Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2018 Jun;11(2):81-88. 10.21053/ceo.2018.00031.
A Systematic Review of Benefit of Silicone Intubation in Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Korea.
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea. hahnjin2@naver.com
- 3Department of Family Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Korea.
- 4Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2412664
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2018.00031
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Insertion of a silicone stent during endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) is the most common procedure to prevent rhinostomy closure. It has been claimed that silicone intubation improves the surgical outcomes of endoscopic DCR. However, many reports have documented an equally high success rate for surgery without silicone intubation. Accordingly, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to clarify the outcomes of endoscopic DCR with and without silicone intubation and determine whether silicone intubation is actually beneficial for patients.
METHODS
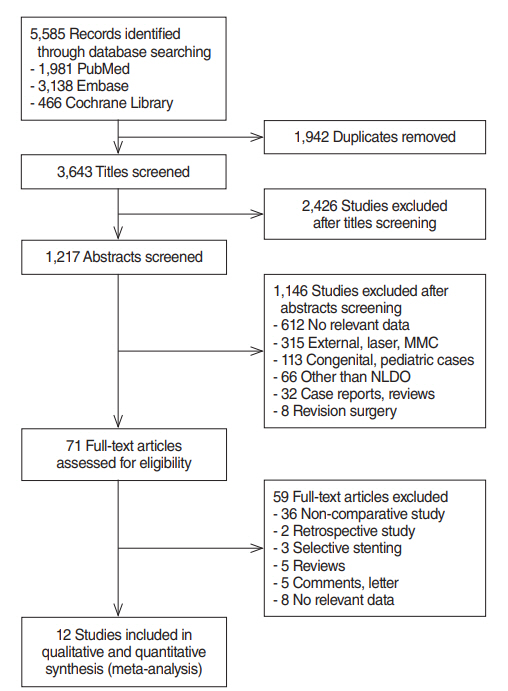
PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases were searched to identify relevant controlled trials evaluating endoscopic DCR with and without silicone intubation. The search was restricted to English articles published between January 2007 and December 2016. Relevant articles were reviewed to obtain information pertaining to interventions and outcomes. We also performed a meta-analysis of the relevant literature.
RESULTS
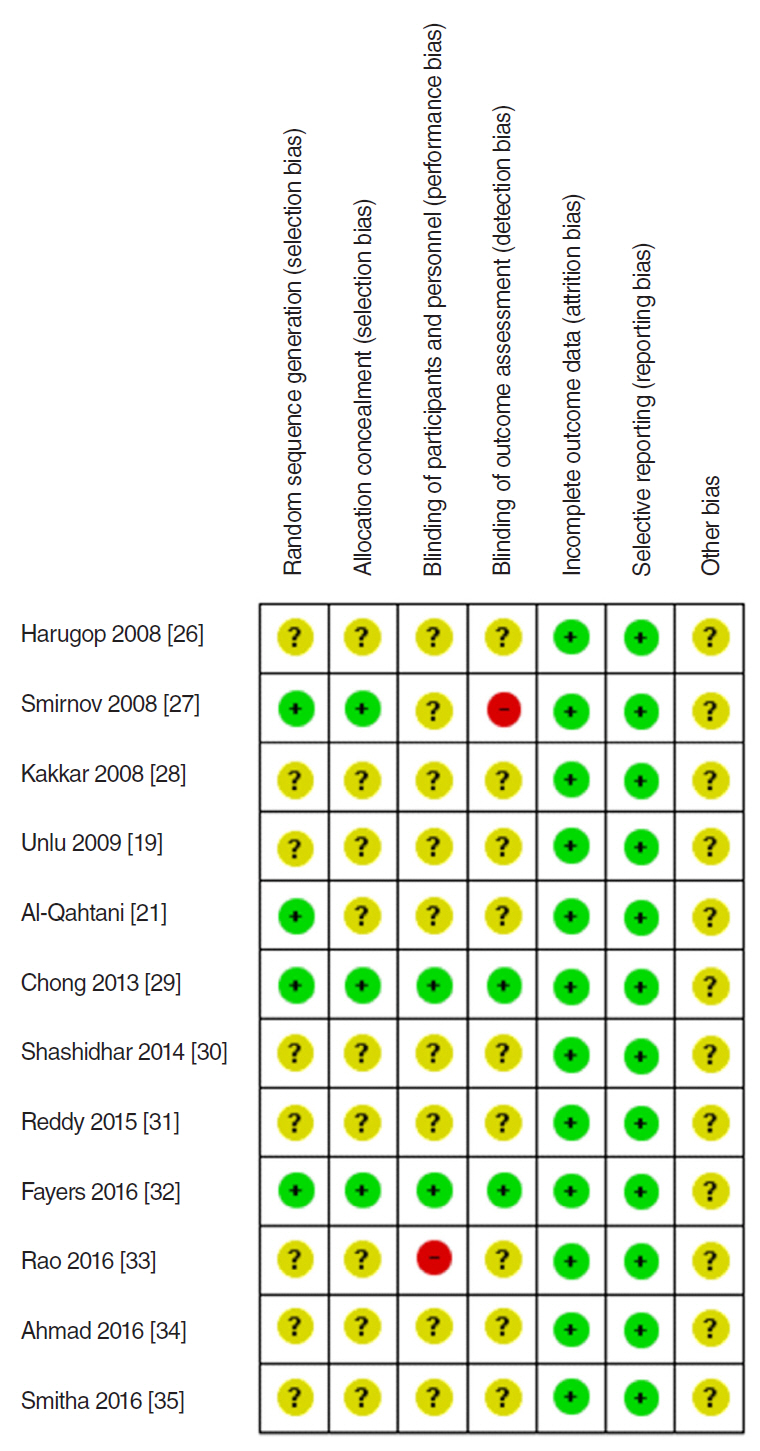
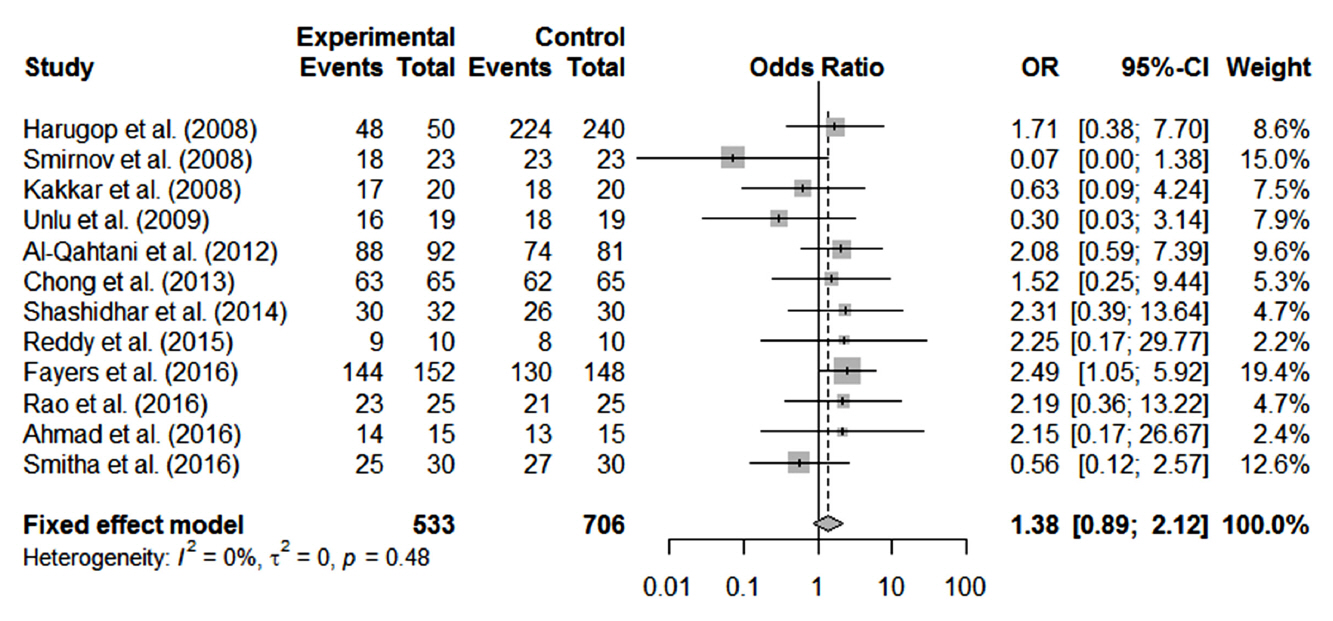
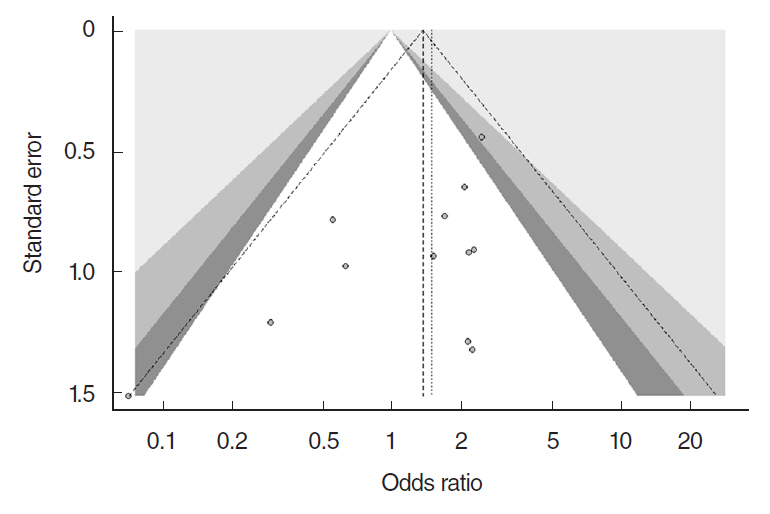
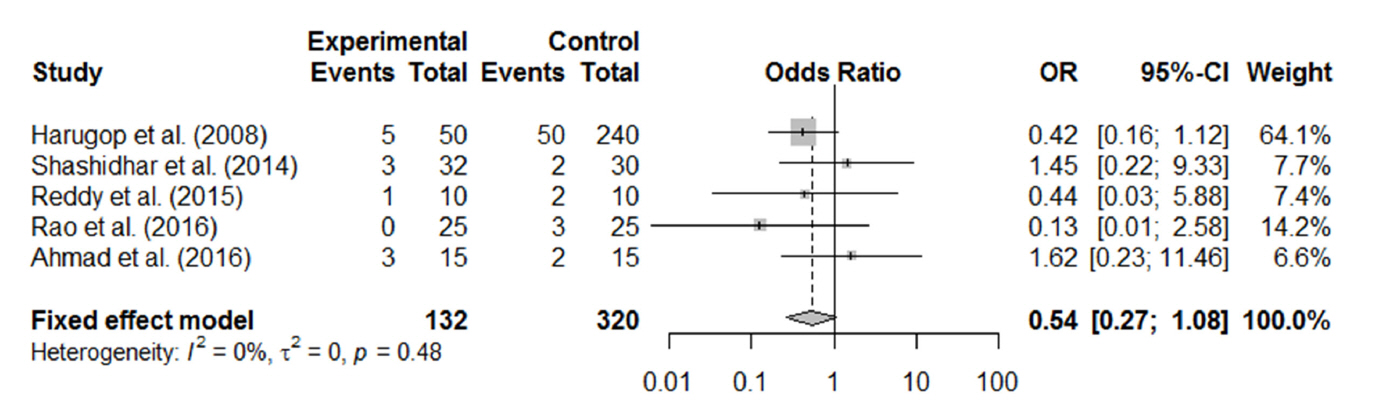
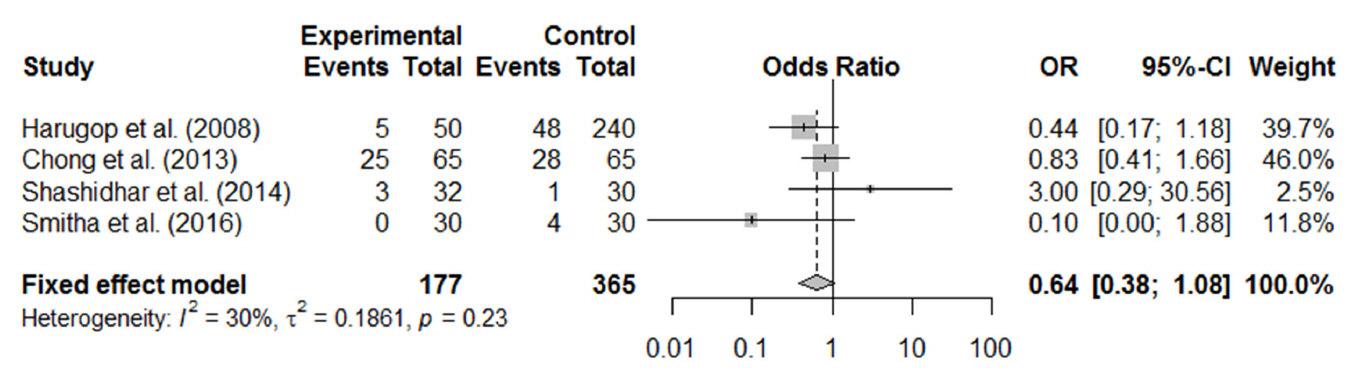
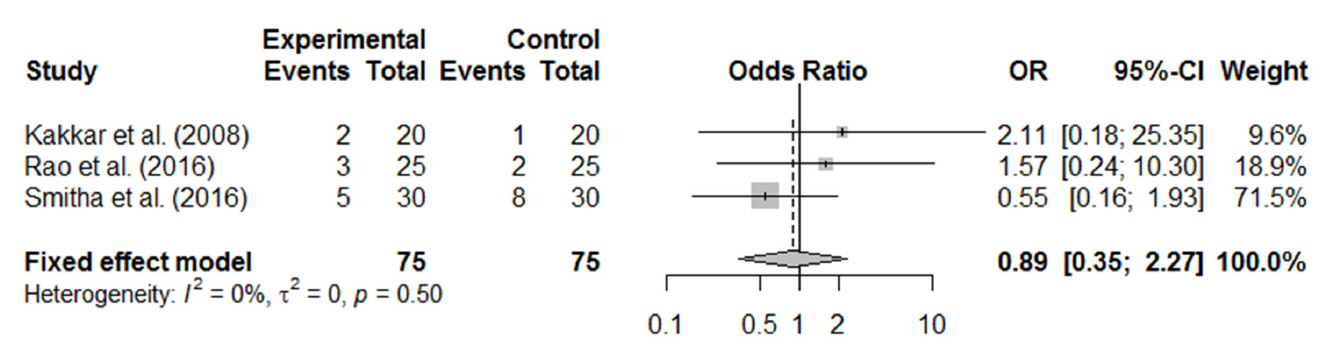
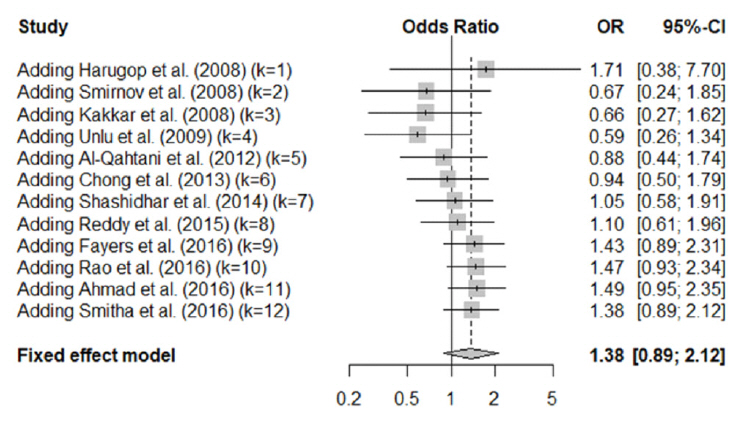
In total, 1,216 patients included in 12 randomized controlled trials were pooled. A total of 1,239 endoscopic DCR procedures were performed, and silicone stents were used in 533 procedures. The overall success rate for endoscopic DCR was 91.9% (1,139/1,239), while the success rates with and without silicone intubation were 92.9% (495/533) and 91.2% (644/706), respectively. There was no statistically significant heterogeneity among the included studies. A meta-analysis using a fixed-effects models showed no significant difference in the success rate between endoscopic DCR with silicone intubation and that without silicone intubation (OR, 1.38; 95% CI, 0.89 to 2.12; P=0.148; z=1.45). Furthermore, there were no significant differences with regard to surgical complications such as synechia, granulation, and postoperative bleeding.
CONCLUSION
The findings of our meta-analysis suggest that the success rate and postoperative complication rate for endoscopic DCR is not influenced by the use of silicone intubation during the procedure.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Nasolacrimal Duct Obstruction Caused by a Lacrimal Sac Retention Cyst
Seung Hyuck Yang, Hahn Jin Jung, Young-Seok Choi, Woo Sub Shim
J Rhinol. 2024;31(1):42-45. doi: 10.18787/jr.2023.00071.
Reference
-
1. Unlu HH, Toprak B, Aslan A, Guler C. Comparison of surgical outcomes in primary endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with and without silicone intubation. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2002; Aug. 111(8):704–9.
Article2. Leong SC, Macewen CJ, White PS. A systematic review of outcomes after dacryocystorhinostomy in adults. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2010; Jan-Feb. 24(1):81–90.
Article3. Feng YF, Cai JQ, Zhang JY, Han XH. A meta-analysis of primary dacryocystorhinostomy with and without silicone intubation. Can J Ophthalmol. 2011; Dec. 46(6):521–7.
Article4. Callejas CA, Tewfik MA, Wormald PJ. Powered endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with selective stenting. Laryngoscope. 2010; Jul. 120(7):1449–52.
Article5. Syed MI, Head EJ, Madurska M, Hendry J, Erikitola OC, Cain AJ. Endoscopic primary dacryocystorhinostomy: are silicone tubes needed? Our experience in sixty three patients. Clin Otolaryngol. 2013; Oct. 38(5):406–10.
Article6. McLachlan DL, Shannon GM, Flanagan JC. Results of dacryocystorhinostomy: analysis of the reoperations. Ophthalmic Surg. 1980; Jul. 11(7):427–30.7. Sprekelsen MB, Barberan MT. Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy: surgical technique and results. Laryngoscope. 1996; Feb. 106(2 Pt 1):187–9.8. Boush GA, Lemke BN, Dortzbach RK. Results of endonasal laser-assisted dacryocystorhinostomy. Ophthalmology. 1994; May. 101(5):955–9.
Article9. Watkins LM, Janfaza P, Rubin PA. The evolution of endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy. Surv Ophthalmol. 2003; Jan-Feb. 48(1):73–84.
Article10. Gu Z, Cao Z. Silicone intubation and endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy: a meta-analysis. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010; Dec. 39(6):710–3.11. Sarode D, Bari DA, Cain AC, Syed MI, Williams AT. The benefit of silicone stents in primary endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Otolaryngol. 2017; Apr. 42(2):307–14.
Article12. Okuyucu S, Gorur H, Oksuz H, Akoglu E. Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with silicone, polypropylene, and T-tube stents; randomized controlled trial of efficacy and safety. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2015; Jan-Feb. 29(1):63–8.
Article13. Tsirbas A, Wormald PJ. Endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy with mucosal flaps. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; Jan. 135(1):76–83.
Article14. Onerci M, Orhan M, Ogretmenoglu O, Irkec M. Long-term results and reasons for failure of intranasal endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy. Acta Otolaryngol. 2000; Mar. 120(2):319–22.15. Metson R, Woog JJ, Puliafito CA. Endoscopic laser dacryocystorhinostomy. Laryngoscope. 1994; Mar. 104(3 Pt 1):269–74.
Article16. Griffiths JD. Nasal catheter use in dacryocystorhinostomy. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1991; Sep. 7(3):177–86.
Article17. Caversaccio M, Hausler R. Insertion of double bicanalicular silicone tubes after endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy in lacrimal canalicular stenosis: a 10-year experience. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2006; Aug. 68(5):266–9.
Article18. Saeed BM. Endoscopic DCR without stents: clinical guidelines and procedure. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; Feb. 269(2):545–9.
Article19. Unlu HH, Gunhan K, Baser EF, Songu M. Long-term results in endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy: is intubation really required. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009; Apr. 140(4):589–95.
Article20. Allen K, Berlin AJ. Dacryocystorhinostomy failure: association with nasolacrimal silicone intubation. Ophthalmic Surg. 1989; Jul. 20(7):486–9.
Article21. Al-Qahtani AS. Primary endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with or without silicone tubing: a prospective randomized study. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2012; Jul-Aug. 26(4):332–4.
Article22. Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0 [Internet]. London: The Cochrane Collaboration;2011. [cited 2018 Feb 8]. Available from: http://www.handbook.cochrane.org.23. Mantel N, Haenszel W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959; Apr. 22(4):719–48.24. Schwarzer G. General package for meta-analysis [Internet]. 2018. [cited 2017 Dec 07]. Available from: http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/meta/meta.pdf.25. Harbord RM, Deeks JJ, Egger M, Whiting P, Sterne JA. A unification of models for meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy studies. Biostatistics. 2007; Apr. 8(2):239–51.
Article26. Harugop AS, Mudhol RS, Rekha BK, Maheswaran M. Endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy: a prospective study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008; Dec. 60(4):335–40.
Article27. Smirnov G, Tuomilehto H, Terasvirta M, Nuutinen J, Seppa J. Silicone tubing is not necessary after primary endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy: a prospective randomized study. Am J Rhinol. 2008; Mar-Apr. 22(2):214–7.
Article28. Kakkar V, Chugh J, Sachdeva S, Sharma N, Ramesh. Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with and without silicone stent: a comparative study. Internet J Otorhinolaryngol. 2008; 9(1):1–5.
Article29. Chong KK, Lai FH, Ho M, Luk A, Wong BW, Young A. Randomized trial on silicone intubation in endoscopic mechanical dacryocystorhinostomy (SEND) for primary nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Ophthalmology. 2013; Oct. 120(10):2139–45.
Article30. Shashidhar KC, Nagalotimath US, Dixit D. Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with and without silicone stenting: a comparative study. Al Ameen J Med Sci. 2014; Jul-Sep. 7(3):244–7.31. Reddy YJ, Reddy YM, Kiran M, Reddy YG, Kumar S. A comparative study of outcomes of dacryocystorhinostomy with and without silicone stenting. IOSR J Dent Med Sci. 2015; Jul. 14(7):82–5.32. Fayers T, Dolman PJ. Bicanalicular silicone stents in endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy: results of a randomized clinical trial. Ophthalmology. 2016; Oct. 123(10):2255–9.33. Rao SV, Rajshekar MM. Dacryocystorhinostomy stent insertion in initial endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy. Clin Rhinol An Int J. 2016; Sep-Dec. 9(3):120–4.34. Ahmad S, Pant B. Role of silicone stenting in endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy: a comparative study. Int J Adv Integr Med Sci. 2016; Jan-Mar. 1(1):4–6.
Article35. Smitha SG, Jagannath B. Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with and without silicone stent: a comparative study. J Med Sci Clin Res. 2016; Sep. 4(9):12861–4.36. Madge SN, Selva D. Intubation in routine dacryocystorhinostomy: why we do what we do. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009; Aug. 37(6):620–3.
Article37. Liang J, Lane A. Is postoperative stenting necessary in endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy. Laryngoscope. 2013; Nov. 123(11):2589–90.
Article38. Longari F, Dehgani Mobaraki P, Ricci AL, Lapenna R, Cagini C, Ricci G. Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with and without silicone intubation: 4 years retrospective study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016; Aug. 273(8):2079–84.39. Mohamad SH, Khan I, Shakeel M, Nandapalan V. Long-term results of endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy with and without stenting. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2013; Apr. 95(3):196–9.
Article40. Mortimore S, Banhegy GY, Lancaster JL, Karkanevatos A. Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy without silicone stenting. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1999; Dec. 44(6):371–3.41. Unlu HH, Ozturk F, Mutlu C, Ilker SS, Tarhan S. Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy without stents. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2000; Jan. 27(1):65–71.
Article42. Zuercher B, Tritten JJ, Friedrich JP, Monnier P. Analysis of functional and anatomic success following endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2011; Apr. 120(4):231–8.
Article43. Gibbs DC. New probe for the intubation of lacrimal canaliculi with silicone rubber tubing. Br J Ophthalmol. 1967; Mar. 51(3):198.
Article44. Deng HY, Wang T, Huang XK, Yang QT, Ling SQ, Wang WH, et al. Comparative study of recessive spherical headed silicone intubation and endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy under nasal endoscopy for nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Sci Rep. 2017; Aug. 7(1):7734.
Article45. Sterne JA, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. BMJ. 2011; Jul. 343:d4002.46. Knisely A, Harvey R, Sacks R. Long-term outcomes in endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015; Feb. 23(1):53–8.
Article47. Yeon JY, Shim WS. Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy without silicone stent. Acta Otolaryngol. 2012; Jun. 132 Suppl 1:S77–81.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Study on Acute Conjunctivitis after Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy with Silicone Tube Intubation
- Results with Silicone Stent in Lacrimal Drainage System
- Silicone Intubation for Nasolacrimal Duct Obstruction in Adult
- Cytologic Study of Removed Silicone Tube in Nasolacrimal Duct Obstruction Patients with the Liquid-based Thin Layer Preparation Technique
- The effect of double silicone tube intubation on surgical outcome of endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy