.
Article4. Cormier B, Rozenholc AT, Gotlieb W, Plante M, Giede CCommunities of Practice (CoP) Group of Society of Gynecologic Oncology of Canada (GOC). Sentinel lymph node procedure in endometrial cancer: a systematic review and proposal for standardization of future research. Gynecol Oncol. 2015; 138:478–85.5. Ballester M, Dubernard G, Lécuru F, Heitz D, Mathevet P, Marret H, et al. Detection rate and diagnostic accuracy of sentinel-node biopsy in early stage endometrial cancer: a prospective multicentre study (SENTI-ENDO). Lancet Oncol. 2011; 12:469–76.
Article6. Larson DM, Johnson KK. Pelvic and paraaortic lymphadenectomy for surgical staging of high-risk endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the endometrium. Gynecol Oncol. 1993; 51:345–8.
Article7. Fanning J, Nanavati PJ, Hilgers RD. Surgical staging and high dose rate brachytherapy for endometrial cancer: limiting external radiotherapy to node-positive tumors. Obstet Gynecol. 1996; 87:1041–4.
Article8. Yokoyama Y, Maruyama H, Sato S, Saito Y. Indispensability of pelvic and paraaortic lymphadenectomy in endometrial cancers. Gynecol Oncol. 1997; 64:411–7.
Article9. Lee KB, Ki KD, Lee JM, Lee JK, Kim JW, Cho CH, et al. The risk of lymph node metastasis based on myometrial invasion and tumor grade in endometrioid uterine cancers: a multicenter, retrospective Korean study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009; 16:2882–7.
Article10. Abu-Rustum NR, Khoury-Collado F, Pandit-Taskar N, Soslow RA, Dao F, Sonoda Y, et al. Sentinel lymph node mapping for grade 1 endometrial cancer: is it the answer to the surgical staging dilemma? Gynecol Oncol. 2009; 113:163–9.
Article11. Chiang AJ, Yu KJ, Chao KC, Teng NN. The incidence of isolated paraaortic nodal metastasis in completely staged endometrial cancer patients. Gynecol Oncol. 2011; 121:122–5.
Article12. Solmaz U, Mat E, Dereli ML, Turan V, Tosun G, Dogan A, et al. Lymphovascular space invasion and positive pelvic lymph nodes are independent risk factors for paraaortic nodal metastasis in endometrioid endometrial cancer. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2015; 186:63–7.
Article13. Chen SS, Lee L. Retroperitoneal lymph node metastases in Stage I carcinoma of the endometrium: correlation with risk factors. Gynecol Oncol. 1983; 16:319–25.
Article14. Creasman WT, Morrow CP, Bundy BN, Homesley HD, Graham JE, Heller PB. Surgical pathologic spread patterns of endometrial cancer. A Gynecologic Oncology Group Study. Cancer. 1987; 60:2035–41.
Article15. Ayhan A, Tuncer ZS, Tuncer R, Yüce K, Küçükali T. Tumor status of lymph nodes in early endometrial cancer in relation to lymph node size. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1995; 60:61–3.
Article16. Hirahatake K, Hareyama H, Sakuragi N, Nishiya M, Makinoda S, Fujimoto S. A clinical and pathologic study on paraaortic lymph node metastasis in endometrial carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 1997; 65:82–7.
Article17. Milam MR, Java J, Walker JL, Metzinger DS, Parker LP, Coleman RL, et al. Nodal metastasis risk in endometrioid endometrial cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 2012; 119:286–92.
Article18. Sueoka K, Umayahara K, Abe A, Usami T, Yamamoto A, Nomura H, et al. Prognosis for endometrial cancer patients treated with systematic pelvic and paraaortic lymphadenectomy followed by platinum-based chemotherapy. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2015; 25:81–6.
Article19. Mahdi H, Jernigan A, Nutter B, Michener C, Rose PG. Lymph node metastasis and pattern of recurrence in clinically early stage endometrial cancer with positive lymphovascular space invasion. J Gynecol Oncol. 2015; 26:208–13.
Article20. Onda T, Yoshikawa H, Mizutani K, Mishima M, Yokota H, Nagano H, et al. Treatment of node-positive endometrial cancer with complete node dissection, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Br J Cancer 1997;75:1836–41.
Article21. Matsumoto K, Yoshikawa H, Yasugi T, Onda T, Nakagawa S, Yamada M, et al. Distinct lymphatic spread of endometrial carcinoma in comparison with cervical and ovarian carcinomas. Cancer Lett. 2002; 180:83–9.
Article22. Mariani A, Dowdy SC, Cliby WA, Gostout BS, Jones MB, Wilson TO, et al. Prospective assessment of lymphatic dissemination in endometrial cancer: a paradigm shift in surgical staging. Gynecol Oncol. 2008; 109:11–8.
Article23. Fujimoto T, Nanjyo H, Fukuda J, Nakamura A, Mizunuma H, Yaegashi N, et al. Endometrioid uterine cancer: histopathological risk factors of local and distant recurrence. Gynecol Oncol. 2009; 112:342–7.
Article24. Dogan NU, Gungor T, Karsli F, Ozgu E, Besli M. To what extent should paraaortic lymphadenectomy be carried out for surgically staged endometrial cancer? Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2012; 22:607–10.
Article25. Odagiri T, Watari H, Kato T, Mitamura T, Hosaka M, Sudo S, et al. Distribution of lymph node metastasis sites in endometrial cancer undergoing systematic pelvic and paraaortic lymphadenectomy: a proposal of optimal lymphadenectomy for future clinical trials. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014; 21:2755–61.
Article26. Altay A, Toptas T, Dogan S, Simsek T, Pestereli E. Analysis of metastatic regional lymph node locations and predictors of paraaortic lymph node involvement in endometrial cancer patients at risk for lymphatic dissemination. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2015; 25:657–64.
Article27. Tomisato S, Yamagami W, Susumu N, Kuwahata M, Takigawa A, Nomura H, et al. Clinicopathological study on paraaortic lymph node metastasis without pelvic lymph node metastasis in endometrial cancer. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2014; 40:1733–9.
Article28. Fotopoulou C, El-Balat A, du Bois A, Sehouli J, Harter P, Muallem MZ, et al. Systematic pelvic and paraaortic lymphadenectomy in early high-risk or advanced endometrial cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2015; 292:1321–7.
Article29. Sautua RR, Goiri K, Calle MA, Marin IJ, Artola AL. Incidence of nodal metastasis and isolated aortic metastases in patients with surgically staged endometrioid endometrial cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2015; 25:875–8.
Article30. Alay I, Turan T, Ureyen I, Karalok A, Tasci T, Ozfuttu A, et al. Lymphadenectomy should be performed up to the renal vein in patients with intermediate-high risk endometrial cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 2015; 21:803–10.
Article31. Kumar S, Podratz KC, Bakkum-Gamez JN, Dowdy SC, Weaver AL, McGree ME, et al. Prospective assessment of the prevalence of pelvic, paraaortic and high paraaortic lymph node metastasis in endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2014; 132:38–43.
Article32. Todo Y, Okamoto K, Takeshita S, Sudo S, Kato H. A patient group at negligible risk of paraaortic lymph node metastasis in endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2016; 141:155–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of minimal uterine serous carcinoma with distant lymph node metastasis without peritoneal dissemination
- Prognosis of the Patients Showing Metastasis to the Para-aortic or/and Supraclavicular Lymph Nodes at the Time of Diagnosis of Recurrence of the Cervical Cancer
- Clinical Implication of Lateral Pelvic Lymph Node Metastasis in Rectal Cancer Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy
- Para-aortic Lymph Node Dissection in Gastric Cancer
- Analysis of para-aortic lymphadenectomy up to the level of the renal vessels in apparent early-stage ovarian cancer