J Vet Sci.
2016 Jun;17(2):199-206. 10.4142/jvs.2016.17.2.199.
Isolation and characterization of antimicrobial-resistant Escherichia coli from national horse racetracks and private horse-riding courses in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Microbiology, BK21 PLUS Program for Creative Veterinary Science Research, and Research Institute for Veterinary Science, College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea. pkt9138@hotmail.com
- 2Department of Animal Science and Technology, College of Biotechnology and Natural Resource, Chung-Ang University 2nd Campus, Anseong 17546, Korea.
- 3Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, Anyang 14086, Korea.
- KMID: 2413169
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2016.17.2.199
Abstract
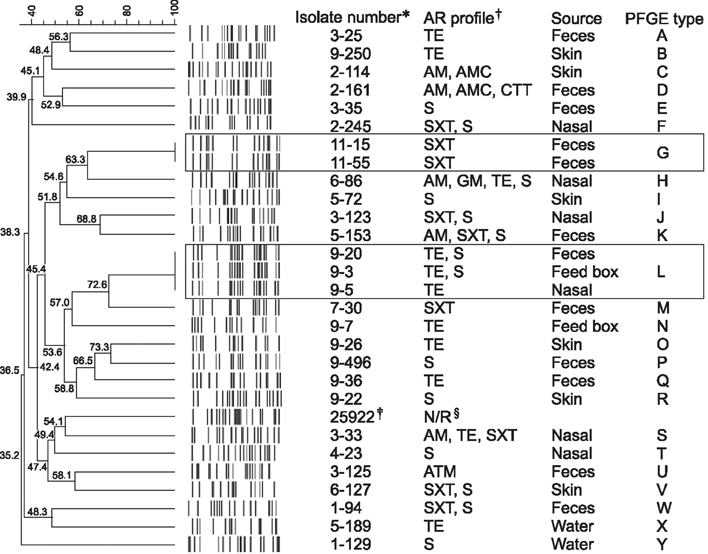
- Limited information is available regarding horse-associated antimicrobial resistant (AR) Escherichia (E.) coli. This study was designed to evaluate the frequency and characterize the pattern of AR E. coli from healthy horse-associated samples. A total of 143 E. coli (4.6%) were isolated from 3,078 samples collected from three national racetracks and 14 private horse-riding courses in Korea. Thirty of the E. coli isolates (21%) showed antimicrobial resistance to at least one antimicrobial agent, and four of the AR E. coli (13.3%) were defined as multi-drug resistance. Most of the AR E. coli harbored AR genes corresponding to their antimicrobial resistance phenotypes. Four of the AR E. coli carried class 1 integrase gene (intI1), a gene associated with multi-drug resistance. Pulsed-field gel electrophoretic analysis showed no genetic relatedness among AR E. coli isolated from different facilities; however, cross-transmissions between horses or horses and environments were detected in two facilities. Although cross-transmission of AR E. coli in horses and their environments was generally low, our study suggests a risk of transmission of AR bacteria between horses and humans. Further studies are needed to evaluate the risk of possible transmission of horse-associated AR bacteria to human communities through horse riders and horse-care workers.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Anti-Bacterial Agents/*pharmacology
*Drug Resistance, Multiple, Bacterial
Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli Infections/epidemiology/microbiology/*veterinary
Feces/microbiology
Horse Diseases/*epidemiology/microbiology
Horses
Phylogeny
Prevalence
Republic of Korea/epidemiology
Sequence Analysis, DNA/veterinary
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahmed MO, Clegg PD, Williams NJ, Baptiste KE, Bennett M. Antimicrobial resistance in equine faecal Escherichia coli isolates from North West England. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2010; 9:12.
Article2. Ahmed MO, Williams NJ, Clegg PD, Baptiste KE, Bennett M. Antibiotic resistance patterns in faecal E. coli: a longitudinal cohort-control study of hospitalized horses. In : Pana M, editor. Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria – A Continuous Chanllenge in the New Millennium. InTech: Rijecka;2012.3. Amyes SG, Smith JT. R-factor trimethoprim resistance mechanism: an insusceptible target site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974; 58:412–418.
Article4. Bennett PM. Plasmid encoded antibiotic resistance: acquisition and transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in bacteria. Br J Pharmacol. 2008; 153:Suppl 1. S347–S357.
Article5. Bryan A, Shapir N, Sadowsky MJ. Frequency and distribution of tetracycline resistance genes in genetically diverse, nonselected, and nonclinical Escherichia coli strains isolated from diverse human and animal sources. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004; 70:2503–2507.
Article6. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically; Approved Standard–Eighth Edition. CLSI document M07-A8. Wayne: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2009.7. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Nineteenth Informational Supplement. CLSI document M100-S19. Wayne: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2009.8. van Duijkeren E, Vulto AG, Slot van Oldruitemborgh-Oosterbaan MM, Mevius DJ, Kessels BGF, Breukink HJ, van Miert ASJPAM. A comparative study of the pharmacokinetics of intravenous and oral trimethoprim/sulfadiazine formulations in the horse. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 1994; 17:440–446.
Article9. Erb A, Stürmer T, Marre R, Brenner H. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli: overview of geographical, temporal, and methodological variations. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007; 26:83–90.
Article10. Gibreel A, Sköld O. High-level resistance to trimethoprim in clinical isolates of Campylobacter jejuni by acquisition of foreign genes (dfr1 and dfr9) expressing drug-insensitive dihydrofolate reductases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998; 42:3059–3064.
Article11. Guardabassi L, Schwarz S, Lloyd DH. Pet animals as reservoirs of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004; 54:321–332.12. Guinée PA, Agterberg CM, Jansen WH. Escherichia coli O antigen typing by means of a mechanized microtechnique. Appl Microbiol. 1972; 24:127–131.
Article13. Ito A, Taniuchi A, May T, Kawata K, Okabe S. Increased antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli in mature biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009; 75:4093–4100.
Article14. Kim JY. The horse industry in Korea: its present condition and prospect. Adv Sci Technol Lett. 2015; 99:256–260.
Article15. Kos VN, Desjardins CA, Griggs A, Cerqueira G, Van Tonder A, Holden MTG, Godfrey P, Palmer KL, Bodi K, Mongodin EF, Wortman J, Feldgarden M, Lawley T, Gill SR, Haas BJ, Birren B, Gilmore MS. Comparative genomics of vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains and their positions within the clade most commonly associated with methicillin-resistant S. aureus hospital-acquired infection in the United States. MBio. 2012; 3:e00112–e00112.16. Lee JC, Oh JY, Cho JW, Park JC, Kim JM, Seol SY, Cho DT. The prevalence of trimethoprim-resistance-conferring dihydrofolate reductase genes in urinary isolates of Escherichia coli in Korea. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2001; 47:599–604.
Article17. Levy SB, Marshall B. Antibacterial resistance worldwide: causes, challenges and responses. Nat Med. 2004; 10:12 Suppl. S122–S129.
Article18. Martinez-Freijo P, Fluit A, Schmitz FJ, Grek VSC, Verhoef J, Jones ME. Class I integrons in Gram-negative isolates from different European hospitals and association with decreased susceptibility to multiple antibiotic compounds. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1998; 42:689–696.
Article19. Nataro JP, Kaper JB. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1998; 11:142–201.20. Ng LK, Martin I, Alfa M, Mulvey M. Multiplex PCR for the detection of tetracycline resistant genes. Mol Cell Probes. 2001; 15:209–215.
Article21. Persson S, Olsen KE, Scheutz F, Krogfelt KA, Gerner-Smidt P. A method for fast and simple detection of major diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli in the routine diagnostic laboratory. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007; 13:516–524.
Article22. Pitout JD, Thomson KS, Hanson ND, Ehrhardt AF, Moland ES, Sanders CC. beta-Lactamases responsible for resistance to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins in Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, and Proteus mirabilis isolates recovered in South Africa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998; 42:1350–1354.
Article23. Recchia GD, Hall RM. Gene cassettes: a new class of mobile element. Microbiology. 1995; 141:3015–3027.
Article24. Sayah RS, Kaneene JB, Johnson Y, Miller R. Patterns of antimicrobial resistance observed in Escherichia coli isolates obtained from domestic- and wild-animal fecal samples, human septage, and surface water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005; 71:1394–1404.
Article25. So JH, Kim J, Bae IK, Jeong SH, Kim SH, Lim SK, Park YH, Lee K. Dissemination of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli in Korean veterinary hospitals. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012; 73:195–199.
Article26. Soufi L, Abbassi MS, Sáenz Y, Vinué L, Somalo S, Zarazaga M, Abbas A, Dbaya R, Khanfir L, Ben Hassen A, Hammami S, Torres C. Prevalence and diversity of integrons and associated resistance genes in Escherichia coli isolates from poultry meat in Tunisia. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2009; 6:1067–1073.
Article27. Sunde M, Norström M. The genetic background for streptomycin resistance in Escherichia coli influences the distribution of MICs. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005; 56:87–90.
Article28. Thakur A, Vashist H, Sharma RB. A review on tuberculosis. Eur J Biomed Pharm Sci. 2015; 2:1106–1126.29. Tsen HY, Lin CK, Chi WR. Development and use of 16S rRNA gene targeted PCR primers for the identification of Escherichia coli cells in water. J Appl Microbiol. 1998; 85:554–560.
Article30. Van TT, Chin J, Chapman T, Tran LT, Coloe PJ. Safety of raw meat and shellfish in Vietnam: an analysis of Escherichia coli isolations for antibiotic resistance and virulence genes. Int J Food Microbiol. 2008; 124:217–223.
Article31. White PA, McIver CJ, Deng YM, Rawlinson WD. Characterisation of two new gene cassettes, aadA5 and dfrA17. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000; 182:265–269.32. Woody BJ, Hoskins JD. Ehrlichial diseases of dogs. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1991; 21:75–98.
Article33. Yu HS, Lee JC, Kang HY, Jeong YS, Lee EY, Choi CH, Tae SH, Lee YC, Seol SY, Cho DT. Prevalence of dfr genes associated with integrons and dissemination of dfrA17 among urinary isolates of Escherichia coli in Korea. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004; 53:445–450.
Article34. Yun SW, Kwon DY, Choi SK, Lee HS, Cho GJ. Characteristics and antimicrobial susceptibility of Escherichia coli isolated from horse. Korean J Vet Res. 2010; 50:231–237.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Horse Riding Simulator Exercise on Thickness of Transverse Abdominis in Healthy Adults
- Effects of Virtual Reality Horse Riding Simulator Training Using a Head-Mounted Display on Balance and Gait Functions in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Preliminary Pilot Study
- The Mental Health and Occupational Characteristic of Horse Stable Hand Workers in Korea
- Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolated from Healthy Volunteers of the Community
- Antimicrobial resistance of escherichia coli isolated from clinical specimens