J Vet Sci.
2017 Jun;18(2):169-173. 10.4142/jvs.2017.18.2.169.
Tissue distribution of marbofloxacin in pigs after a single intramuscular injection
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Animal Science and Technology, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471023, China. yfscau@126.com
- 2Key Laboratory for Feed Biotechnology of the Ministry of Agriculture, Feed Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing 10081, China.
- 3College of Food and Bioengineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471023, China.
- KMID: 2412569
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2017.18.2.169
Abstract
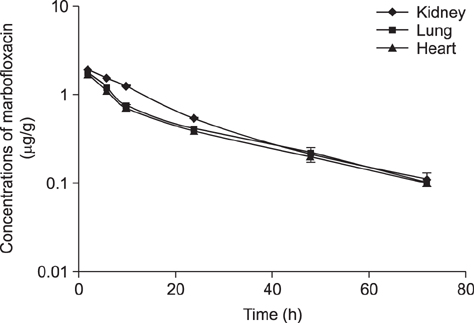
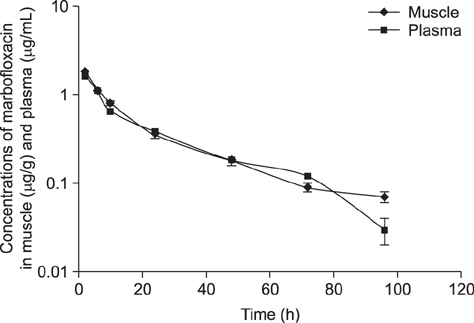
- Tissue distribution of marbofloxacin was studied in pigs after a single intramuscular injection at 2.5 mg/kg body weight. Samples of plasma, muscle, liver, kidney, heart, lung, and muscle at the injection site were randomly collected from five pigs at 2, 6, 10, 24, 48, 72, and 96 h after administration. Marbofloxacin concentrations were determined by using high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection and were subjected to non-compartmental analysis to obtain kinetic parameters. The elimination half-life (t(1/2λz)) of marbofloxacin at the injection site was 22.12 h, while those in kidney, plasma, liver, lung, heart, and muscle were 16.75, 21.48, 21.84, 24.00, 24.45, and 28.91 h, respectively. Areas under the concentration-time curve from 0 h to (∞) (AUC(0-∞)s) were calculated to be 31.17 h·µg·mL⻹ for plasma and 32.97, 33.92, 34.78, 37.58, 42.02, and 98.80 h·µg·g⻹ for heart, muscle, lung, liver, kidney, and injection site, respectively. The peak concentration (C(max)) of marbofloxacin was 1.62 µg/mL in plasma and 1.71, 1.74, 1.86, 1.93, 2.45, and 7.64 µg/g in heart, lung, muscle, kidney, liver, and injection site, respectively. The results show that marbofloxacin was fast absorbed, extensively distributed, and slowly eliminated from pigs after a single intramuscular administration.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Anti-Bacterial Agents/administration & dosage/analysis/*pharmacokinetics
Chromatography, High Pressure Liquid/veterinary
Fluoroquinolones/administration & dosage/analysis/*pharmacokinetics
Injections, Intramuscular/veterinary
Kidney/chemistry
Liver/chemistry
Lung/chemistry
Male
Muscle, Skeletal/chemistry
Myocardium/chemistry
Swine/metabolism
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Fluoroquinolones
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aliabadi FS, Lees P. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic integration of marbofloxacin in calf serum, exudate and transudate. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2002; 25:161–174.
Article2. Anadón A, Martínez-Larrañaga MR, Díaz MJ, Martínez MA, Frejo MT, Martínez M, Tafur M, Castellano VJ. Pharmacokinetic characteristics and tissue residues for marbofloxacin and its metabolite N-desmethyl-marbofloxacin in broiler chickens. Am J Vet Res. 2002; 63:927–933.
Article3. Appelbaum PC, Hunter PA. The fluoroquinolone antibacterials: past, present and future perspectives. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2000; 16:5–15.
Article4. de Lucas JJ, Rodríguez C, Waxman S, González F, Uriarte I, San Andrés MI. Pharmacokinetics of marbofloxacin after intravenous and intramuscular administration to ostriches. Vet J. 2005; 170:364–368.
Article5. Ding H, Li Y, Chen Z, Rizwan-ul-Haq M, Zeng Z. Plasma and tissue cage fluid pharmacokinetics of marbofloxacin after intravenous, intramuscular, and oral single-dose application in pigs. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2010; 33:507–510.
Article6. Ding H, Wang L, Shen X, Gu X, Zeng D, Zeng Z. Plasma and tissue pharmacokinetics of marbofloxacin in experimentally infected chickens with Mycoplasma gallisepticum and Escherichia coli. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2013; 36:511–515.
Article7. Goudah A, Abd El-Aty AM, Regmi NL, Shin HC, Shimoda M, Shim JH. Single-dose pharmacokinetics of marbofloxacin in Egyptian buffalo (Bubalus bubalis L.) steers. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2007; 120:215–220.8. Goudah A, Hasabelnaby S. The disposition of marbofloxacin after single dose intravenous, intramuscular and oral administration to Muscovy ducks. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 34:197–201.
Article9. Illambas J, Potter T, Cheng Z, Rycroft A, Fishwick J, Lees P. Pharmacodynamics of marbofloxacin for calf pneumonia pathogens. Res Vet Sci. 2013; 94:675–681.
Article10. Kietzmann M, Braun M, Schneider M, Pankow R. Tissue distribution of marbofloxacin after ‘systemic’ administration into the isolated perfused bovine udder. Vet J. 2008; 178:115–118.
Article11. Laraje R, Talmi A, Bounaga R, Bengoumi M, El Hraiki A, Laurentie M. Comparative pharmacokinetics of marbofloxacin after a single intramuscular administration at two dosages to camels (Camelus dromedarius). J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 29:229–231.
Article12. Ligabue M, Lucchetti D, Catone T, Fabrizi L, Marvasi L, Zaghini A, Coni E. Rapid depletion of marbofloxacin residues in rabbit after therapeutic treatment. J Food Prot. 2005; 68:2480–2484.
Article13. Marín P, Álamo LF, Escudero E, Fernández-Varón E, Hernandis V, Cárceles CM. Pharmacokinetics of marbofloxacin in rabbit after intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous administration. Res Vet Sci. 2013; 94:698–700.
Article14. Schneider M, Paulin A, Dron F, Woehrlé F. Pharmacokinetics of marbofloxacin in pigs after intravenous and intramuscular administration of a single dose of 8 mg/kg: dose proportionality, influence of the age of the animals and urinary elimination. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2014; 37:523–530.
Article15. Sidhu PK, Landoni MF, Aliabadi FS, Lees P. PK-PD integration and modeling of marbofloxacin in sheep. Res Vet Sci. 2010; 88:134–141.
Article16. Spreng M, Deleforge J, Thomas V, Boisramé B, Drugeon H. Antibacterial activity of marbofloxacin. A new fluoroquinolone for veterinary use against canine and feline isolates. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 1995; 18:284–289.
Article17. Vallé M, Schneider M, Galland D, Giboin H, Woehrlé F. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic testing of marbofloxacin administered as a single injection for the treatment of bovine respiratory disease. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 35:519–528.
Article18. Vilalta C, Giboin H, Schneider M, El Garch F, Fraile L. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic evaluation of marbofloxacin in the treatment of Haemophilus parasuis and Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae infections in nursery and fattener pigs using Monte Carlo simulations. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2014; 37:542–549.
Article19. Vilalta C, Schneider M, López-Jimenez R, Caballero JM, Gottschalk M, Fraile L. Marbofloxacin reaches high concentration in pig tonsils in a dose-dependent fashion. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 34:95–97.
Article20. Yang F, Yang YR, Wang L, Huang XH, Qiao G, Zeng ZL. Estimating marbofloxacin withdrawal time in broiler chickens using a population physiologically based pharmacokinetics model. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2014; 37:579–588.
Article21. Zhu Y, Tan Y, Wang C, Zhang N, Liu Y, Liu L, Li C, Lu X, Cao J. Pharmacokinetics and tissue residues of marbofloxacin in crucian carp (Carassius auratus) after oral administration. Aquac Res. 2009; 40:696–709.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infection Caused by Mycobacterium abscessus Developed after Intramuscular Injection: A Case Report
- Nicolau Syndrome after Intramuscular Injection: 3 Cases
- Intramuscular neural distribution of the teres minor muscle using Sihler’s stain: application to botulinum neurotoxin injection
- Anaphylactic shock caused by intramuscular injection of midazolam during the perioperative period: a case report
- Comparison of Two Intramuscular Injection Techniques on the Severity of Discomfort and leasions at the Injection Site